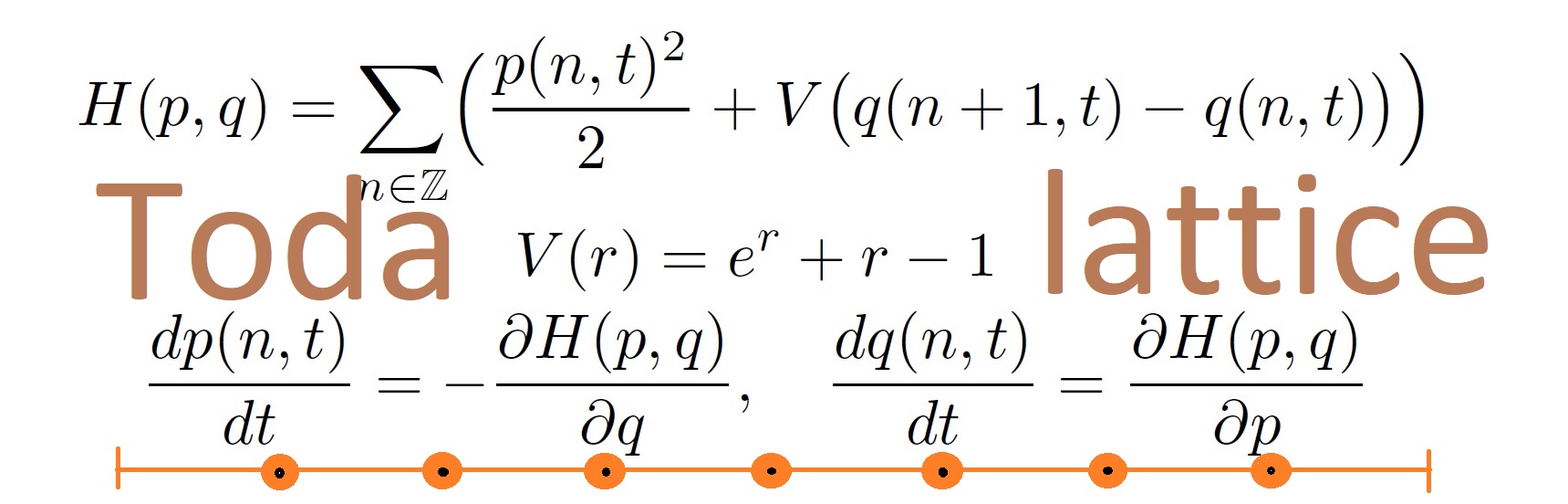MATHEMATICS
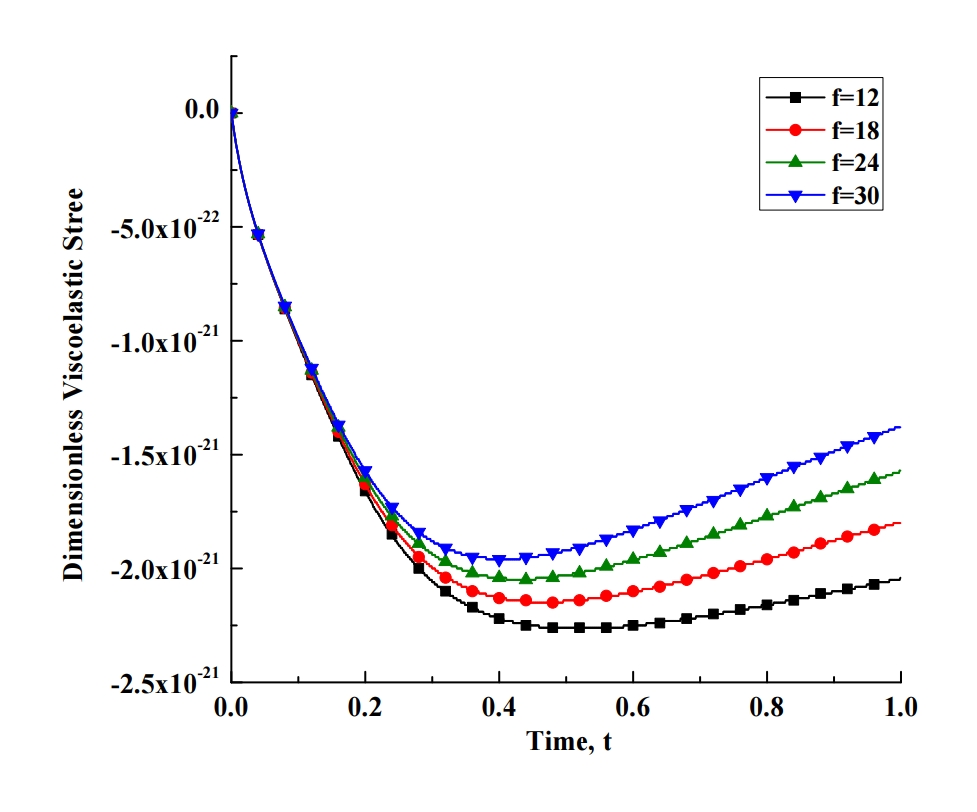
Smoking and pollution are highly hazardous to human health. Most of the environmental particles are very small in size i.e. micro or nanoparticles. When these particles are inhaled, they enter from the nose and flow with the air stream into various portions of the lungs. The alveolar region, a porous media due to number of alveoli, serves as an internal biofilter medium to filter deposited particles. To analyze the behavior of this biofilter medium, we considered the periodic permeability of lungs (due to periodic breathing) together with the viscoelasticity of the lung tissues. The flow of viscous air through the porous media is modeled by using one dimensional momentum equation with Darcy’s law and the velocity of particles by second law of Newton. To model the viscoelasticity, we used Kelvin-Voigt model. The finite difference method is used to solve the governing equations and MATLAB is used to solve the computational problem. The effects of various parameters, such as the Darcy number, porosity, and the breathing frequency are analyzed for flow of air, particle and viscoelasticity of lung graphically. Results show that by increasing the breathing frequency, decreasing the porosity, and decreasing the Darcy number, the viscoelastic stress increases.
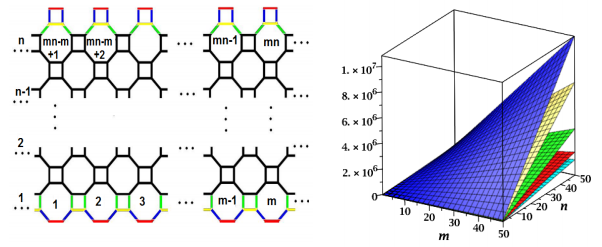
Topological indices are numerical values associated with chemical constitution describing the structures of chemical compounds and helping to predict different physicochemical properties. In this report, some newly designed topological descriptors, namely, neighborhood Zagreb index (MN), neighborhood version of Forgotten