MATHEMATICS
By taking advantage of Wang’s results on the scalar product of four eigenfunctions of the 1D harmonic oscillator, we explicitly calculate the trace of the Birman–Schwinger operator of the one-dimensional harmonic oscillator perturbed by a Gaussian potential, showing that it can be written as a ratio of Gamma functions.
We consider a family of 2 × 2 operator matrices Aµ(k), k ∈ T3 := (−π, π]3, µ > 0, acting in the direct sum of zeroand one-particle subspaces of a Fock space. It is associated with the Hamiltonian of a system consisting of at most two particles on a three-dimensional lattice ℤ3, interacting via annihilation and creation operators. We find a set Λ := {k(1), ..., k(8)} ⊂ T3 and a critical value of the coupling constant µ to establish necessary and sufficient conditions for either z = 0 = min/ k∈T3 σess(Aµ(k)) ( or z = 27/2 = max/k∈T3 σess(Aµ(k)) is a threshold eigenvalue or a virtual level of Aµ(k(i)) for some k(i) ∈ Λ.
The FitzHugh–Nagumo model on a metric graph is studied. System of delayed differential equations is used to model a pair of FitzHughNagumo excitable systems with time-delayed fast threshold modulation coupling. The model can be used for description of signal transmission in different nanostructures, microsystems or neural networks. The effect of time delay on the impulse transmission is studied.
PHYSICS
Linear optical quantum computing can be realized using photonic integrate circuits (PICs). It is advantageous in comparison to other physical implementations of quantum computing due to simplicity of qubit encoding using photons and low decoherence times. Passive components like beamsplitters and phaseshifters are key elements for such PICs. In this article, we present modeling of linear optical controlled-Z gate with imperfections of beamsplitters and phaseshifters taken into account. Results showed that errors occur which cannot be detected by projection measurements and post-selection proposed by Knill, Laflamme and Milburn. We studied how these errors and success probability changes with the increase of dimensional errors using Monte-Carlo simulation. The obtained results can be used for design and calibration stages of chip manufacturing.
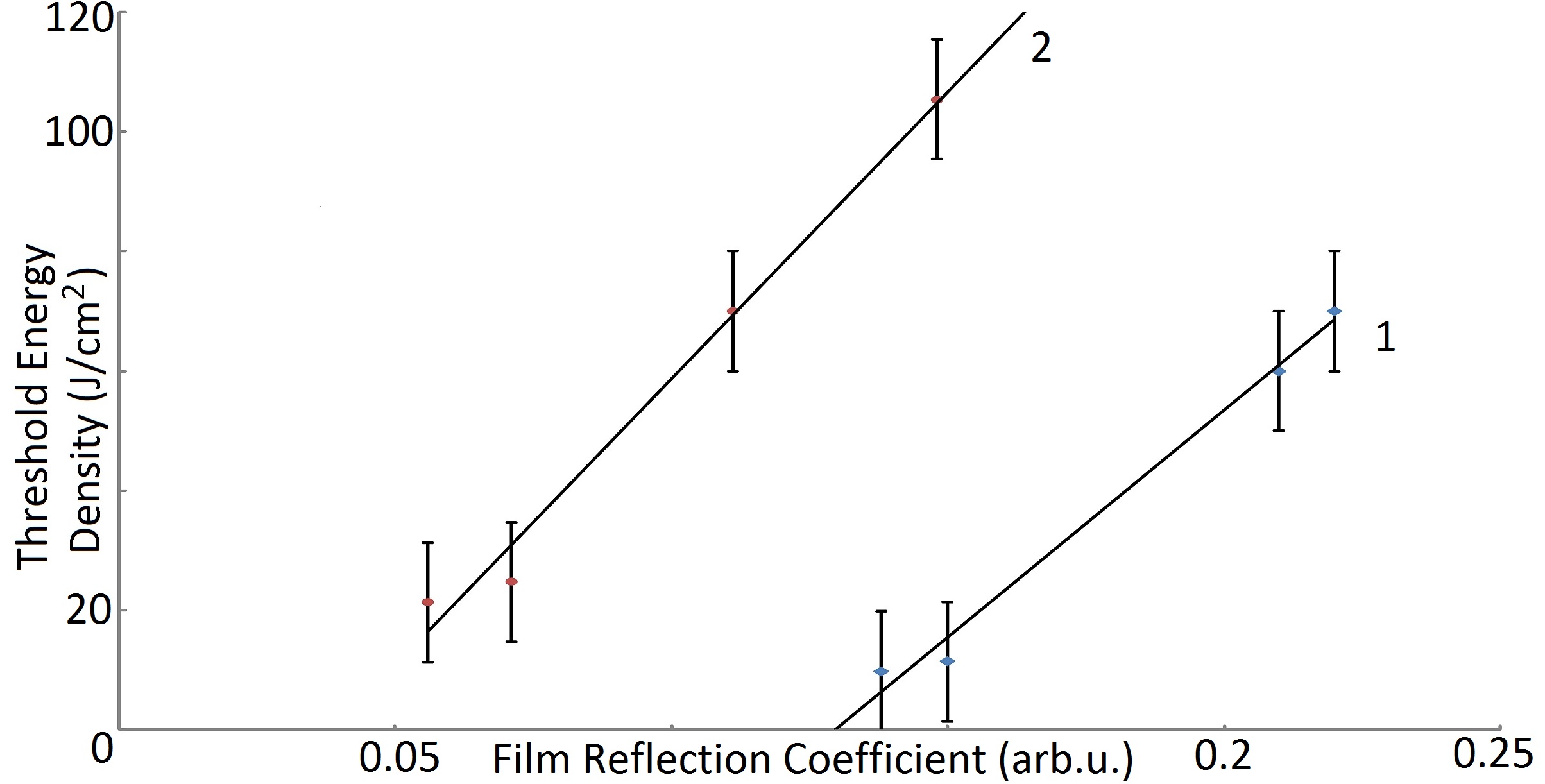
This study concerns the composites optical characteristics dependence on the chemical composition of the oxide nanofilms from TiO2–MexOy and on the existence of a SiO2 barrier layer. The laser ablation destruction threshold energy density values decrease with the light transmission growth in the visible range of the composites for oneand double-layer nanofilms. These properties measurement results dependences for the composites with oneand double-layer nanofilms can be connected with various structure and composition of the complexes which were formed in the films.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
In this paper, we present a facile method for replacing conventional Pt-based counter electrode (CE) in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) for the alternative low-cost nanostructured material containing reduced graphene oxide (RGO). Pt-NPs/RGO-based nanohybrid layers were synthesized at low temperature on a conductive glass substrate using microwave-assisted heating reduction strategy. The obtained material was characterized using XRD, SEM and TEM measurements and used for fabrication layered CEs on glass substrates. Photovoltaic characteristics of the DSCs based on Pt nanoparticle-functionalized RGO CEs were investigated under simulated AM1.5G solar illumination at an intensity of 1000 W/m2. The obtained results have shown that Pt-NPs decorated RGO surfaces can be successfully used as CEs in high-efficiency DSCs and may be promising as low-cost electrodes in energy storage devices.
