MATHEMATICS
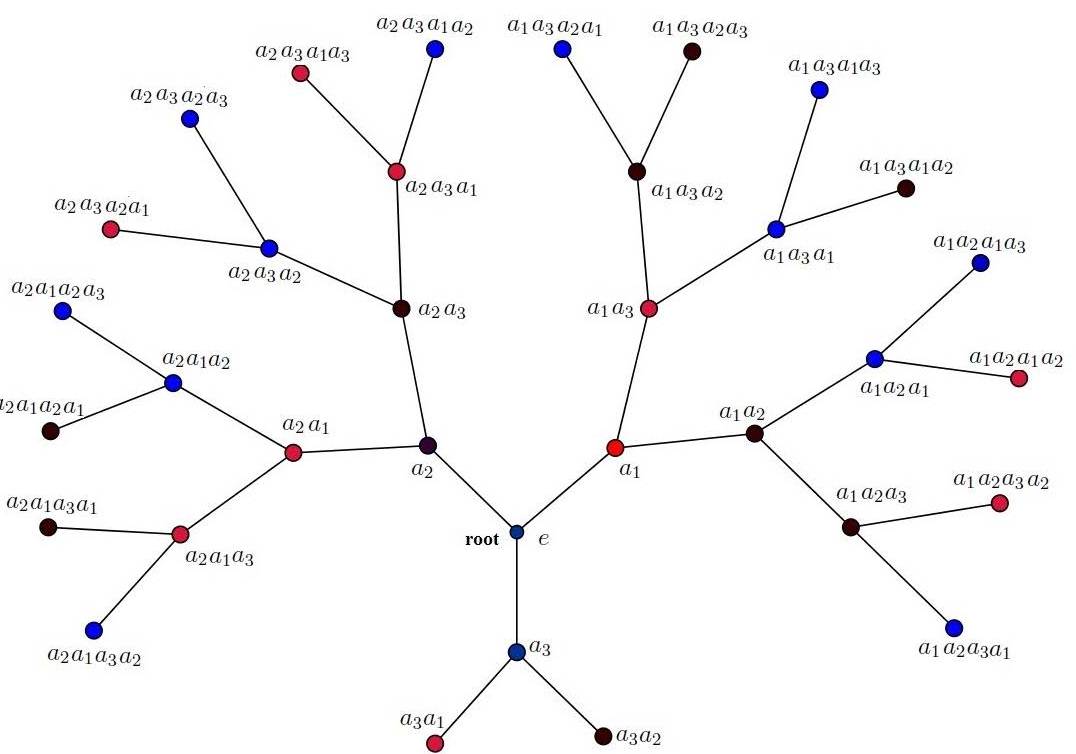
In this paper, fixed points of Lyapunov integral equation are found and considered the connections between Gibbs measures for four competing interactions of models with uncountable (i.e. [0,1]) set of spin values on the Cayley tree of order two.
PHYSICS
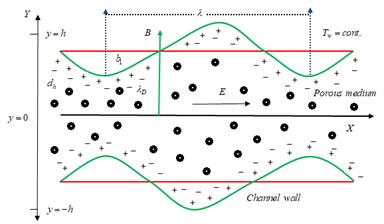
Pumping of peristaltic fluid is a vehicle via liquid that is accomplished due to a dynamic rush through a distensible cylinder containing liquids which extends along its length. Peristaltic pumping occurs in a lower pressure region to a higher pressure region. As a principle of peristaltic pumping, various applications are used for the blood pumping in different parts of the human body, pharmacological drug delivery systems and in industries, sanitary fluid transport, etc. Therefore, peristaltic pumping via a non-Darcy porous medium in an electroosmotic flow has been discussed in the current investigation. To exhibit the existence of a porous medium, Darcy Forchheimer model is deployed. The electro-magnetohaydrodynamic flow of fluid passing a symmetric channel and the novelty of the study are due to the entropy analysis. Analytical approach such as perturbation technique is employed to reduce the higher order coupled transformed equation into its lower order decoupled form and then numerical treatment is made to obtain the approximate solutions. The characteristics of the contributing parameters are presented via graphs and the numerical computations are exhibited through tabular form. Present outcome warrants a good correlation with earlier result in particular case. However, the main findings are elaborated in the results and discussion section.