topological index (FN), modified neighborhood version of Forgotten topological index (FN∗ ), neighborhood version of second Zagreb index (), neighborhood version of hyper Zagreb index (HMN) are obtained for the TURC4C8(S), armchair nanotube TUAC6, V-phenylenic nanotube V PHX[m,n], and V-phenylenic nanotori V PHY [m,n].
We study the problem of computing the solution to finite Toda lattice. Specifically, we describe the evolution of moments of the spectral measure of a Jacobi matrix entering in the Lax pair.
PHYSICS
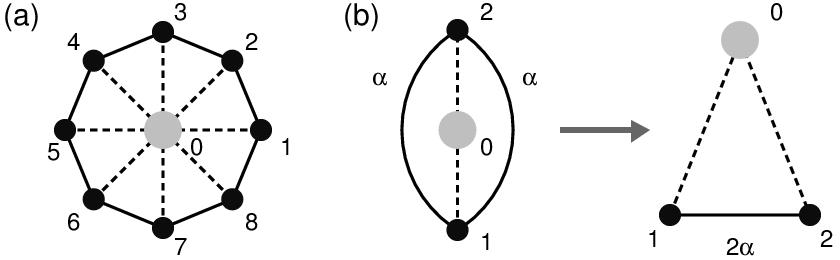
The Lagrange variety approach introduced by Schmidt and Luban [J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 36, 6351 (2003)] is applied to geometrically frustrated wheels (centered regular polygons). It is shown that the lowest energy configurations are planar or collinear. The latter one, characteristic for nonfrustrated classical systems, is also observed in the presence of competing interactions in a well-determined range (0,αc) of the energy function parameter α. The ‘critical’ value αc = 1/4 is universal, i.e., it does not depend on a system size. In this domain, the geometric frustration is present, but there is no non-trivial degeneracy.
In this paper, the statistical and dynamical equivalence between rectangular cell and lower symmetry cell is presented. The achievement of this equivalence will improve theoretical investigations of nanostructures as thin film or quantum rods.
Electron transmission through nanosystems encounter different scattering processes. We focus on the scattering by impurities, which were implemented by considering a model based on the pseudo-Gaussian well. We discuss typical signatures of this phenomenon.