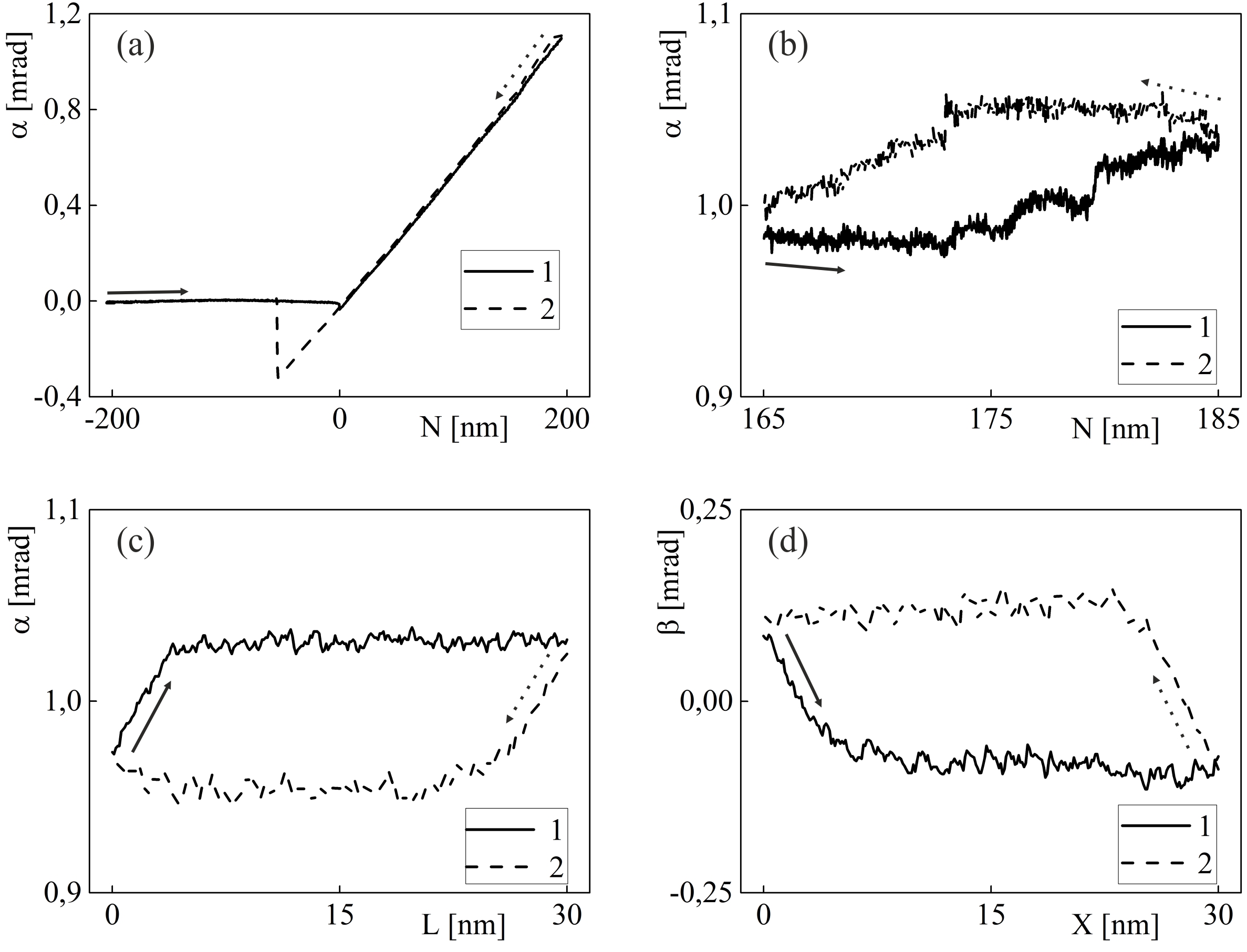
To improve the accuracy of atomic force microscopy in nanomechanical experiments, an analytical model is proposed to study the static interaction of a cantilever in contact with a sample. The model takes into account: the cantilever probe is clamped by the sample or slides along its surface, the geometric and mechanical characteristics of the sample and the cantilever, their relative orientation. The cantilever console bending and torsion angles as functions of the sample displacements in three orthogonal directions have been measured by atomic force microscopy with an optical beam deflection scheme.The measurements are in good agreement with the simulation.