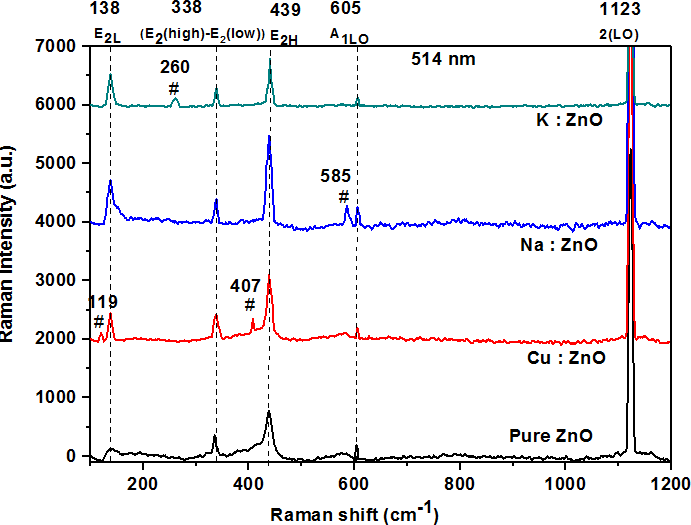
Pure ZnO and copper (IB group), sodium (IA group) and potassium (IA group) and doped ZnO thin films on glass substrate by chemical bath deposition method have been studied for Hall effect measurements, resistivity, Raman and photoluminescence (PL). The influence of dopant content on carrier concentration, electrical resistivity, and Hall mobility of the thin films are analyzed. Electrical conductivity measurements of ZnO are carried out by two probe method and activation energy for the electrical conductivity of pure and doped ZnO is found out. The Raman scattering of the pure ZnO and doped ZnO shows the first and second orders of polar and non-polar modes. Raman spectra confirms the hexagonal wurtzite structure of pure and doped ZnO with E2 (high) mode at 439 cm−1 and presence of other possible defects. Photoluminescence (PL) at room temperature results indicate the emission occurs at close band lines and the outcomes are identified with a few inherent imperfections in the doped ZnO thin films. The PL results demonstrate the upgraded optoelectronic properties, specifically, the carriers for long life span is executed by the oxygen opportunities. Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence confirm existence of zinc interstitials (Zni) as well as oxygen vacancies (Vo). Resistivity as low as 15 Ω-cm, Hall mobility as high as 6.2 cm2/Vs and effective carrier concentration as high as 1.70×1017e−/cm3 have been obtained.
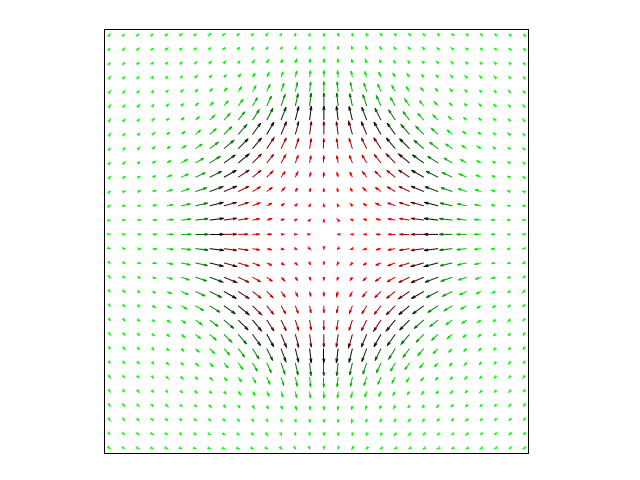
A method for calculating the magnetic dipole-dipole interaction in topological magnetic systems has been developed. It can be used to calculate stable states and minimum energy paths that determine the magnetic transition in chiral magnetic structures. Instead of directly summing the dipole interactions between magnetic moments/magnetic elements, we solve a local equation for demagnetizing fields. The states corresponding to the local energy minimum can be found using the Lagrange method for the conditional extrema. The efficiency of the algorithm has been demonstrated by calculating the dependence of the size and shape of magnetic skyrmions and anti-skyrmions on the magnitude of magnetization.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
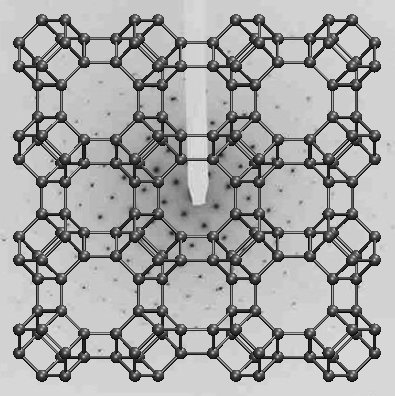
We report on supercritical fluid synthesis of an intermediate carbon phase – austite – at a pressure of 180 MPa and temperatures 500–700◦C from soot as a precursor and supercritical carbon dioxide as a solvent. According to the results of electron and X-ray diffractions, spectral measurements and density-functional theory calculations, the observed carbon phase is proved to be cubic with a lattice parameter value of 8.96±0.05 A and a˚ possible structural type as for KFI zeolite.
The behavior of nanoparticle ensembles was studied using of NaRF4 hexagonal phases. The evolution of particles in the process of rapid and productive synthesis from flux as a result of a chemical reaction was investigated. A low-temperature synthesis process in the medium of sodium nitrate was used. Synthesis of the samples of up-conversion phosphor NaY0.78Yb0.2Er0.02F4 was performed from rare-earth nitrates at 350 – 430 ◦C for 15 – 500 min. NaF was used as the fluorinating agent. Powder X-ray phase analysis and scanning electron microscopy revealed a rapid transformation of the cubic alpha modification into a hexagonal phase, followed by the transformation of nanoparticles into hexagonal prisms of micron sizes. The up-conversion luminescence energy yield increased as the reaction time increased.
