MATHEMATICS
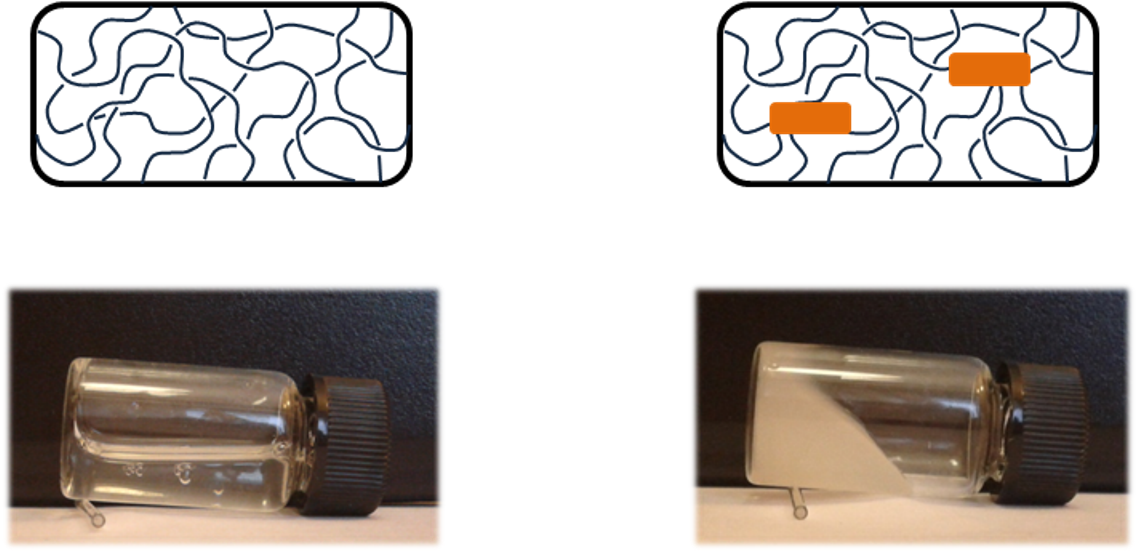
A metric graph model is suggested for the Stokes flow concentrated in the vicinity of a network embedded in R3. As a basic problem, we consider the case corresponding to strong variation of the viscosity and density in a cylinder of small radius. An equation for the main term of the asymptotics is obtained. As for a graph structure, coupling conditions are assumed at the graph vertices.
PHYSICS
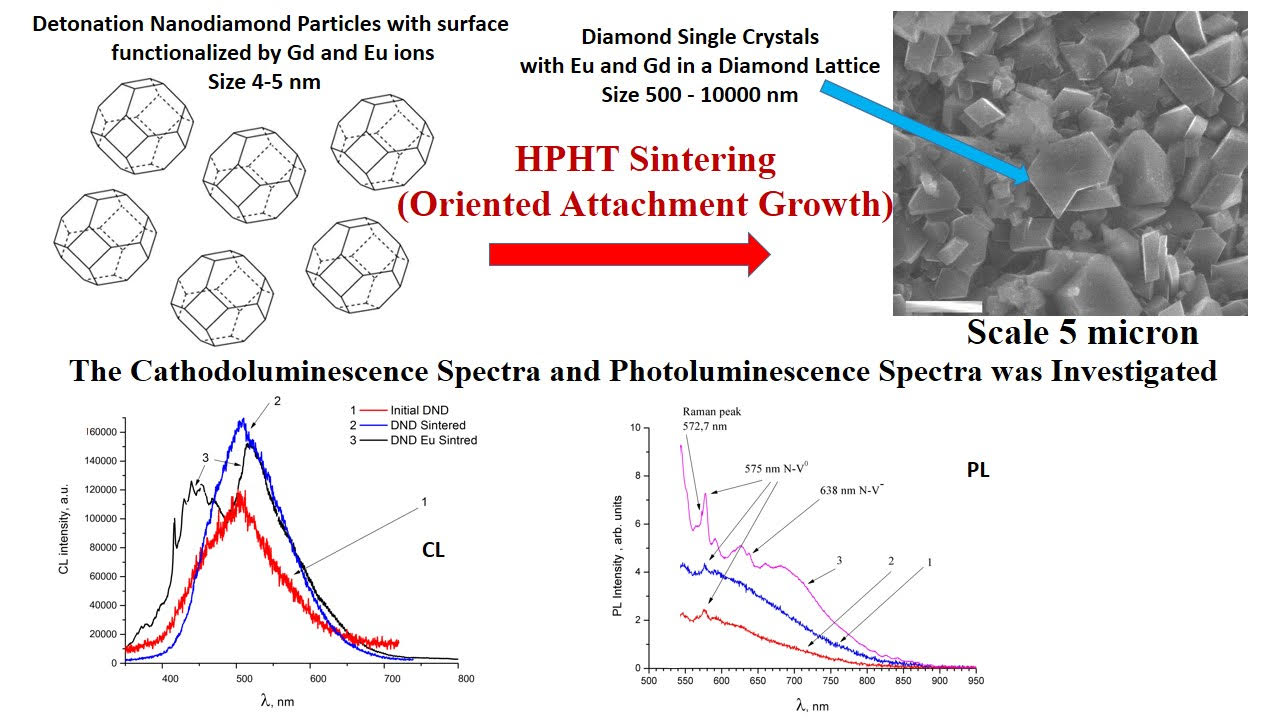
The photo- and cathodoluminescence spectra (PL, CL) of diamond single crystals synthesized under high-pressure and at high-temperature (HPHT sintering) from detonation nanodiamonds (DND) particles with Gd and Eu ion-functionalized surfaces have been studied. The HPHT sintering was made under pressures (P ∼ = 7 GPa) and temperature (T = 1300 – 1500 ◦C). The DND particles have sizes of 4 – 5 nm, hydrocarbons and/or alcohols were used at the HPHT synthesis instead of traditional metal catalysts. The initial and synthesized crystals were characterized by X-ray microanalysis, mass-spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), PL and CL. Mass spectra confirmed that Gd and Eu atoms were inserted into the volume of diamond single crystals in the HPHT sintering. A significant conversion of the PL and CL spectra of synthesized diamond single crystals compared with HPHT diamond crystals were observed. Transformation of the point defect assemblies inherent to the diamond crystal can explain the observed spectra.
Heitler–Heisenberg multispin states were studied via irreducible representations of the united symmetry with respect to permutations and space transformations group. The mean energy is given in explicit form in terms of the characters of the joint group irreducible representations. The system’s Fockian covariance incorporates its exchange integral of the self-consistent states into the Heisenberg chain theory. External fields account is delivered in perturbation theory frame. Its application to statistical physics approach leads to the thermodynamic parameter evaluation. The nanotube example with space symmetry including rotations and translations, is studied. Its symmetry introduces basic closest neighbor exchange integrals that enter the statistical sum.
