MATHEMATICS
New Jacobi Elliptic functions expansion scheme, more general than the hyperbolic tangent function method, is derived to construct the exact wave solutions in terms of Jacobi Elliptic functions. The coupled 1D nonlinear Schrodinger–Zakharov (CNLSZ) system is taken as the model ¨ equation for wave-wave interaction in ionic media. It is shown that more new solutions can be obtained at their limit condition.
PHYSICS
This work is devoted to the study of the influence of the additional processing at 100, 200 and 300 ◦C on the morphology, microrelief, elemental composition of the surface and the electrophysical properties of glass/ITO/copper nanoparticle film structures. Studies have shown that with an increase in the processing temperature of the investigating samples reduces the amount of organic matter protecting the copper particles from oxidation. The conductivity of copper nanoparticles increases. The morphology of the surface and the elemental composition of the samples were studied by scanning electron microscopy. The microrelief of the surface and the measurement of the copper nanoparticles current-voltage characteristics were carried out using a scanning probe microscope in atomic force and scanning tunneling microscopy modes.
We investigate physical properties of a single vibronic intramolecular excitation propagating through a macromolecule, whose vibrational state can be described as a squeezed vacuum state. For a theoretical description of such a process, the partial dressing method of the vibronic excitation due to its interaction with phonons is used. We study the influence of the model parameters and strength of squeezing on the vibron dressing. It is demonstrated that for certain critical values of the model parameters a polaron crossover can occur, at which there is a sharp change in the migration nature of a vibron from the practically free to the heavy quasiparticle dressed by a phonon cloud. Increasing the strength of phonon squeezing is shown to increase the critical values of the model parameters, so that for high phonon squeezing the polaron crossover takes place in the very strong-coupling and adiabatic regime.
Studying natural flintstone samples’ properties, including optical transparency and thermal conductivity, by various physical methods (X-ray diffraction, atomic force microscopy, optical microscopy, etc.) revealed that said specimens contain chalcedony nanoparticles bund into the complex hierarchial structure.
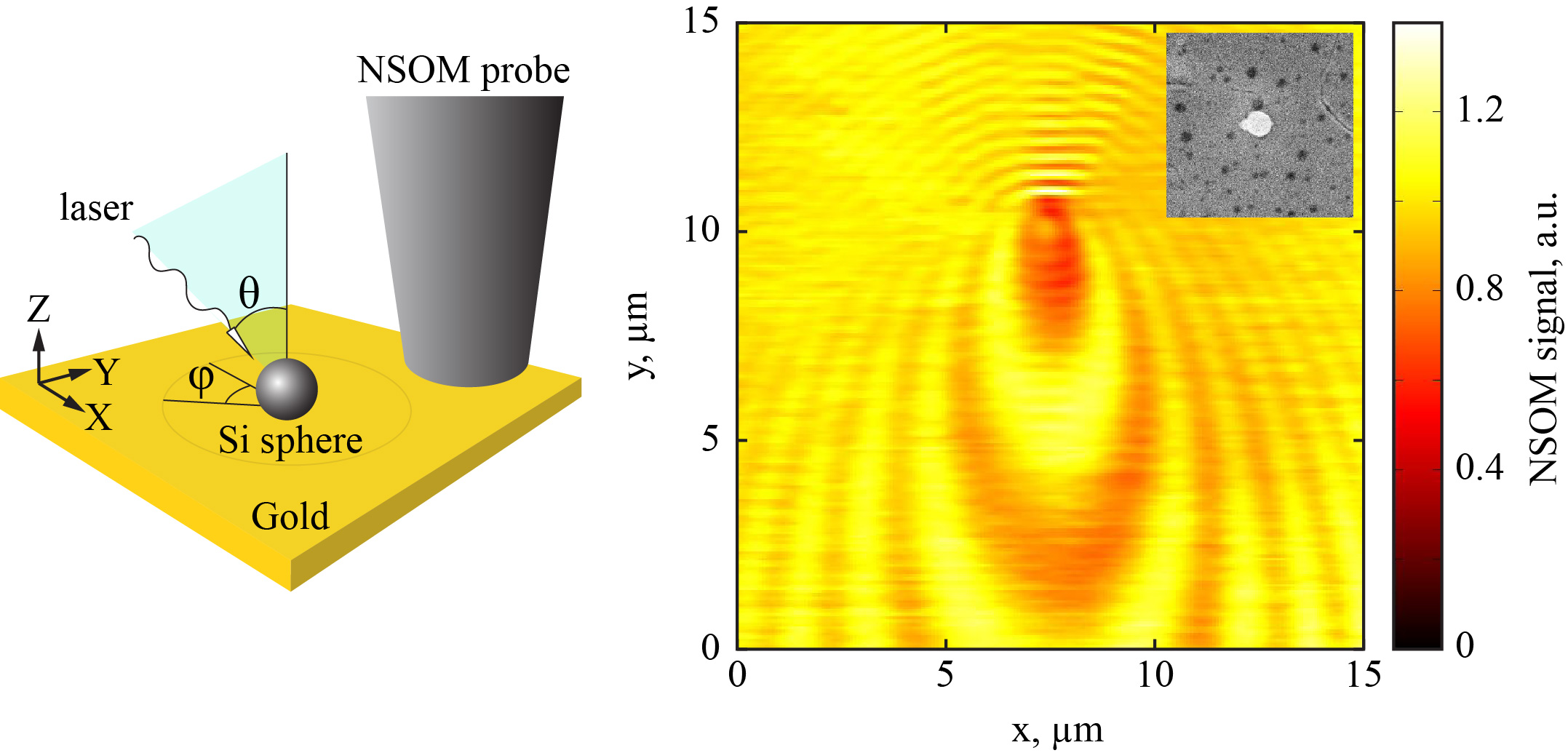
An optical nanoantenna is a device that transforms far-field electromagnetic radiation into near-field and vice versa. Naturally, it can serve as a conduit between free space light and localized optical modes, including surface waves. With the recent rise of all-dielectric nanophotonics, nanoantennas made of high-index materials were found to offer unparalleled means for manipulation of light due to presence of equally strong electric and magnetic responses in the visible spectral range. Here, we demonstrate excitation of surface plasmon polaritons by single silicon nanosphere on gold layer measured by means of scanning near-field optical microscopy. The interference patterns observed in the measured near-field maps allow us to retrieve information on directivity and relative excitation efficiency of surface plasmon polariton in the longer wavelength part of the visible spectral range. Our results demonstrate that all-dielectric nanoantennas could prove to be a valuable tool for controlling directivity and efficiency of excitation of surface waves.