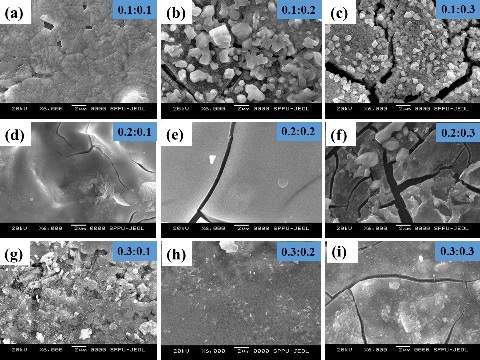
Thin films of binary oxides (MoO3–In2O3) of different normality proportions of 0.1N:0.1N, 0.2N:0.1N, 0.3N:0.1N, 0.1N:0.2N, 0.2N:0.2N, 0.3N:0.2N, 0.1N:0.3N, 0.2N:0.3N and 0.3N:0.3N were prepared by a spray pyrolysis technique on glass substrates at 400◦C. The prepared films were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy dispersive analysis by x-ray spectra (EDAX). The electrical and gas sensing properties of the films were studied using static gas sensing apparatus. The electrical analysis confirmed that the resistivity of films increased by adding MoO3 as the dopant in In2O3. The maximum resistivity of film was found 1.75×104 Ωm for 0.3N (MoO3) and 0.1N (In2O3) binary oxide films. The films were tested against five different target gases. The composition ratio 0.3N:0.1N films showed the 70.50% sensitivity for 300 ppm CO gas at 150◦C. The response time (15 s) and recovery time (25 s) was found to be quick. The % selectivity was maximum for 0.3N:0.1N films.
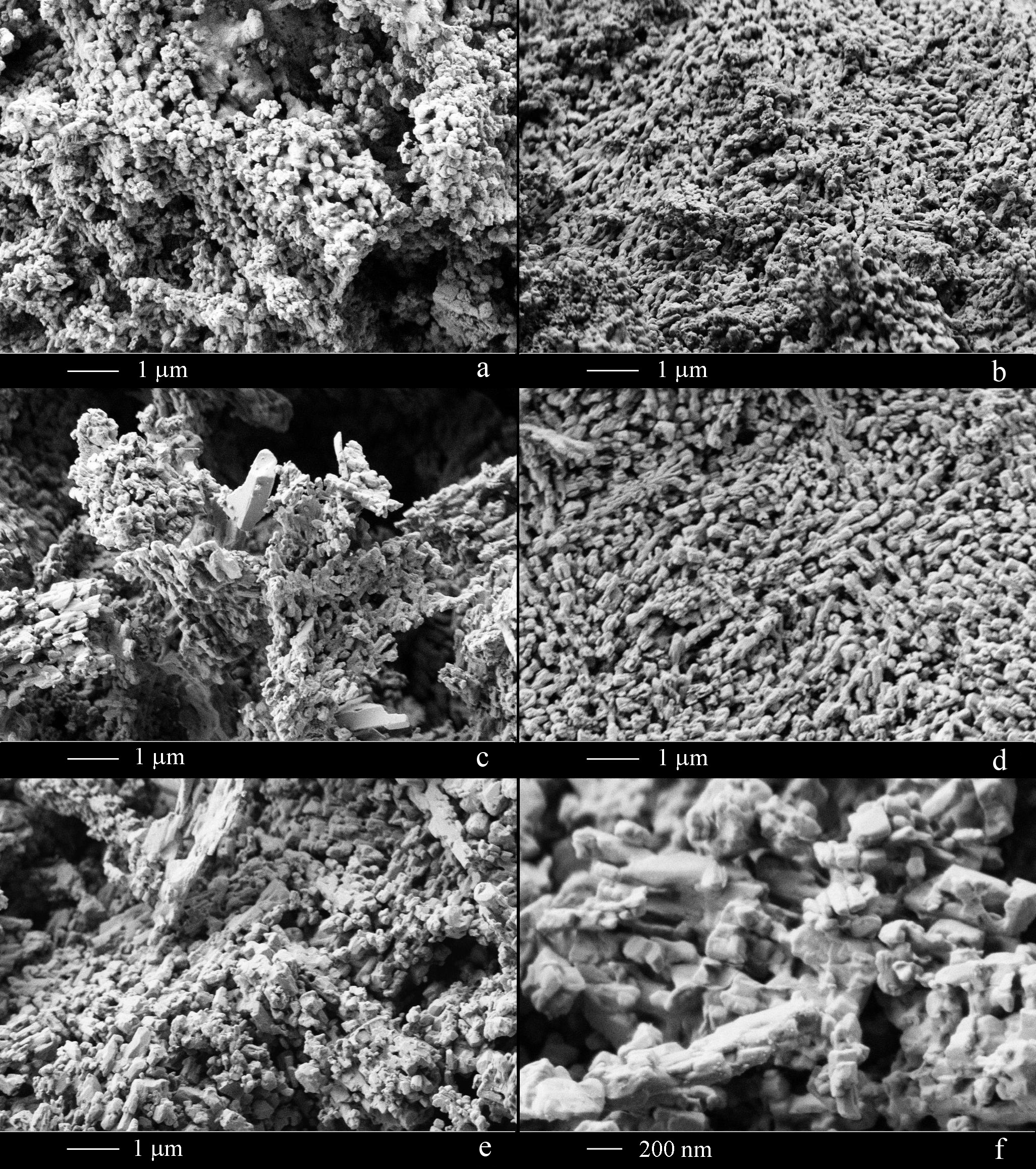
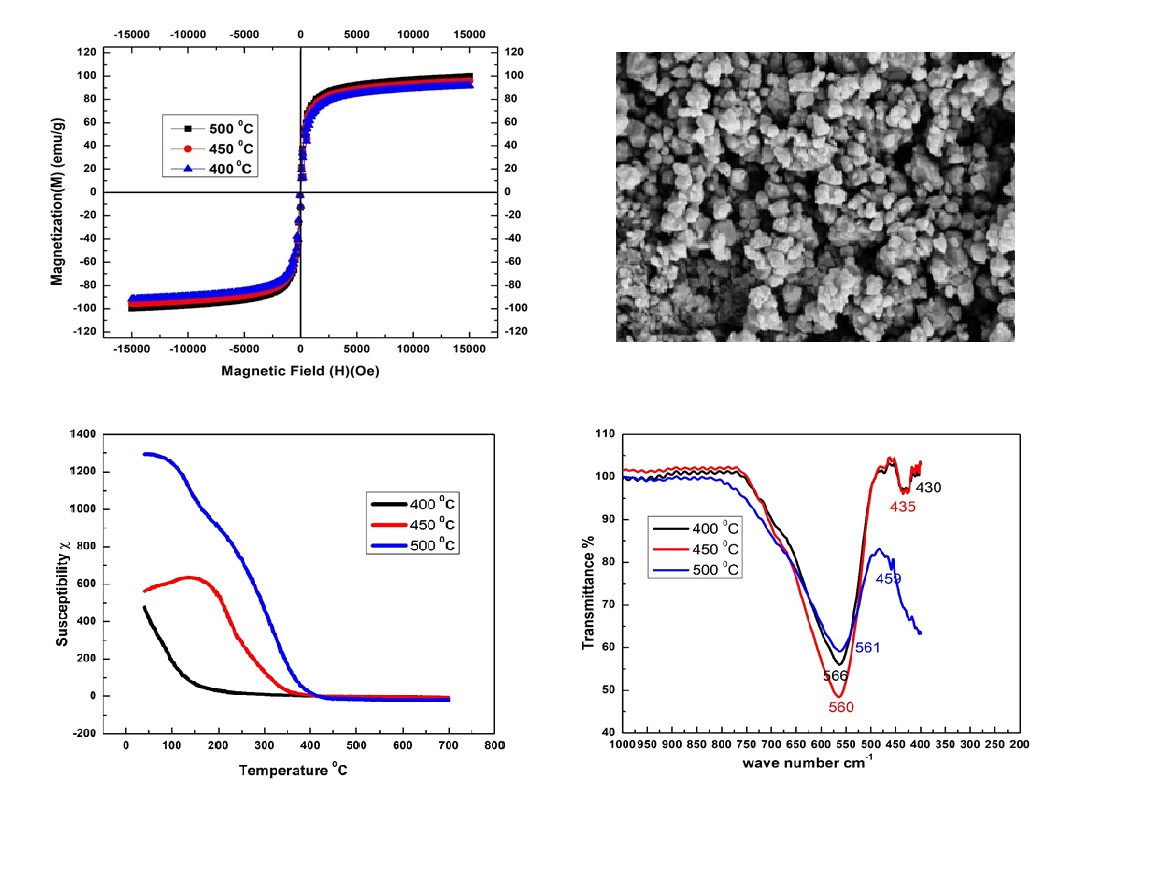
NiMgZn ferrites with chemical composition Ni0.2Mg0.3Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanomaterials were synthesized using the sol-gel technique. The various properties of the samples prepared at three different calcination temperatures (T) of 400, 450 and 500 ◦C/5 hr were studied. The X-ray diffraction study confirmed the single-phase cubic spinel structure (JCPDS 08-0234) for 400 & 500 ◦C calcined samples and with Fe2O3 as an impurity phase for 450 ◦C calcined sample with lattice parameter values 8.296 to 8.376 A. The surface morphology and EDX spectra observed with field emission˚ scanning electron microscope (FESEM) images confirmed the nano-sized irregular shaped grain development at low calcination temperatures. The force constants are determined using FTIR spectroscopy confirmed the M–O bonds present in ferrites. Optical band gap properties studied and found that NiMgZn ferrites have band gaps in semiconducting region from 1.68 to 1.75 eV. The susceptibility-temperature (χ-T) dependence is studied using a Bartington MS2B Dual Frequency instrument in heating and cooling modes and magnetic transition temperature (Tc) were determined. The highest magnetic susceptibility of 1293 is observed for 500 ◦C calcined material. By using VSM, the M–H loop, magnetic properties are studied, which showed that this material is ferrimagnetic. Also, the magnetic moments and saturation magnetizations (Ms) are calculated. The maximum saturation magnetization 97.20 emu/g is observed for 400 ◦C calcined sample.