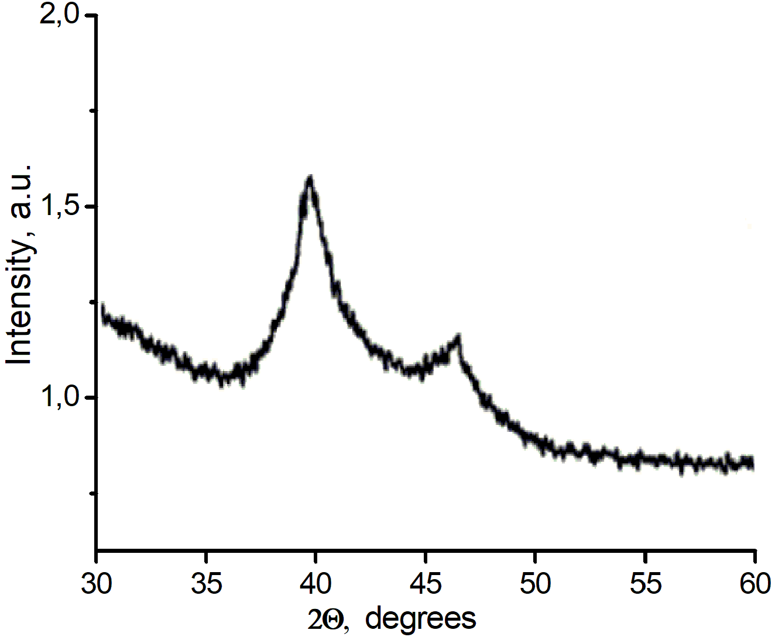
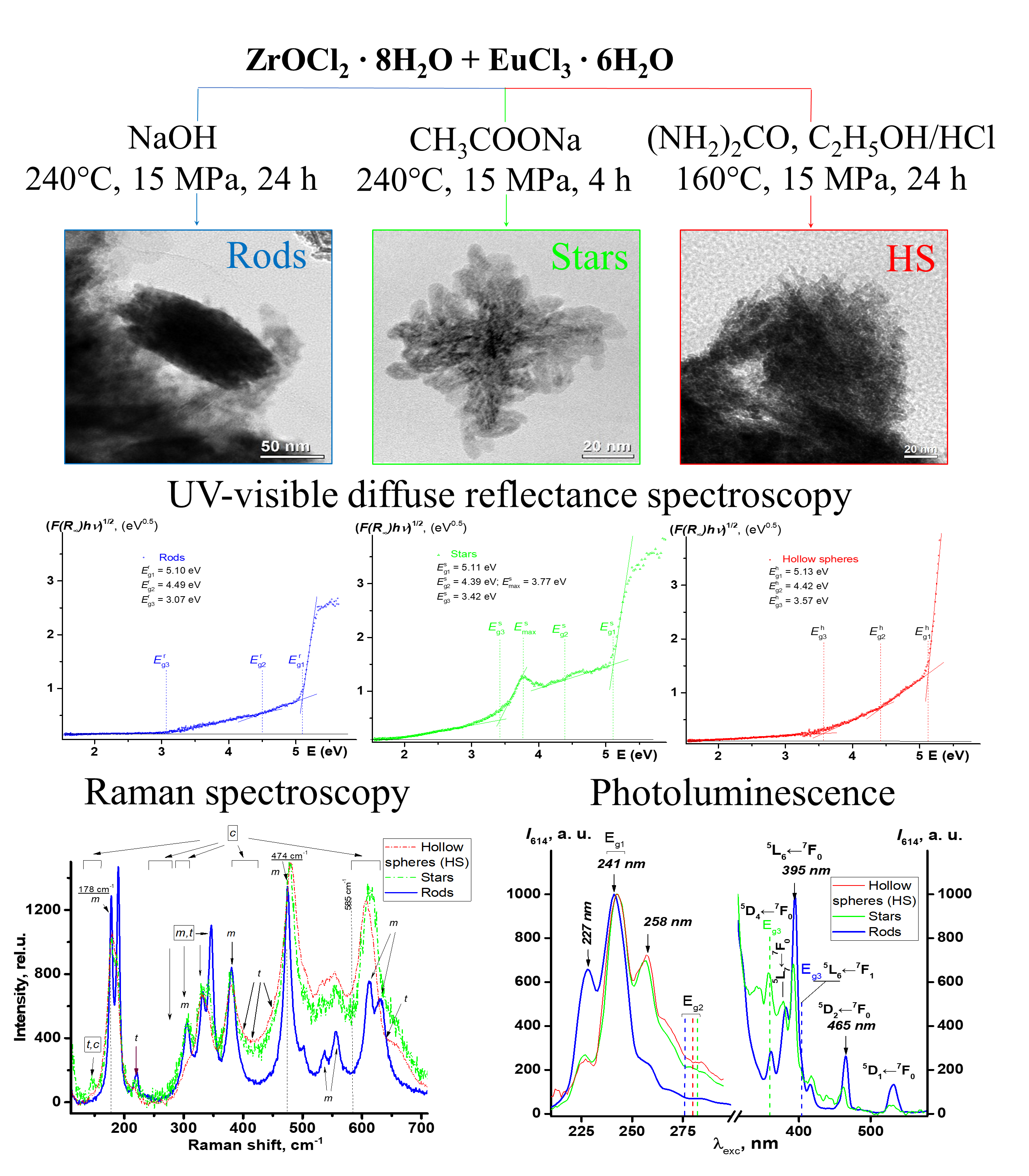
Eu3+-doped ZrO2 nanostructures in the form of rods, stars, and hollow spheres were prepared by varying hydrothermal conditions. X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflection spectroscopy, a low-temperature nitrogen adsorption method, Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence spectra were used to characterize the polymorph modification, surface and optical properties of the Zr0.98Eu0.02O2 nanophosphors. The Eu3+ content in a zirconia monoclinic lattice, remained constant for all types of obtained nanostructures in order to reveal the morphology influence on the efficiency of electronic excitation energy transfer from the host matrix to photoactive centers. The decrease of the average size of the coherent scattering regions in the series rods → stars → hollow spheres, is associated with increasing the specific surface area values. At that, in the photoluminescence spectrum, the splitting of the sublevels associated with the monoclinic lattice 5D0 → 7F1 disappears.