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
Thin composite graphene oxide (GO) membranes prepared from the mixture of GO nanoflakes and nanoribbons are proposed to enhance membrane stability at elevated pressure gradients. It is shown that addition of 5 – 15 % of GO nanoribbons to medium flake graphene oxide during deposition allows up to a 60 % increase in the porosity of GO membranes. The membranes illustrate strong barrier properties to permanent gases with a permeance below 0.01 m3 /(m2 ·bar·h), while revealing high permeance to water vapor over 50 m3 /(m2 ·bar·h). This results in H2O/N2 selectivity up to 12500 at water vapor fluxes over 1 m3 /(m2 ·h) at relative humidity of feed stream of 90 %. Despite ∼ 10 % loss of membrane performance with addition of nanoribbons, the membranes reveal an improved stability to pressure gradients. Irreversible permeance loss of composite membranes does not exceed 10 % as compared to ∼ 35 % performance loss for pure medium flake graphene oxide (MFGO) after long term exposure to 0.1 MPa pressure difference. An improved stability is invoked for the prevention of the irreversible conglomeration of GO flakes and appearance of permanent channels for water transport along the edges of nanoribbons.
Thermoelectric materials based on a mixture of Ge–Si nanopowders were fabricated and investigated. The materials were obtained by spark plasma sintering technique using the modes corresponding to the initial stages of sintering of the powder particles. The possibility for controlling the electrical characteristics of materials (type and magnitude of conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient) by varying the sintering parameters was shown. It was found that the analysis of electrical characteristics allows one to draw conclusions about the degree of mixing for silicon and germanium in the sintered material.
using ascorbic acid and its optical behavior has been investigated. The characterization of BFO-MMT nano composites has been done using FT-IR, UV-visible, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). Also, electron hole recombination has been investigated by photoluminescence (PL). From the analytical techniques, it has been found BFO entered into the layered host which was proved by elongation of basal plane and therefore agglomerated BFO was formed. The particle size can be calculated by Scherrer formula, is in good agreement with SEM. The strong absorption band in UV-Visible region attributed BFO nano composites can be used for photo catalytic degradation of Rhodamine-B (Rh-B). From the electrochemical studies, BFO-MMT clay nano composites showed a good specific capacitance at a scan rate of 10 mVs−1 .