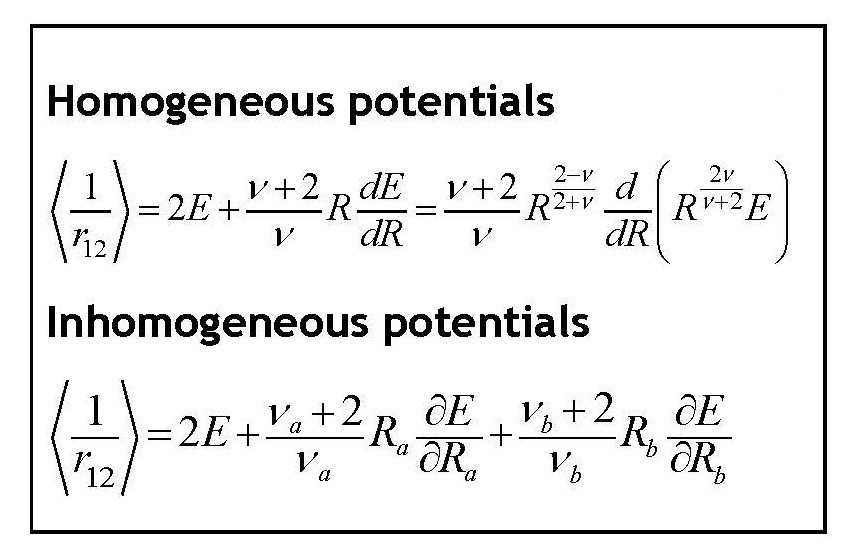
Singly-excited singlet-triplet pairs of states of two-electron spherically symmetric systems, that are degenerate in the absence of inter-electronic repulsion, are revisited. In addition to the obvious two-electron atom we consider the two-electron quantum dot confined by either a harmonic potential or by an infinite spherical well, the confined two-electron atom, and three variants of an atom immersed in a plasma, modeled by the screened Coulomb (Debye) potential. The validity of Hund’s multiplicity rule is confirmed, and the contribution of the interparticle repulsion energy to the singlet-triplet splitting is examined. One feature that all these systems share is that the triplet wave function is contracted relative to that of the corresponding singlet. This feature, which is a consequence of the virial theorem, affects both the behavior of the outer electron ionization energies and the relative magnitudes of the inter-particle repulsion energies in the singlet vs. the triplet. Whereas in atomic highly positive ions the interelectronic repulsion is lower in the triplet than in the corresponding singlet state, this ordering is reversed in neutral atoms. Such reversal does not take place in quantum dots. Confined and screened systems exhibit more nuanced behavior. The analysis utilizes appropriate variants of the virial and Hellmann–Feynman theorems.
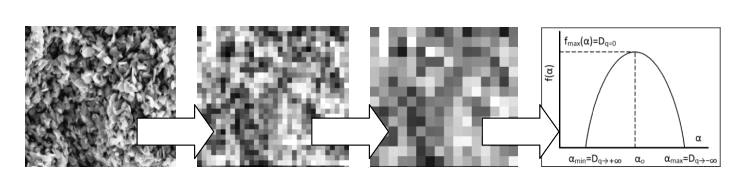
The article presents a developed gradient-pixel method of fractal analysis and results of multifractal characterization of nano- structured materials with a high proportion of non-autonomous phases obtained from micrographs of their surface chips with high-resolution scanning microscopes. Compared with the black and white binarization option, the gray gradation improves the quality of multifractal analysis of nanostructured materials and expands its capabilities, in particular, the selection of multi-scale composite inclusions in the structure of the material and nano-objects on transparent or opaque basis. Establishing the characteristics of these dependencies permits linking the indicators of structural and phase nonuniformity in the development of new materials with changes in their physicochemical properties. In comparison with the fractal dimension of the Sierpinski carpet as a classic regular monofractal computed on the outlined basis, quite accurately coinciding with the known analytical value, the resulting spectrum of fractal dimensions of the synthesized chemical-catalytic and thermoelectric nanomaterials indicates the multifractal nature of their structural and phase nonuniformity according to the Renyi generalized equation.