Impact of nanoparticles of various types as fillers on the stability of the poly(pyromellitimide)-based nanocomposite films’ properties in alkaline hydrolysis was studied. It was shown that the introduction of nanoparticles into the polymer can lead to an increase in excess free volume. This fact is evidenced by scanning electron microscopy and densitometric studies. The increase of the excess free volume was shown to provoke a rise of the diffusion intensity of the hydrolyzing agent in the films volume during their exposure to an alkaline medium. This effect leads to film swelling and, thereby, to increases of the intensity of the destructive action of hydrolysis on the material. Chemical surface pretreatment of the nanofiller allows one to obtain a composite with an increased packing density compared to that for a composite with unmodified nanoparticles. However, the hydrolytic stability of such a film still remains somewhat inferior to that of the pristine polyimide.
The milling of aluminum powders in non-aqueous solvents is used in the production of high-quality pigment pastes of flake shapes with thickness from some microns to hundreds of nanometers. In Russia, such pigments are not produced at a large scale, however, spherical powders made from aluminum and its alloys are manufactured. Starting the production of pigments from screenings of powder production will not only solve the problem of fine fractions disposal, but also reduce the cost of the target fractions powders. The fraction of powders with an average d50 of less than ∼20 µm should be disposed. In this research, by varying the laboratory conditions, the parameters for milling screenings of A8 aluminum powder, AK9ch and 1201 aluminum alloys were selected. The milling was performed in non-aqueous solvents: a highly refined commercial petroleum solvent and liquid paraffin oil. The prospects of using wet milling for the manufacture of pigment pastes from alloys has been demonstrated including average thicknesses of the flakes about 40–80 nm. Thus, it has been demonstrated that wet and bead grindings lead to thinning of metal powder particles to thicknesses of less than 100 nm.
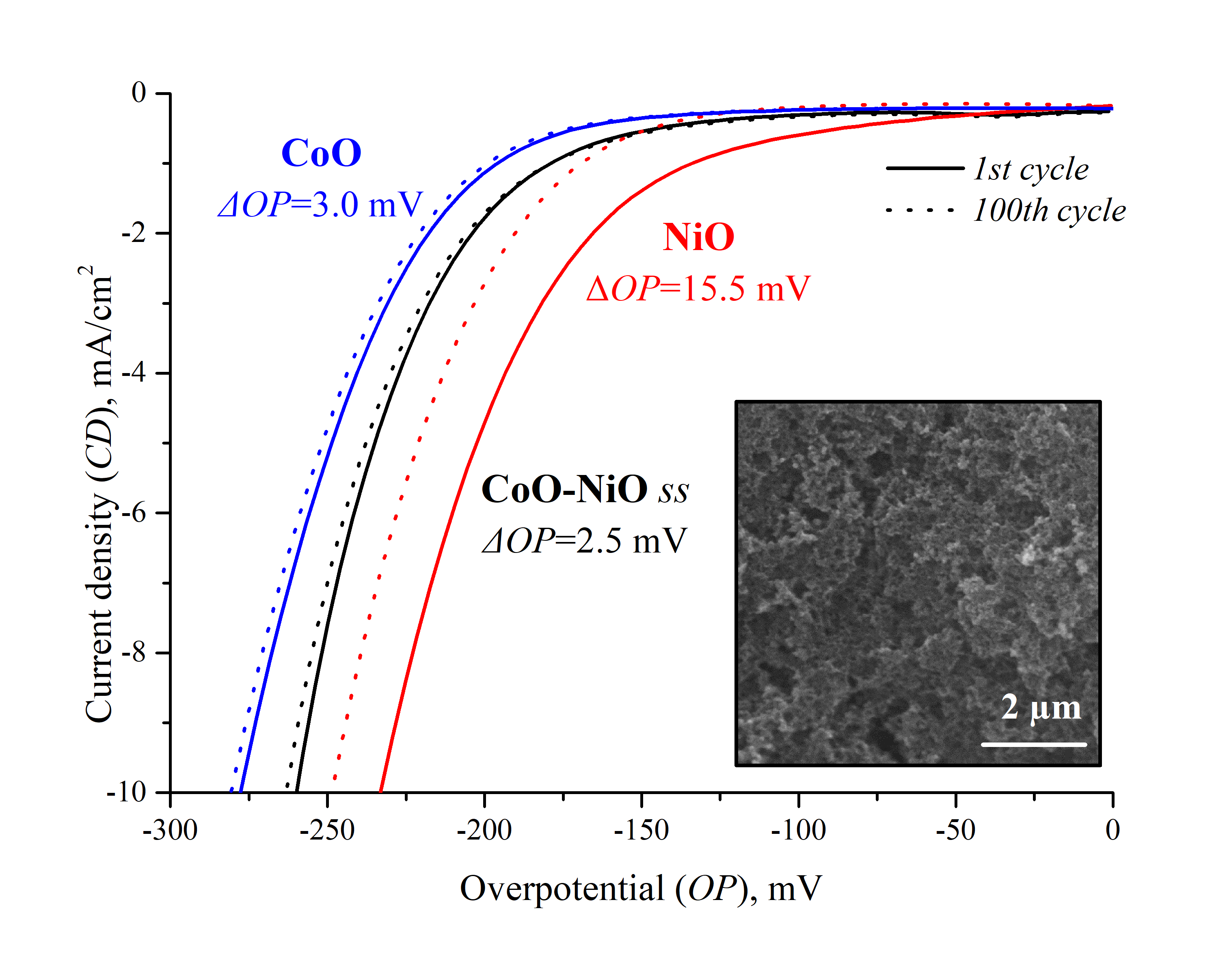