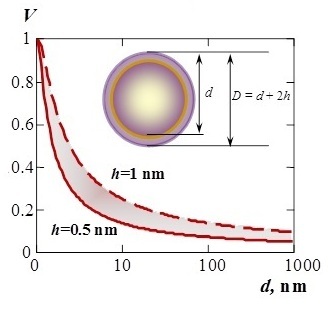
The review addresses physico-chemical aspects of interaction between macro-, micro- and nano- structured units of matter with the analysis of interface and grain boundary entities (nonautonomous phases) mechanisms and formation, as well as methods of their control in order to achieve the desired functional properties of nanostructured materials. Construction of these materials involves identification of thermodynamic and kinetic regularities in the organization processes, state and genesis parameters of nonautonomous phases formed as specific nanosized structures in a limited space between the macroscopic volume phases and with the limited amount of substance, which differ significantly on their properties, structure and composition from the appropriate characteristics of volume phases. Studying them is based on the application and development of theoretical and experimental methods of non-equilibrium thermodynamics, chemical kinetics, nonlinear dynamics and fractal analysis to determine the conditions of self-organization or materials directed synthesis with a high content of nonautonomous phases.
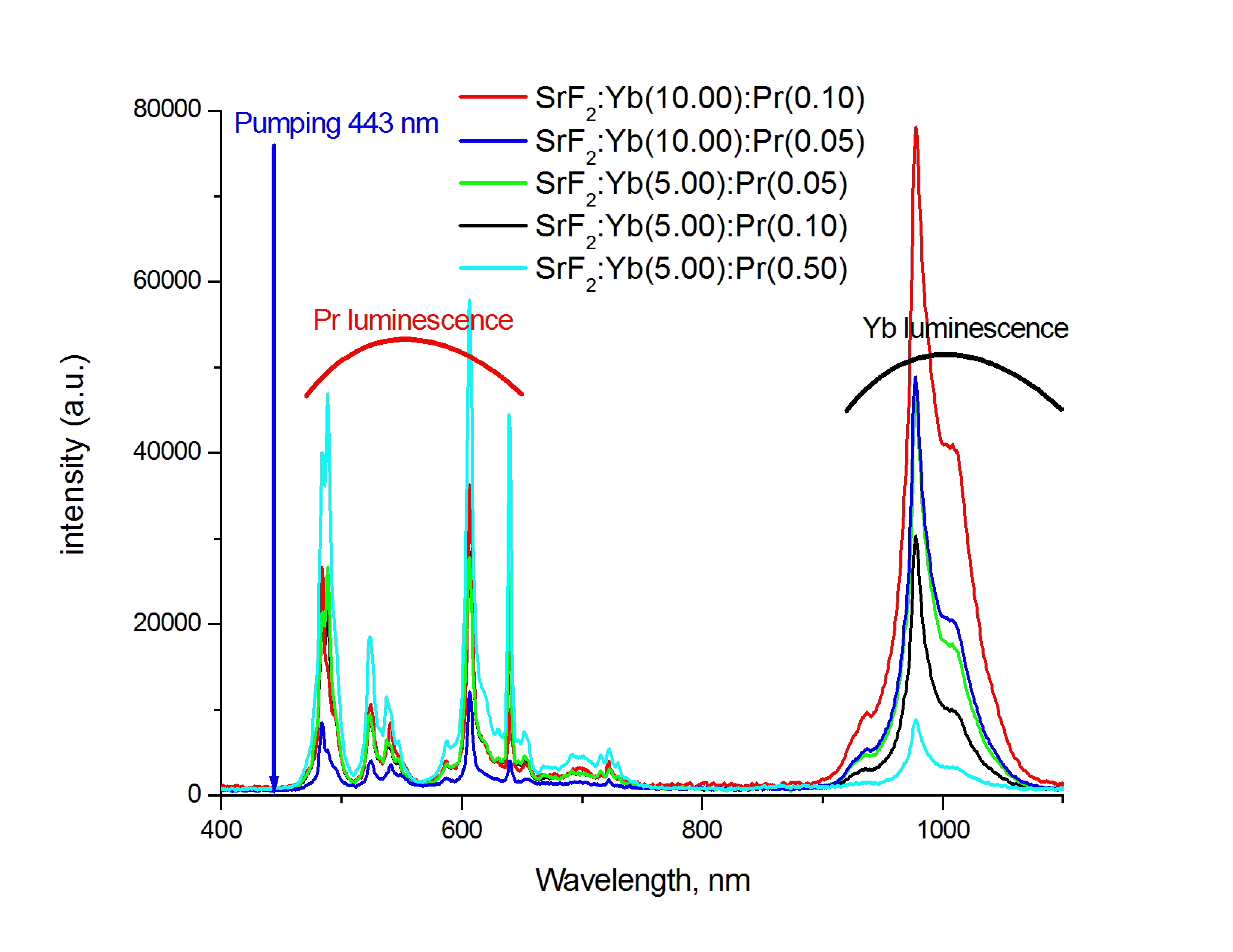
Single-phase praseodymium- and ytterbium-doped strontium fluoride solid solutions were prepared by co-precipitation from aqueous nitrate solutions followed by annealing at 600 ◦C. Based on EDX analysis, the content of rare-earth elements in solid phase is slightly higher rather than in initial aqueous solution. All the characteristic praseodymium and ytterbium luminescent bands were present. The most intense luminescence in 800 – 1100 nm range was registered in SrF2:Pr (0.1 mol.%):Yb (10.0 mol.%) solid solution. Using the integrating sphere, the values of the quantum yield were estimated. The maximum quantum yield was 1.1 % for Sr0.9495Pr0.0005Yb0.05F2.0505 solid solution.