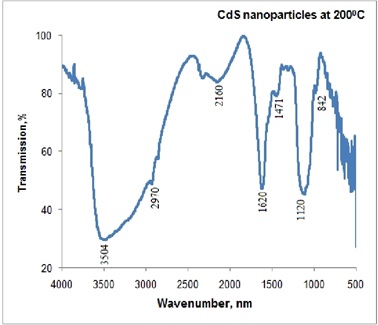
Large scale cadmium sulfide nanoparticles were synthesized by simple chemical route. The microstructure of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles was characterized by X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD) FESEM, FTIR and UV-visible spectroscopy. The XRD results showed that there was a transformation from cubic to hexagonal crystalline phase. The W–H plots show the size and nature of the strain incorporated in peak broadening of X-ray diffraction peaks. Some of the observed peak broadening can be attributed to crystallite size and microstrain effects, dislocation density, hkldependent peak broadening and peak shifts are clearly associated with stacking faults. The refractive index of the CdS nanoparticles was estimated to 2.22. The optical band gap of the synthesized CdS nanoparticles was calculated by Tauc relation and found to be 3.45 eV. The dependence of the blue shift and optical band gap on the quantum size effect was confirmed by UV-Visible spectroscopy. FTIR study confirmedthat the –C–O and –OH groups of thioglycerol can readily bind with CdS nanoparticles.
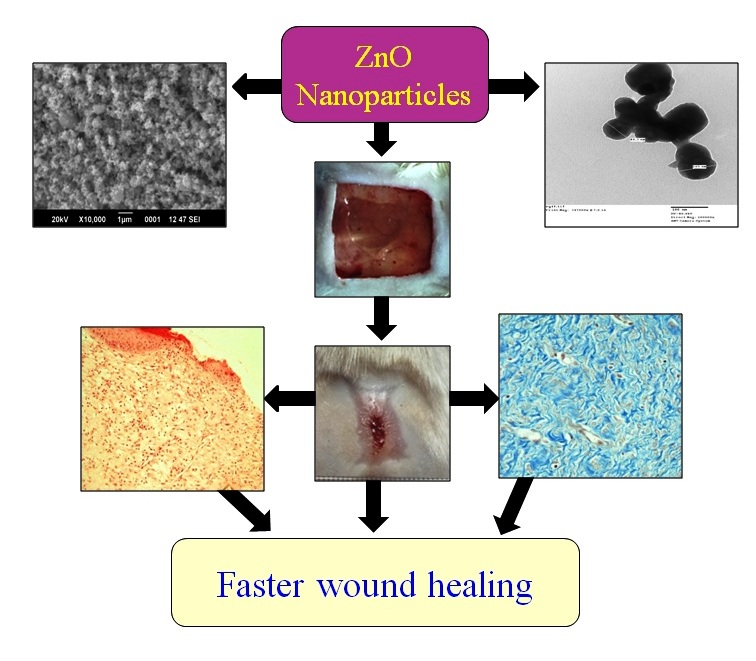
Development of nanotechnology has led to massive breakthroughs in the area of wound healing. Recently, metal oxide nanoparticles have shown a broad range of applications in biomedical fields. The lack of potent healing agents for complicated wounds and healing potentials of zinc oxide (ZnO) motivated us to evaluate the wound healing potentials of nano ZnO in comparison to its bulk form in rats. In the present study, single open excision wounds (2×2 cm2) were created on the backs of fifteen rats and divided into Group I, II and III. On the wounds of group I, II and III, topical application of ointment base, bulk ZnO (20 %) and ZnO nanoparticles (2 %) was done for 14 days, respectively. Significantly smaller wound area and increased percent wound contraction was evident in the ZnO nanoparticles-treated group. Histopathological analysis revealed that the ZnO nanoparticle-treated wounds possessed reduced numbers of fibroblasts and blood vessels. However, collagen fibers in ZnO treated group were compactly arranged in thick bundles with a well-organized manner and orientation. The newly formed epithelial layer was also covering more area of healing tissue in the ZnO nanoparticle-treated group. The ZnO nanoparticle-treated group also revealed the higher overall wound maturity score, as compared to other groups. In view of this, it might be concluded that topical application of ZnO nanoparticles (2 %) caused faster wound healing and the healing was better than bulk ZnO treatment, even at ten-fold lower concentration.