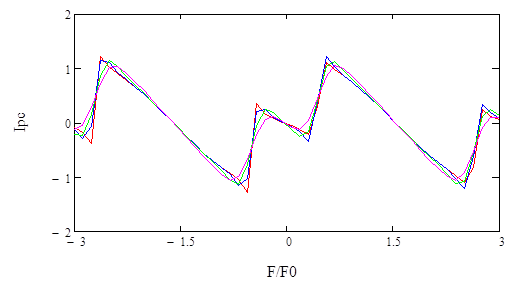
The persistent current in a chain of two quantum rings threaded by an Aharonov–Bohm flux is studied in the presence of electron-phonon interactions and Rashba spin-orbit coupling. The chain is modeled by the Holstein–Hubbard–Rashba Hamiltonian, the phonon’s degrees of freedom were eliminated by the conventional Lang–Firsov transformation, the effective electronic Hamiltonian was diagonalized by using the Hartree–Fock approximation. The equations for ground state energy, persistent current and Drude weight were also obtained. The persistent current was calculated by differentiating the GS energy. The dependence of ground state energy, persistent current and Drude weight as a functions of flux for different values of Rashba spin-orbit interaction was numerically shown. The effects of Aharonov–Bohm flux, temperature, chemical potential spin-orbit interaction and electron-phonon interaction on the persistent current were also investigated.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
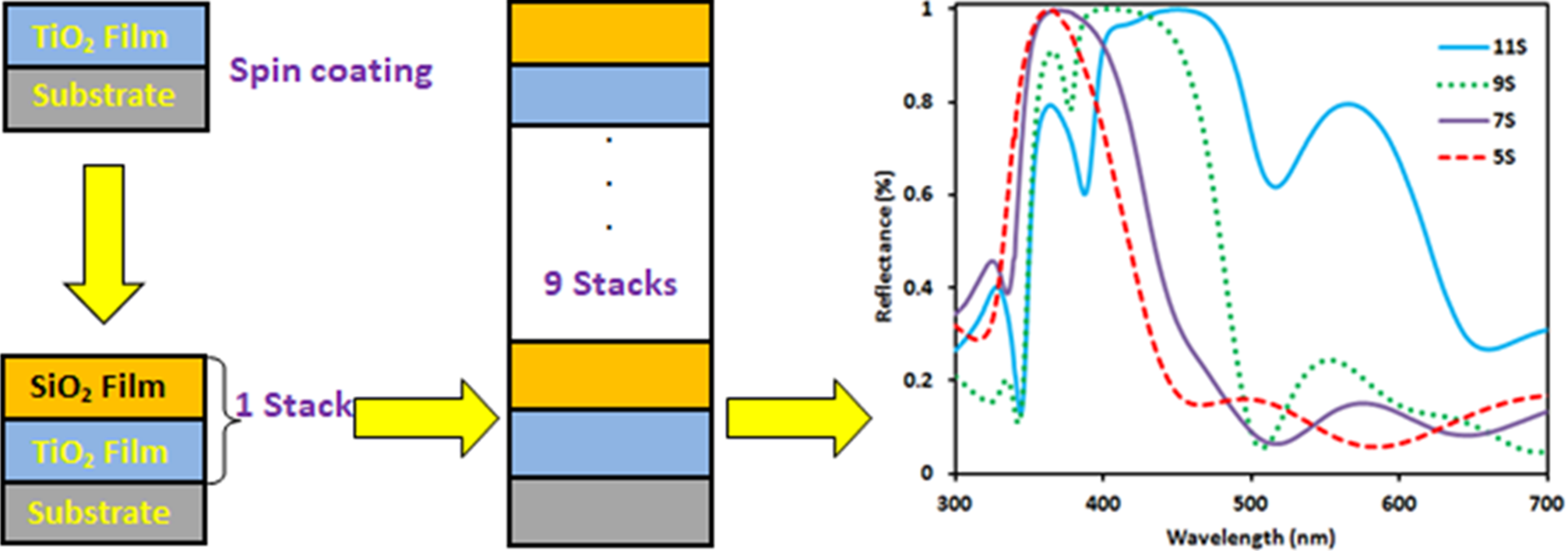
The TiO2/SiO2 alternating multilayers of one-dimensional photonic crystals (1DPCs) was fabricated by the sol-gel process and a spin coating method. This study investigated the possibility of creating a better solar cell back reflector by introducing maximum and broader reflection towards longer wavelength spectral region with effect of optimal thin films. After the fabrication of 1DPCs, the optical properties were investigated by Raman spectroscopy, Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), UV-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). From the results, the Raman spectra exhibited notable peaks and indicates the presence of anatase TiO2 and SiO2 layered structures. Furthermore, the highest reflectance was observed in the visible region and shifting into the longer wavelength spectral region due to the increment of alternative layers (stacks). These structural and morphological results are encouraging for the realization of TiO2 and SiO2 materials for various applications, including LED and photovoltaics.