Currently, nanocrystalline NiO is well known as one of the best non-noble metal electrode material with low overpotential (OP) but mediocre stability. On the contrary, CoO has remarkable stability but the high values of OP. In this work, a method is proposed to achieve the stability of nickel oxide-based electrode materials while maintaining a low OP via the synthesis of a nanocrystalline CoO–NiO solid solution. Nanocrystals of CoO–NiO solid solution were synthesized by successive ionic layer deposition (SILD). XRD, SEM, and EDX analysis show that the CoO– NiO sample consists of 3 – 5 nm isometric crystallites of the solid solution mentioned above and Ni/Co ratio is equal to 45.4 % / 54.6 % at. Electrochemical investigation of the nanocrystalline CoO–NiO solution as electrode material shows OP values of −240 mV at a current density (CD) of 10 mA/cm2, Tafel slope values of 78 mV/dec for hydrogen production from water-ethanol solution (10 % vol.) and high cyclic stability – only 3 mV degradation at 10 mA/cm2 after 100 cycles of cyclic voltammetry. Thus, it was shown that the synthesis of a solid solution within the proposed approach makes it possible to maintain the high electrocatalytic properties inherent in NiO, but with high stability in a wide range of overpotential and in the high cyclic load inherent in CoO.
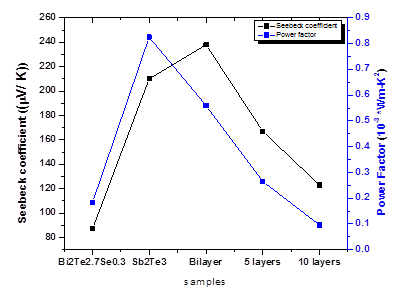
Selenium is known to be a semiconductor with many applications, and when it is doped in some chemical compounds, it changes the electrical properties of that compound which directly affect its thermoelectric performance. The present work is to synthesized multilayers of Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 / Sb2Te3 by e-beam evaporation technique on glass substrate at room temperature. Prepared thin films were characterized by XRD and also study their electrical, optical and thermoelectrical properties to enhance the thermoelectric performance of Thermoelectric (TE) devices.
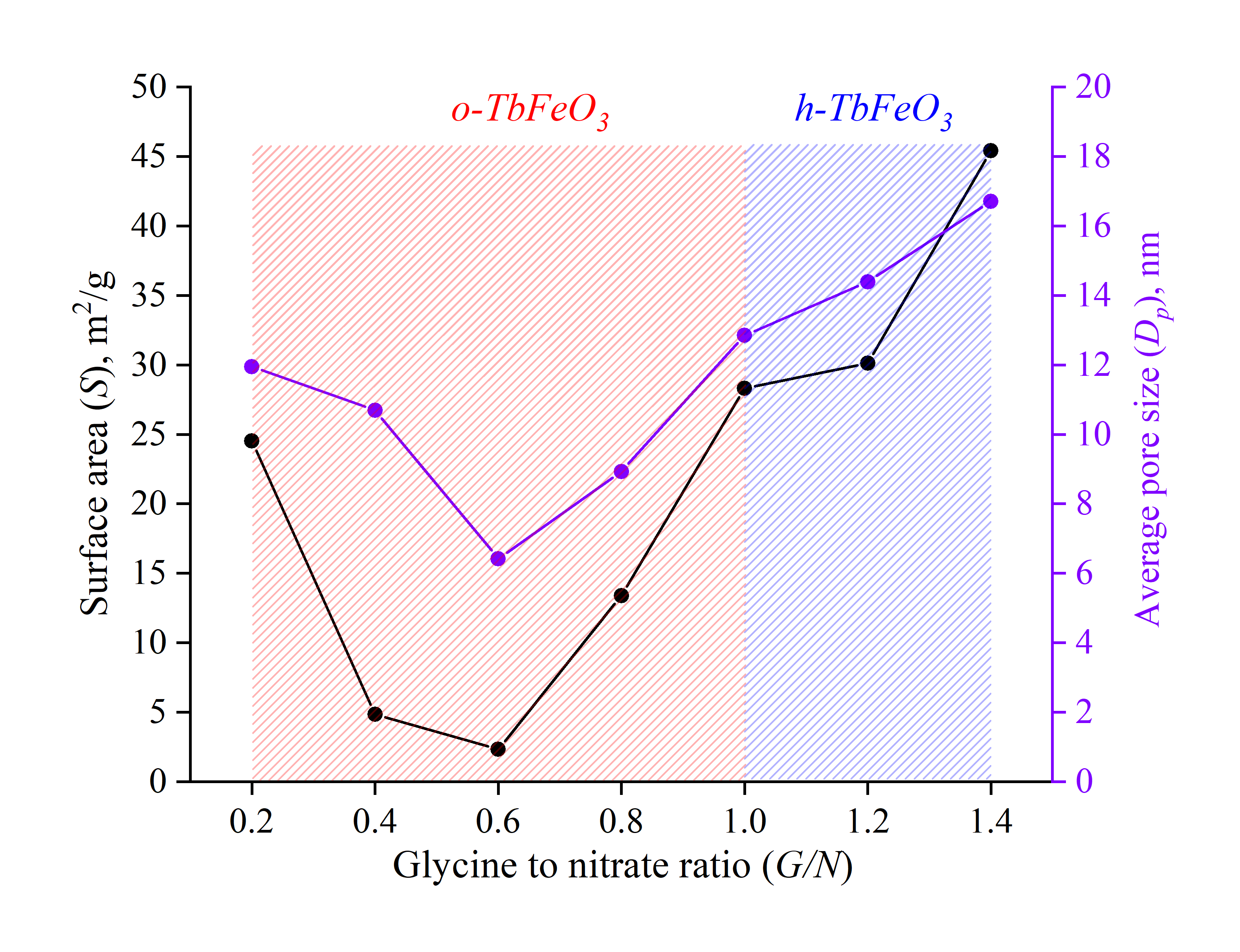
In this research, the formation process of nanocrystalline terbium orthoferrite (TbFeO3) obtained via a solution combustion technique was studied using powder X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, 57Fe Mo¨ssbauer spectroscopy, N2 adsorption analysis, and FTIR spectroscopy. It was shown that glycine-nitrate combustion method permits one to obtain TbFeO3 of three different modifications: orthorhombic o-TbFeO3 (Pbnm), hexagonal h-TbFeO3 (P63/mmc) and amorphous am-TbFeO3. It was found that the average crystallite sizes of orthorhombic and hexagonal TbFeO3 were 29±3 and 15±2 nm, respectively. The formation mechanism of different structural forms of terbium orthoferrite was investigated on the basis of nanopowders morphology, specific surface areas, average pore sizes, and crystallite sizes.