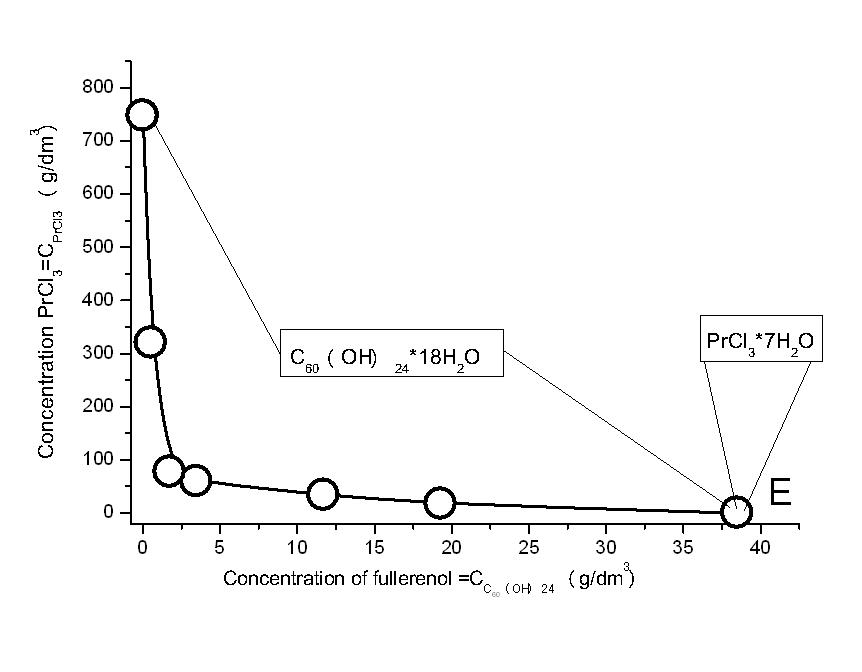
Solubility diagram was investigated by the method of saturation in ampules at 25 ± 0.02◦C for 4 hours. The solubility diagram of the PrCl3– C60(OH)24–H2O ternary system at 25 ◦C occurs as simple eutonics, consisting of two branches, corresponding to the crystallization of crystalhydrates: PrCl3 · 7H2O and C60(OH)24 · 18H2O. The diagram contains one non-variant point each – eutonics, which corresponds to saturation with pair of crystal-hydrates simultaneously. The diagram also contains very short branch of PrCl3 · 7H2O crystallization, and long branch of C60(OH)24 · 18H2O, where the effect of fullerenol salt-out is distinctly observed.
Praseodymium orthoferrite nanoparticles were synthesized by a simple co-precipitation method via the hydrolysis of Pr (III) and Fe (III) cations in boiling ethanol with 5% aqueous ammonia. The single-phase PrFeO3 product formed after annealing the precipitates at 650, 750, and 850◦C for 1 h had an average crystal size of 20–30 nm (XRD, SEM, TEM). The synthesized nanopowders were soft ferromagnetic materials with low coercive force and excessive magnetization values.
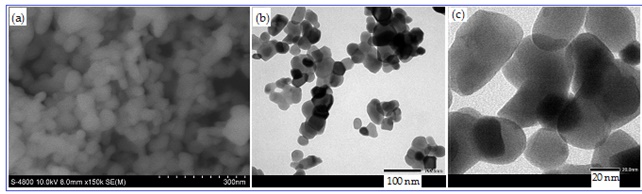
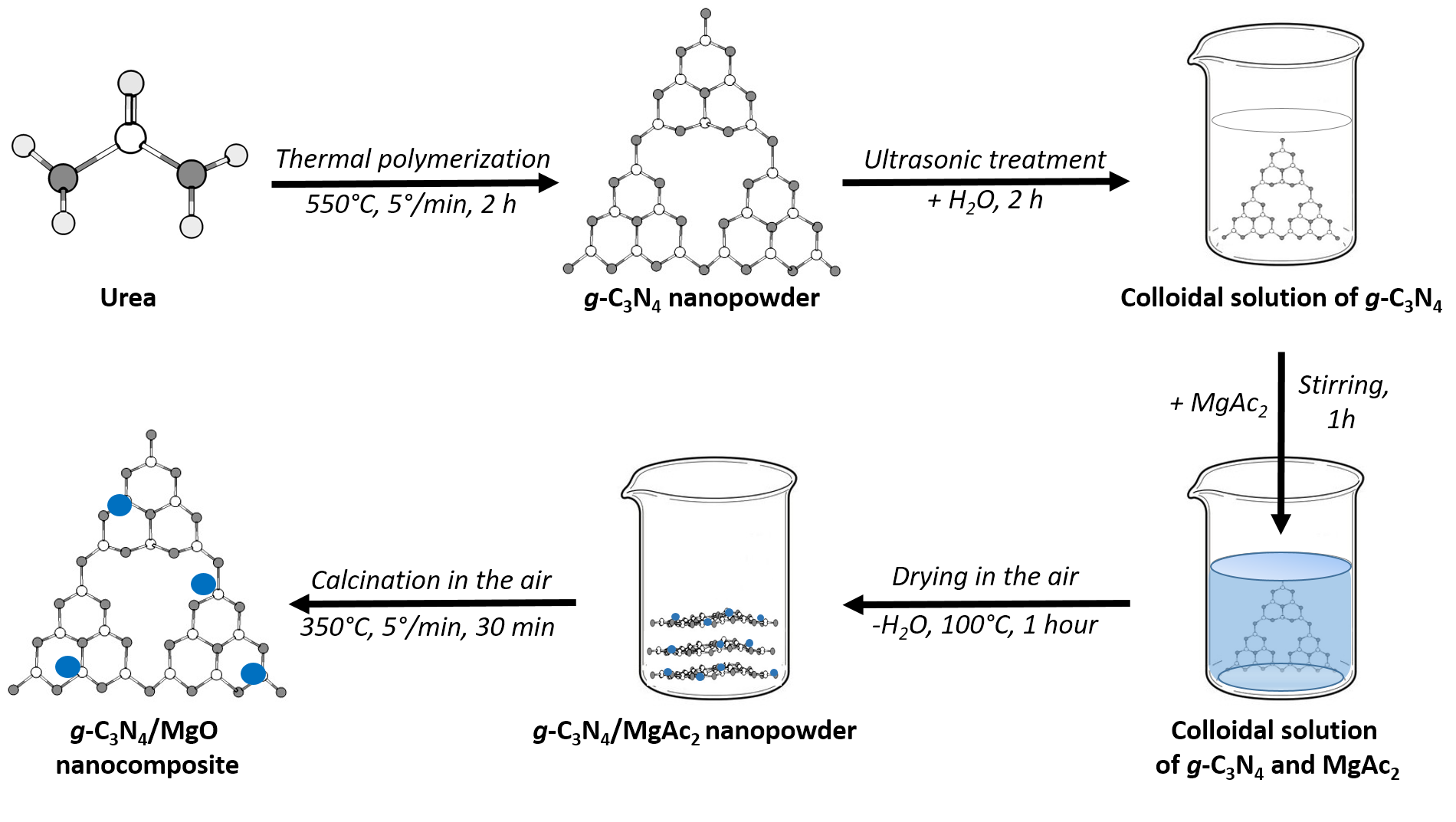
In this work, a simple wet-chemical route was proposed to synthesize g-C3N4/MgO (5% wt.) with enhanced electrocatalytic activity toward hydrogen evolution from water-ethanol (10% vol.) solution. It was found that synthesized nanocomposite is a single phase and chemically pure, consisting of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and cubic magnesium oxide (MgO, periclase) with an average crystallite size of 15.5 nm and 9.5 nm, respectively. It