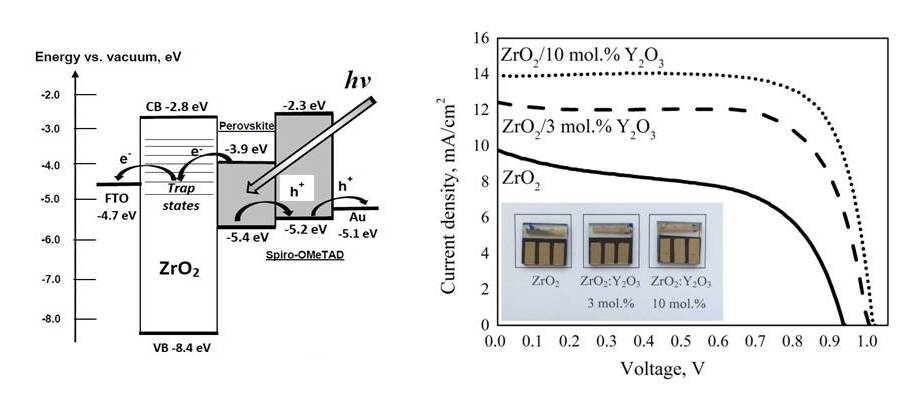
Very wide-bandgap undoped and Y2O3-doped ZrO2 nanoparticles were synthesized and their structural, optical, morphological and energy characteristics were investigated. It was found that the bandgap value in ZrO2 decreases with Y2O3 doping. The developed materials were used for fabrication of nanostructured photoelectrodes for perovskite solar cells (PSCs) with the architecture of glass/FTO/ZrO2– Y2O3/CH3NH3PbI3/spiro-MeOTAD/Au. The power conversion efficiency in the PSCs based on ZrO2–Y2O3 photoelectrodes was significantly higher than that for undoped ZrO2 photoelectrodes. We have found that nanostructured layers, based on very wide-bandgap materials could efficiently transfer the injected electrons via a hopping transport mechanism.
Soft hydrogels based on a transient network of wormlike surfactant micelles containing bentonite nanoclay tactoids as physical cross-links were developed. The network was composed of mixed micelles of nontoxic zwitterionic surfactant oleylamidopropyldimethylcarboxybetaine and an anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate. It was demonstrated that before nanoclay addition the solution has pronounced viscoelastic properties with zero-shear viscosity of 100 Pa s and plateau modulus around 7 Pa, which were attributed to the formation of an entangled micellar network. The solution demonstrated pronounced shear thinning behavior provided by the elongation of wormlike micellar chains in flow direction. Upon addition of non-exfoliated nanoclay particles, the zero-shear viscosity increases by an order of magnitude, while the useful property of shear-induced thinning is retained. Oscillation amplitude tests show that viscoelastic fluid becomes hydrogel upon addition of nanoclay, because elastic response was observed even at large stress amplitudes. This behavior was attributed to the formation of nanoclaywormlike micelles junctions. Prepared soft hydrogel is a promising candidate for injection applications, because of its self-assembled structure providing pronounced shear-thinning behavior and fast recovery of rheological properties at rest. In this nanocomposite material, nanoclay tactoids strengthen the hydrogels and can serve as reservoirs for the delivery of various substances.