The Heisenberg theory of ferromagnetism is widened to include external electric field action. The material relations are derived by means of differentiation of logarithm of partition function with respect to the magnetic and electric fields. The mean energy coefficients as the exchange integrals combinations are expressed via characters of irreducible representations of corresponding permutation groups by the Heitler method. The thermodynamic equations of state for polarization and magnetization, as functions of the electric and magnetic fields, are derived and illustrated by figures. The magnetization and hysteresis curves in magnetization – magnetic field components plane are built. The theory is applied to nanoparticles, the particle partition function is modeled as the product of the surface and bulk parts. The statistical sum is constructed having explicit expressions for the mean energy in terms of exchange integrals and number of closest neighbors for surface and bulk atoms. The relative contribution of the surface and bulk terms is evaluated.
An implementation of the non-collinear Alexander–Anderson model for itinerant electrons in magnetic systems is presented where self-consistency is reached for specified directions of the magnetic moments. This is achieved by means of Lagrange multipliers and a variational principle for determining the transverse and longitudinal components of the magnetic moments as well as the average number of d-electrons using direct optimisation. Various optimisation algorithms are compared and the limited memory Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno algorithm is found to give the best performance. An application to antiferromagnetic Cr crystal is presented where spin-dynamics and curvature of the energy surface are calculated to compare results obtained with and without the constraints on the orientation of the magnetic moments.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
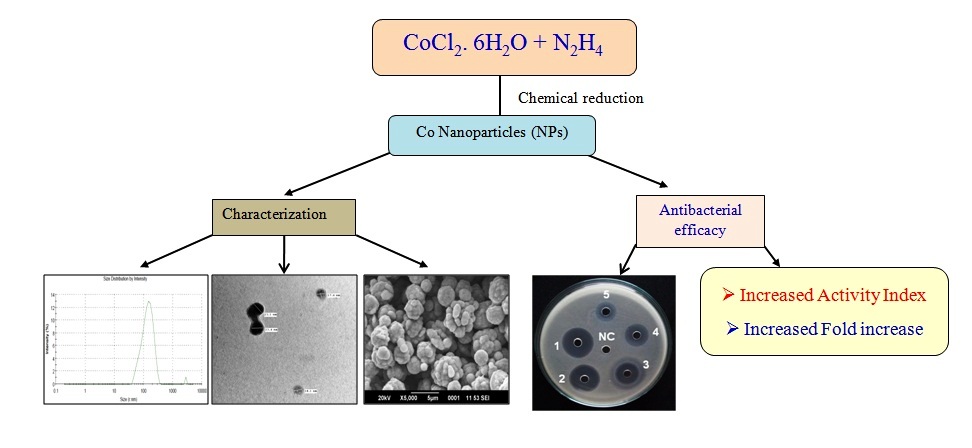
Synthesis of compounds that can prevent bacterial resistance is of huge interest and gaining immense popularity. Cobalt (Co) is one of the cheaper transition metals and its nano form has not been studied in details for antibacterial actions. Comparative analysis of Co nanoparticles with bulk Co and standard antibacterials are also lacking. In our study, concentration dependent action of Co nanoparticles was observed from 0.125 to 128.0 µg/ml against S. aureus and E. coli. Zone of inhibition of Co nanoparticles was better against E. coli than S. aureus. Co nanoparticles were markedly betterthan bulk Co, oxytetracycline and gentamicin. Activity index and fold increase of Co nanoparticles were higher at most of the concentrations. In conclusion, Co nanoparticles showed better antibacterial action than other tested compounds against S. aureus and E. coli particularly at lower concentrations, and their use may be extended in different biomedical fields in future.
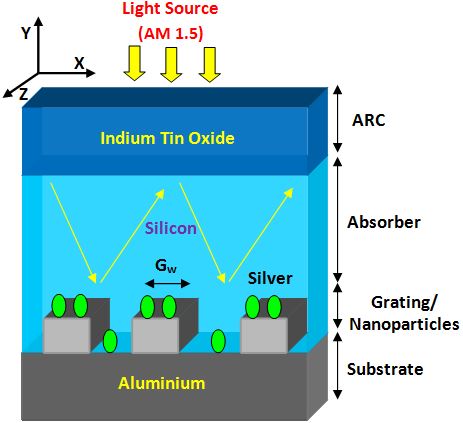
In this work, ultrathin silicon solar cell design employed with the aid of periodic silver (Ag) nanoparticles substituted on an aluminium (Al) grating to improve the optical performance by using rigorous coupled-wave analysis (RCWA) method. The enhanced light absorption was observed in the silicon absorber region, due to the photonic and plasmonic modes between the metal and dielectric surface. With the optimal structure, maximum short-circuit current densities were observed at transverse magnetic (∼ 36.13 mA/cm2) and electric (31.59 mA/cm2) modes. Further, we have demonstrated the effectiveness of the different ultrathin silicon solar cells with plasmonic structures and compared.