was shown that magnesia nanoparticles are evenly distributed on the surface of g-C3N4 nanosheets and uniform distribution of components is observed over the nanocomposite volume. It was found that this feature leads to an improvement in the electrocatalytic characteristics of the synthesized nanocomposite. So, the g-C3N4/MgO-coated electrode has an overpotential of −251 mV, which is better than for a g-C3N4coated (−264 mV) or pure nickel (−293 mV) electrode. Moreover, the nanocomposite-based electrode posses a low Tafel slope (−106.7 mV/dec) and high cyclic and chronopotentiometry stability.
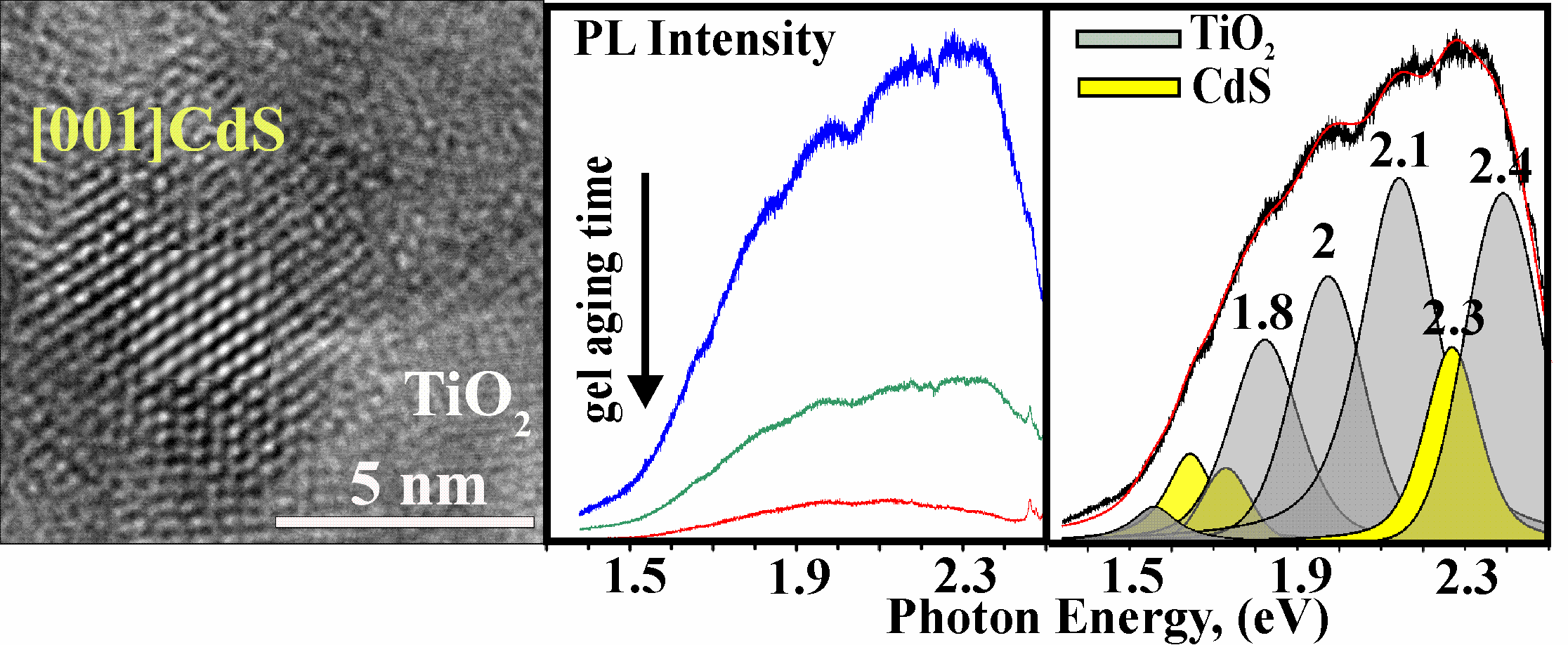
A series of sol-gel TiO2/CdS, TiO2 powders and coagulated CdS nanoparticles were studied by XRD, HRTEM and Raman spectroscopy to elucidate the effect of low-temperature gel aging time on visible photoluminescence (PL) emission of the TiO2/CdS composites. With an increase in aging time a content of amorphous titania and incorporated CdS nanoparticles decreases in composites. For all composites, visible PL emission includes bands attributed to surface oxygen vacancies and hydroxyl group of TiO2 nanocrystals, as well as yellow-green and red bands related to lattice defect states of CdS nanoparticles. It was found that gel aging time is a crucial parameter to influence visible PL emission in composites. This emission is suppressed with increasing aging time, and its evolution shows that healing of oxygen vacancy defects and hydroxyl group affect visible emission more significantly than improving crystallinity degree. The correlation between visible PL emission in TiO2/CdS and their visible-light photocatalytic activity was discussed.