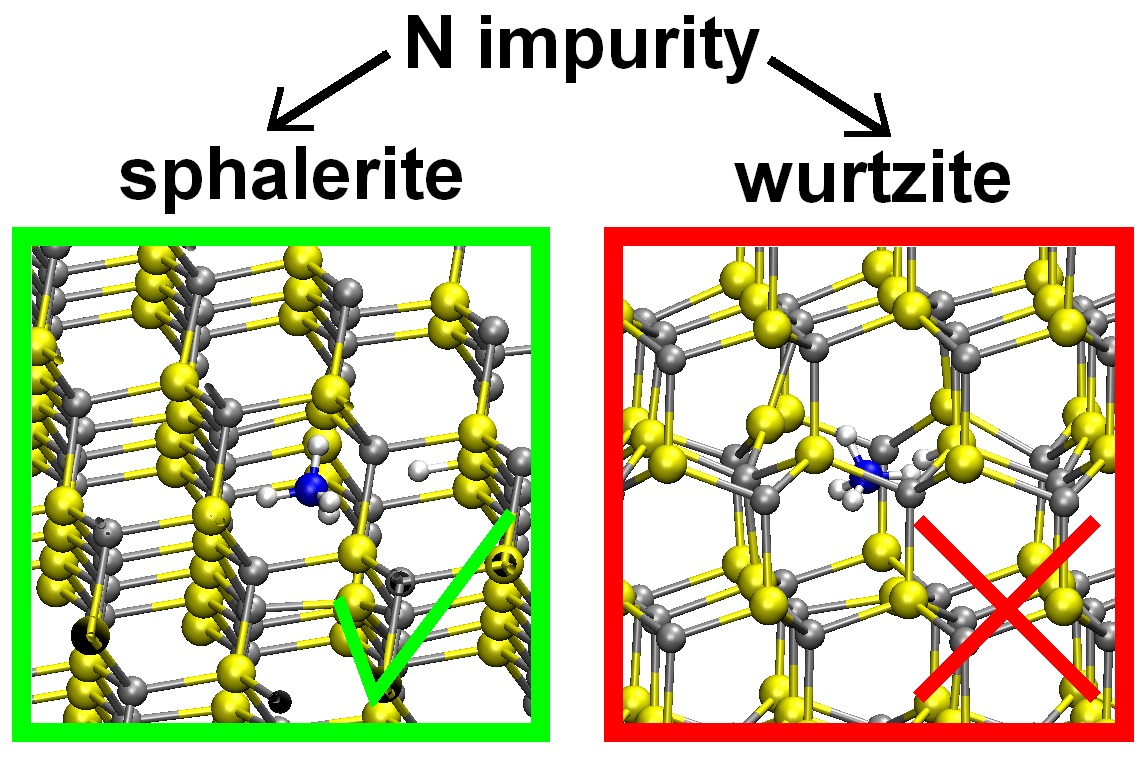
The ZnS polymorphs – sphalerite and wurtzite – have the very close formation energies, setting their coexistence in nature. Moreover, numerous cases of a disordered phase formation based on these polymorphs have been registered. However, sphalerite is a common mineral, while wurtzite is rare. Perhaps the wider distribution of sphalerite can be explained by means of stabilizing effect from impurities. In this paper, the most stable form and the localization of nitrogen impurities in both ZnS polymorphs is screened using the methods of quantum chemistry. The influence of impurity on polymorphic wurtzite-sphalerite equilibrium is disclosed. According to the obtained results, the introduction of nitrogen impurities facilitates the domination of sphalerite over wurtzite.