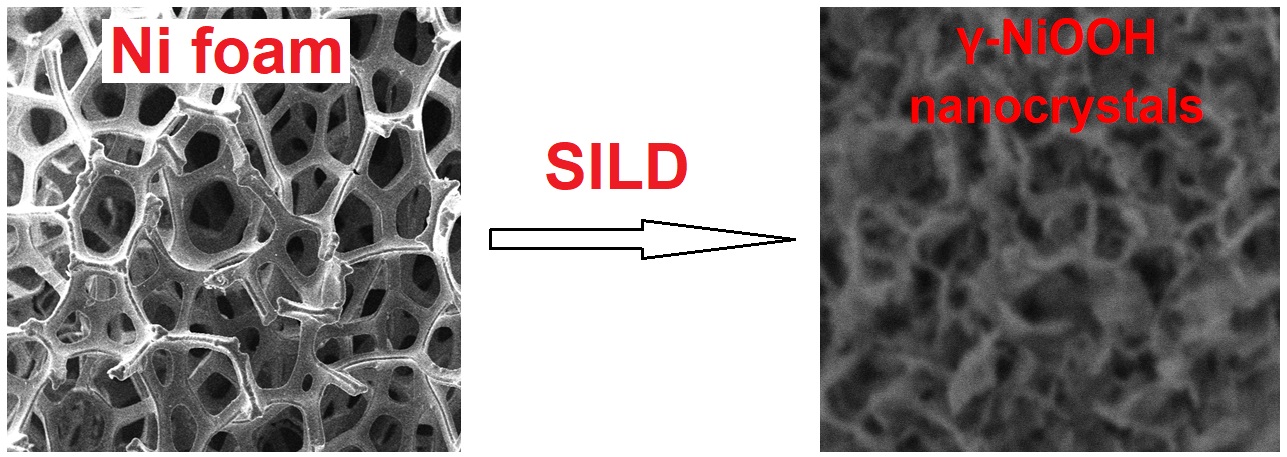
Nickel oxyhydroxide nanolayers were synthesized on the surface of nickel foam and single crystalline silicon through Successive Ionic Layer Deposition (SILD) method by using aqueous solutions NiSO4 and K2S2O8. The obtained nanolayers were characterized by SEM, XRD, FTIR and XPS spectroscopy. The electrochemical properties of the electrodes were defined from polarization curves. SEM images revealed that nanolayers are formed by nanosheets with a thickness of 6 – 10 nm. The nanolayers were shown to exhibit electrocatalytic properties during the oxygen evolution reaction upon water splitting in the alkaline medium. By setting the number of SILD cycles, these properties can be changed precisely. For a number of samples, synthesized after 30 – 120 SILD cycles, it was found that in the oxygen evolution reaction the lowest overpotential value of 260 mV and the lowest Tafel slope of 54 mV/dec are achieved for the sample, synthesized after 90 SILD cycles.