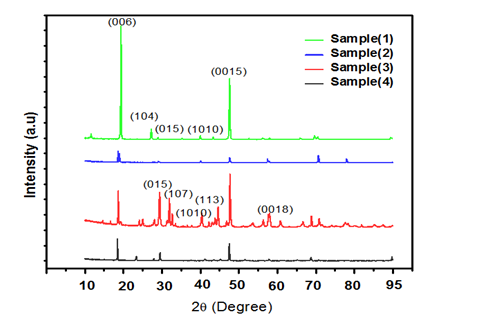
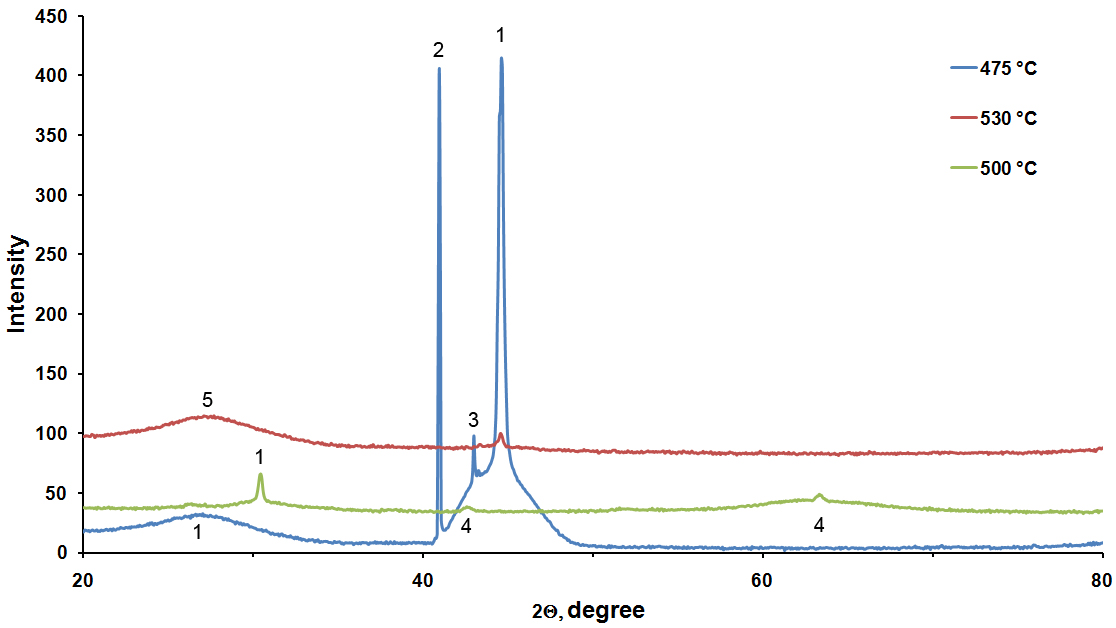
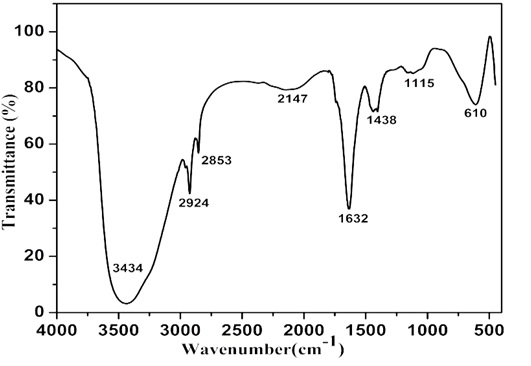
In recent years, bismuth selenide has attracted a good deal of attention due to its unique properties. Bismuth selenide is a topological insulator which has surface conductivity that makes it an attractive compound for practical applications. Employing the solid state reaction, bulk bismuth selenide compounds in four different stoichiometric ratios of Bi/Se have been prepared at 850 ◦C in a muffle furnace. The synthesized bismuth selenide compounds were characterized using XRD. Two most intense peaks were identified, corresponding to the (006) and (0015) planes which conform with the formation of bismuth selenide. Thin films of these compounds were deposited on Soda lime glass substrate by thermal evaporation method. Thin films were characterized by EDAX, SEM and RAMAN. Two clear vibration modes are observed corresponding to E2g and Amodes. Optical properties of thin films were also studied. Electrical band gap is found to increase with the increment in the amount of Bismuth in thin films.