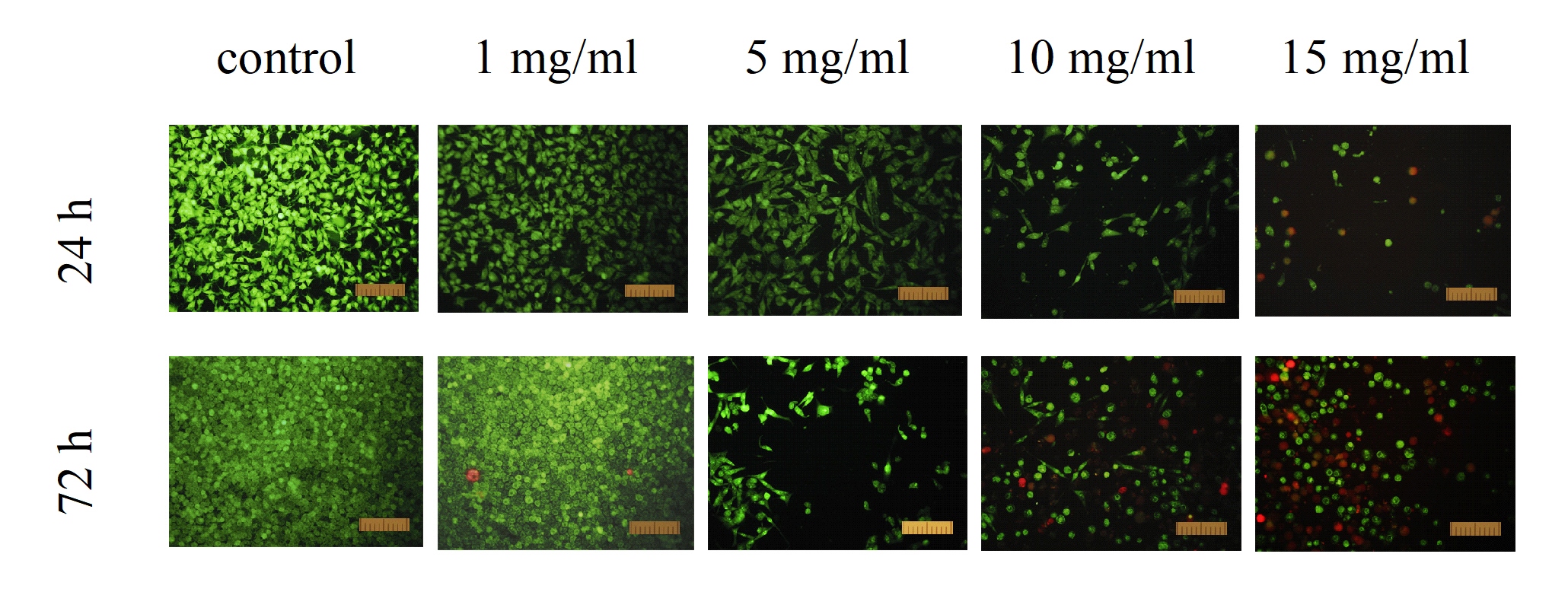
In this study, photochromic PVP-stabilized tungsten oxide nanoparticles (WO3-x NPs) were shown to exhibit a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on mouse fibroblasts in vitro. WO3-x NPs reduce viability and proliferative activity of the cells via induction of intracellular oxidative stress leading to apoptosis and cell death. WO3-x NPs modulate the mRNA expression of a wide range of genes responsible for oxidative stress and the cell redox-system.
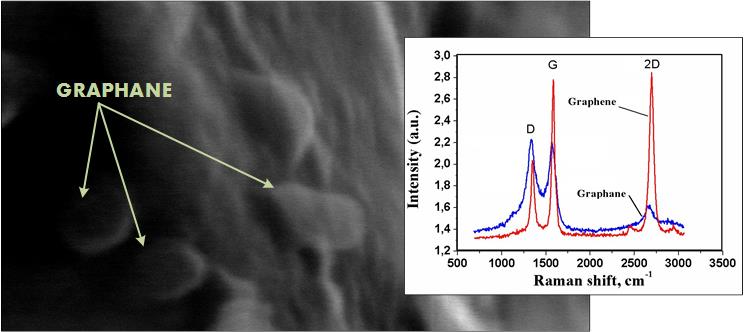
We study graphene synthesis in a plasma-jet reactor. Graphene is obtained via decomposition of hydrocarbons in the plasma produced in the DC plasma torch. The products of synthesis are characterized using the following methods: electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, thermal analysis and express-gravimetry. We make the conclusion that, at the few-layer graphene samples, their hydrogenation takes place. The maximal hydrogen-to-carbon ratio was 1:4.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)