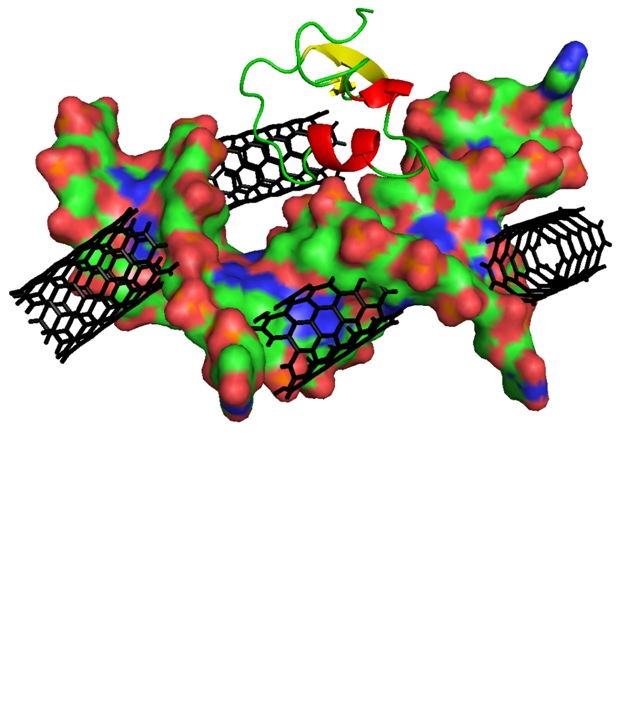
Most of the experimental biophysical and biochemical observations of proteins are in dilute solutions, while inside the cell is a crowded environment.The effect of crowding on the structure and activity of biomolecules is not completely clear. In this work, molecular dynamics simulation was used to study the effect of single walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) on the H–NS protein in the presence and absence of double-stranded nucleic acid. The values of root mean square deviation (RMSD) and its distribution, radius of gyration (Rg) and its distribution and root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) were calculated. Changes in the secondary structure of the H–NS were also calculated. The contributions of each residue of H–NS in free energy of binding between H–NS and DNA were calculated. The results indicate that the SWCNT unfolds the structure of the H–NS. In terms of contribution of residues in secondary structures, in the presence of a SWCNT, the sheet secondary structure of the H–NS changes more than helices secondary structure. In the triple system, which includes H–NS, SWCNT and DNA; Ala-1, Arg-3, Lys-6, Lys-17, Arg-24, Lys-30, Lys-31, Lys-38 and Lys-46 residues have a favorable effect on the interaction of the H–NS with the DNA.