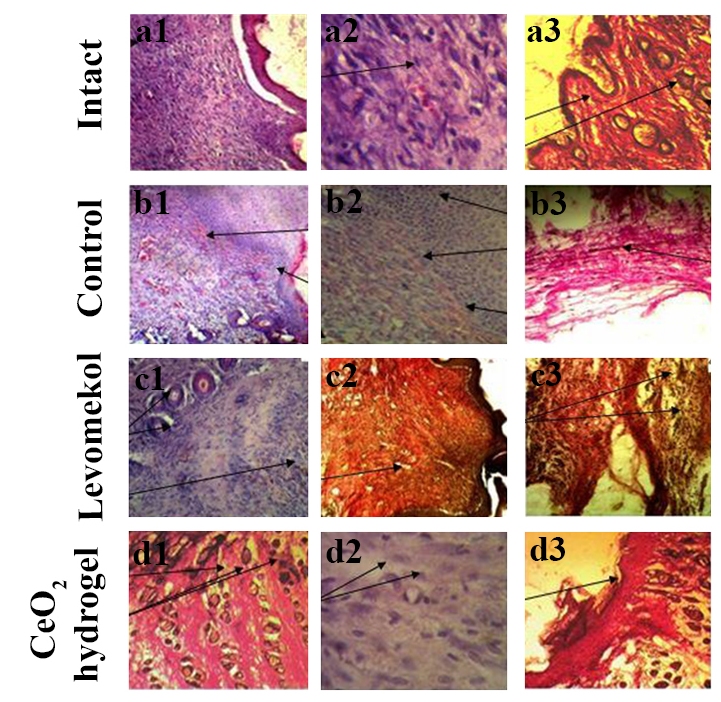
Nanocrystalline cerium oxide (CeO2) is considered as one of the most promising inorganic materials for biomedical purposes. The unique redoxactivity, high biocompatibility and low toxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles open great prospects in their biomedical usage as a therapeutic agent, including acceleration of skin regeneration processes after injuries of various etiologies. As part of this work, a hydrogel based on natural polysaccharides modified with CeO2 nanoparticles was synthesized and its therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of planar full thickness and linear skin wounds in rats was shown. Basing on wound surface area measurements, results of skin wounds tensiometry and histological analysis it was found that polysaccharide hydrogel significantly reduces planar and linear wound healing times. Polysaccharide hydrogel modified with CeO2 nanoparticles facilitates rapid reduction of wound defect area and the scar formation with complete tissue regeneration in the wound area. Additionally, composite hydrogels reduce the manifestations of non-specific signs of inflammation and intoxication. Thus, polysaccharide hydrogel modified with CeO2 nanoparticles can be regarded as an effective wound healing substance in the therapy of skin injuries of various etiologies.
The kinetic parameters and the limiting stage of the defining process were established by studying the thermal oxidation of SnO2/InP heterostructures (thickness of SnO2 layer ∼ 50 nm). It was established that SnO2 does not have a chemical stimulating effect on the film growth rate; however, it is effective as a modifier of their structure and properties. SnO2 provides the formation of nanoscale films with semiconductor properties.
Lanthanum fluoride (LaF3:Ce3+, Pr3+, Nd3+) was synthesized by water soluble LaCl3 + CeCl3+ PrCl3 + NdCl3 and NH4F as starting materials in de-ionized water as solvent using microwave assisted technique. The structure of LaF3:Ce3+, Pr3+, Nd3+ nanocrystals analyzed by XRD and TEM analysis is found to be in hexagonal structure and average crystalline particle size is 20 nm (JCPDS standard card (32-0483) of pure hexagonal LaF3 crystals). The absorption edge in UV spectra is found at 250 nm corresponding to energy of 4.9 eV. It further shows a wide transparent window lying between 200 nm–800 nm. For LaF3; Ce3+, Pr3+, Nd3+ nanocrystals emission of blue color (458 nm) has been observed with at an excitation wavelength of 254 nm. The measured relative second harmonic generation (SHG) efficiency of LaF3: Ce3+, Pr3+, Nd3+ in de-ionized water with respect to KDP crystal is 0.186.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)