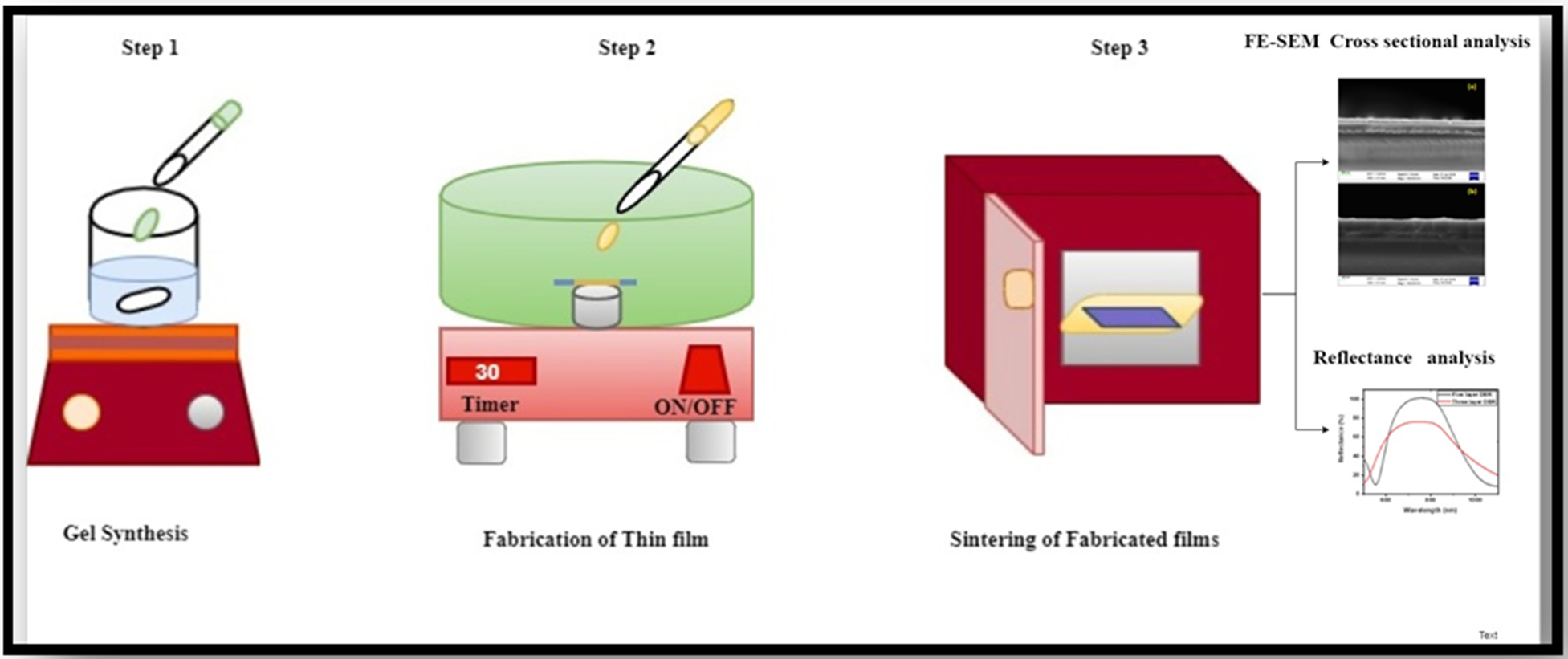
We report the fabrication of three- and five-layered based TiO2/SiO2 dielectric structures as the back-end reflector application in thin film silicon solar cells. These dielectric structures are prepared by the combined sol-gel and spin-coating techniques. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of both the three- and five-layered based structures confirmed the anatase phase of TiO2 with its dominant peak at 2θ = 25◦. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) study demonstrated the formation of three and five alternate layers of TiO2 and SiO2 films. Comparatively, five-layered based reflector yielded the maximum (100 %) reflectance in the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength region as evidenced by the UV-Vis spectroscopy investigation.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)