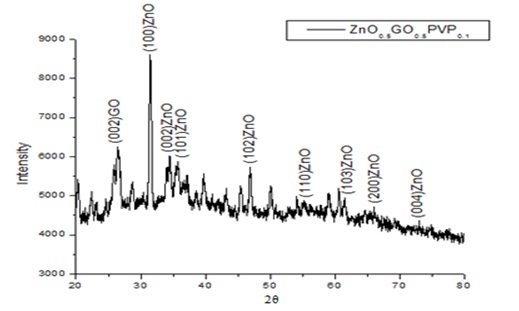
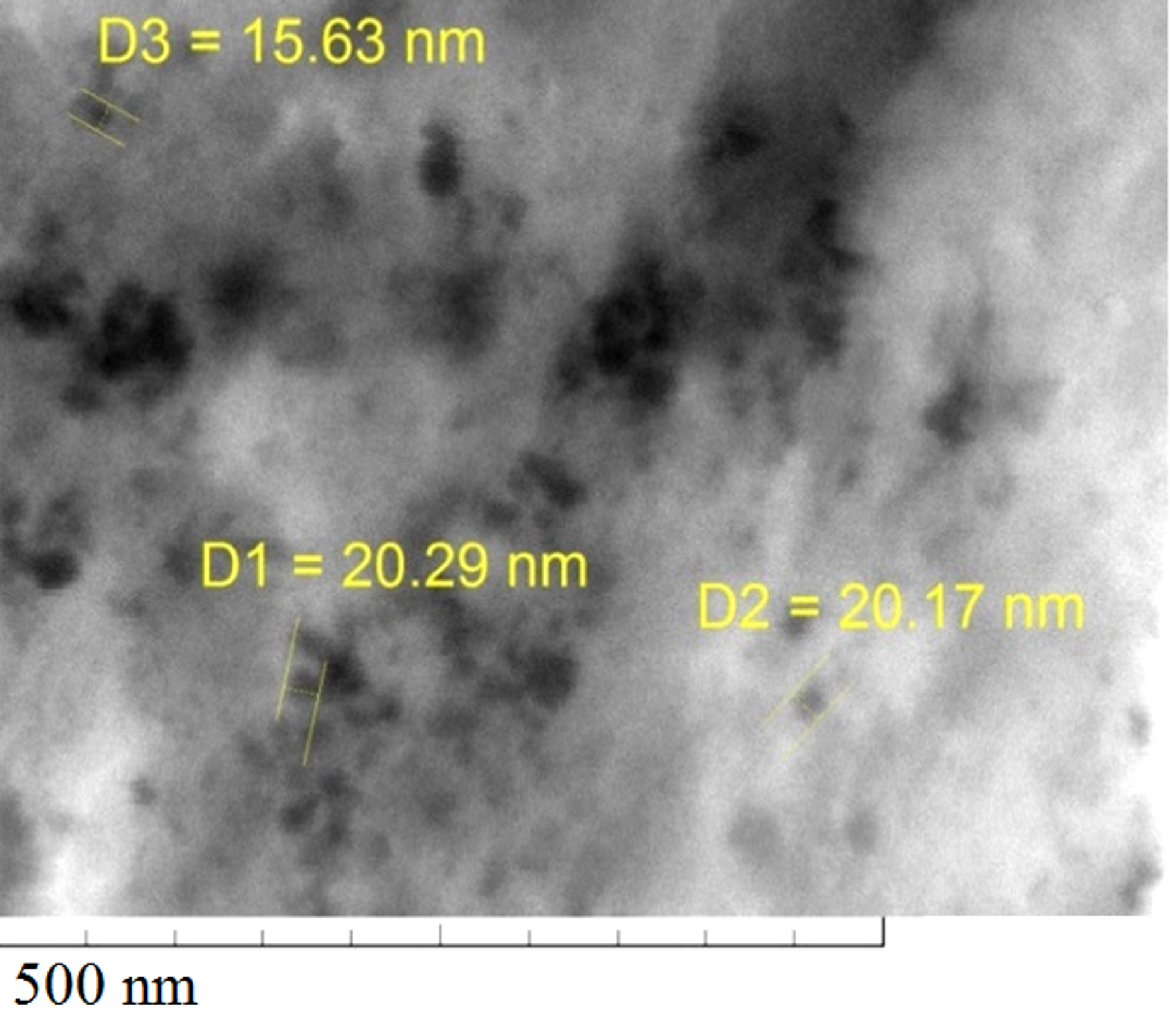
Zinc Oxide-Graphene Oxide (ZnO–GO) nanocomposites were prepared using solvents polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and N-Methyl-2 Pyrrolidone (NMP) by sol-gel technique and their optical, structural and morphological properties were investigated. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) studies show the presence of planes of GO and ZnO confirming the formation of composites. The particle sizes were calculated using Scherrer’s formula and were found to be in the nanometer range. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images show the formation of layered structures dispersed non-uniformly over clusters of particles. Energy Dispersive X-Ray (EDX) spectra confirm the presence of carbon, zinc and oxygen in the composites. The optical absorbance of ZnO–GO synthesized using PVP was higher than ZnO–GO with NMP with the absorption edge shifting to shorter wavelength in the presence of NMP. The band gap values were found to be in the range of 2.7–3.0 eV. The band gap of ZnO–GO synthesized using NMP was higher than ZnO–GO synthesized using PVP.
The investigation of indium antimonide quantum dots has been carried out by the methods of differential normalized tunnel current-voltage characteristics, electron microscopy, particle size analysis and spectral dependence of the absorption coefficient. Qualitatively and quantitatively consistent measurement results were obtained with an error less than 15 %. It is concluded that the analysis of normalized differential tunnel current-voltage characteristics is an effective method of express-analysis that can be used in investigation of quantum-sized objects properties.
The processes taking place with a spray unit during aluminum dispersion have been analyzed. It has been shown that the major process which occurs in a nipple during aluminum flowing is the reduction of silicon with aluminum and, also, with magnesium from the melt (in case when aluminum-magnesium or magnesium-containing alloys are used). The reduction of silicon results in the formation of nanoscale particles with crystalline size 20–50 nm and leads to the degradation of the nipple material, which is accompanied by its cracking and the formation of nanoscale channels and the flow of melt into the material through these channels. This phenomenon leads to the rupture and/or blockage of the nipple.