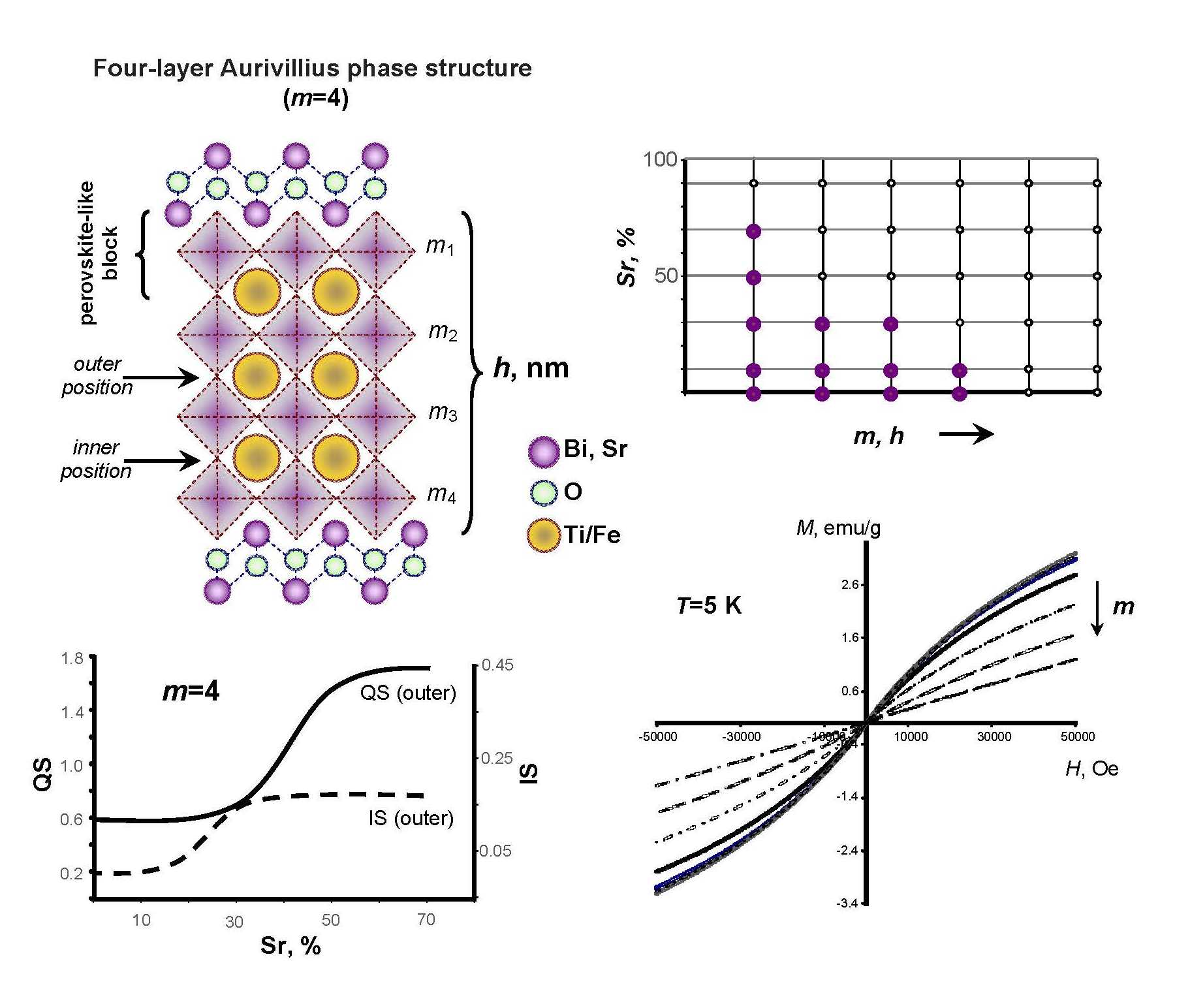
Specific features of the formation of Aurivillius phases (Bi1−xSrx)m+1Fem−3Ti3O3(m+1)−δ (m = 4−7; x = 0.0−0.7) with a perovskitelike block having a nanometric thickness (h) of 2 – 3 nm are described. It has been established that the degree of isomorphous substitution in the bismuth sublattice and thermal stability of phases tend to reduce with the increasing h. It has been demonstrated that the magnetic ions inside the perovskite-like block can have antiferromagnetic interaction exchange that influences magnetic properties of the Aurivillius phases.
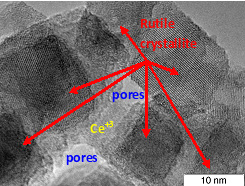
A method for the low-temperature synthesis of titania with the 3D rutile nanostructure was developed, and the effect of introduced cerium ions on the thermal stability of the material was studied. According to XRD, TEM, Raman spectroscopy and BET data, the introduction of 3 – 10 wt.% Ce into the rutile matrix decreases the growth of nanorutile crystallites under the action of high temperatures ranging from 300 – 1000 ◦C and provides the formation of a more porous structure in comparison with unmodified samples. Cerium cations are stabilized in the region of interblock boundaries or in the structural defects of rutile TiO2 and are released as the bulk CeO2 phase only at 1000 ◦C, which does not exert a stabilizing effect at this temperature.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)