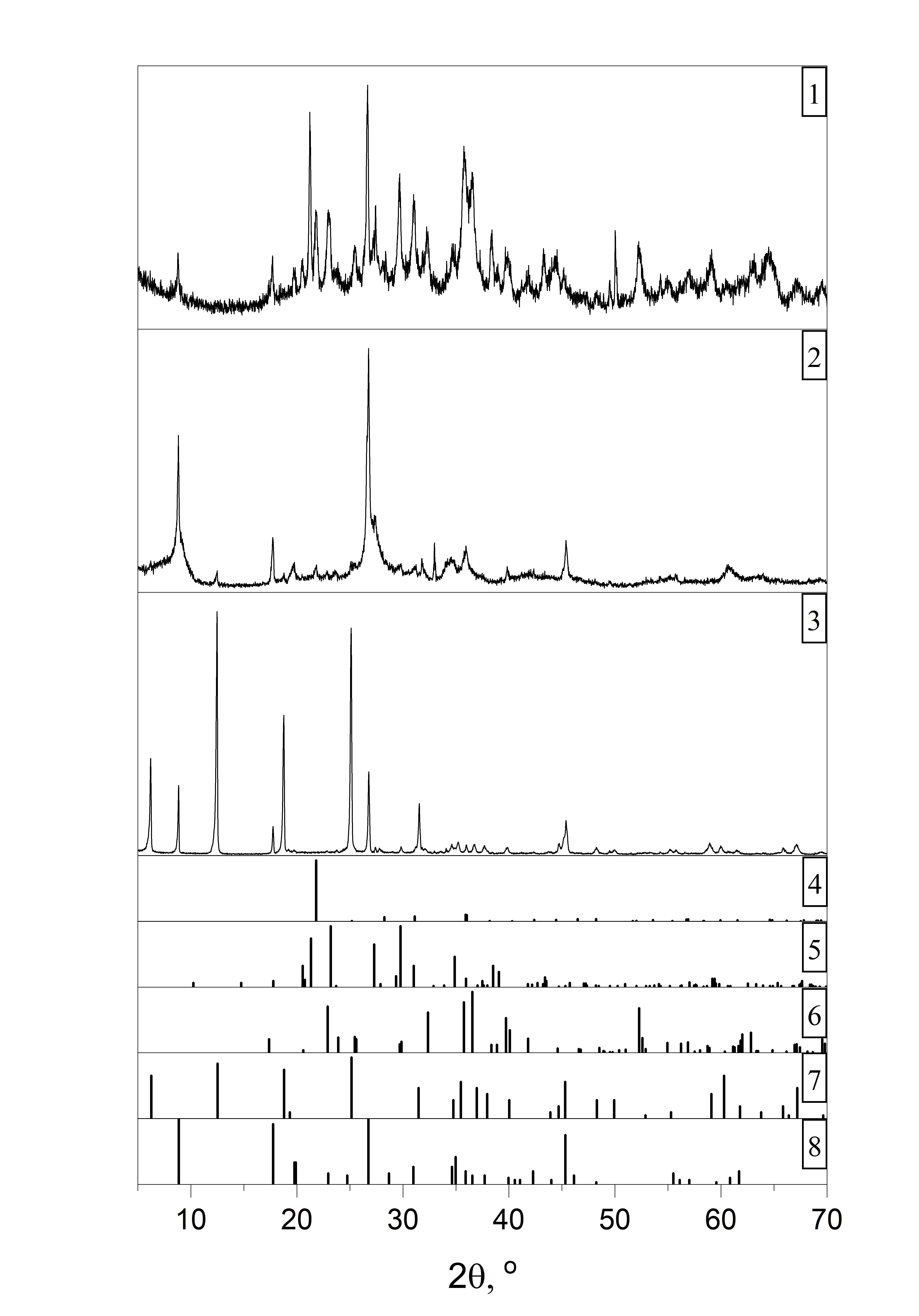
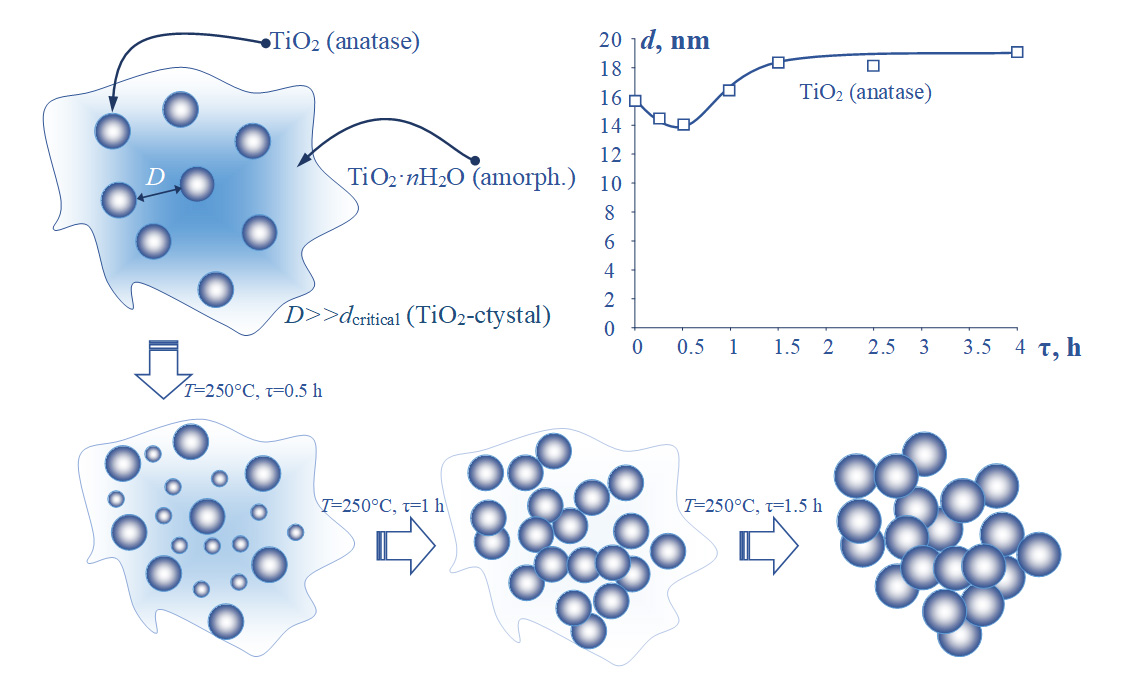
The effects of heterogeneous impurities on the process of titanium dioxide nanoparticle formation during hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic properties of synthesized particles were studied. Pre-formed TiO2 nanoparticles of anatase and rutile modifications were used as the heterogeneous impurity. It is shown that the heterogeneous impurities may be considered neither as geometric constraints precluding the crystallization, nor as crystallization centers.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)