MATHEMATICS
In this paper, we prove the uniqueness of a solution of the boundary value problem for an elliptic type equation of the second kind with the conormal and integral condition.
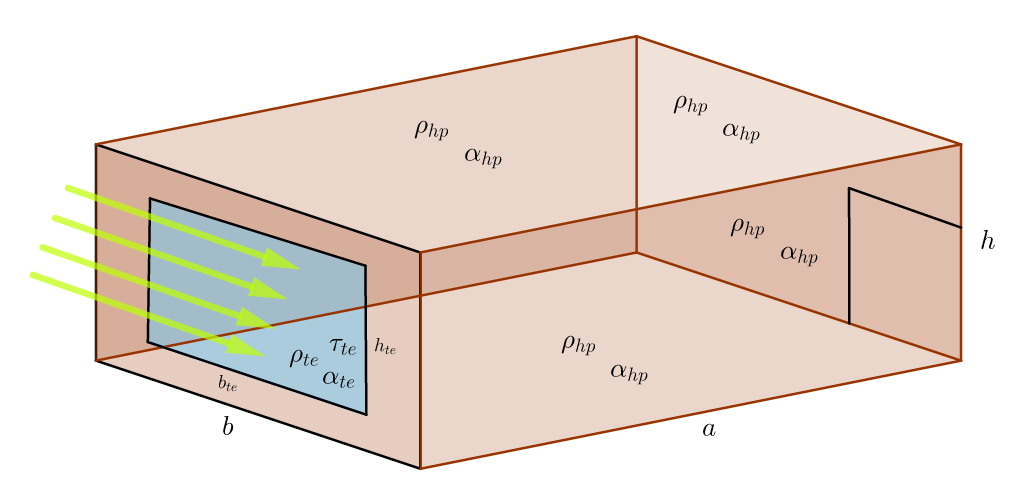
In this article, the method of determining ray absorption ability by premises with insolation passive heating system by numerical experiments was studied. A heated premise (HP), having a translucent enclosure (TE), walls covered with a special smooth enclosure, was chosen as the object of study. The dynamics of the solar rays were studied as a billiard system and the reflection equations are given. Verification of result reliability was performed.
In this paper, we study the global solvability and unsolvability conditions of a nonlinear filtration problem with nonlinear boundary flux. We establish the critical global existence exponent and critical Fujita exponent of nonlinear filtration problem in inhomogeneous medium. An asymptotic representation of the solution with a compact support is obtained, which made it possible to carry out a numerical experiment.
PHYSICS
In this paper, we have considered hexagonal double-layered boron and its adsorption properties in particular. The main adsorption characteristics have been elucidated by using the semi-empirical quantum-chemical scheme MNDO. We have investigated both external adsorption and internal infiltration of atoms (H, O, F, Cl) between boron monolayers.
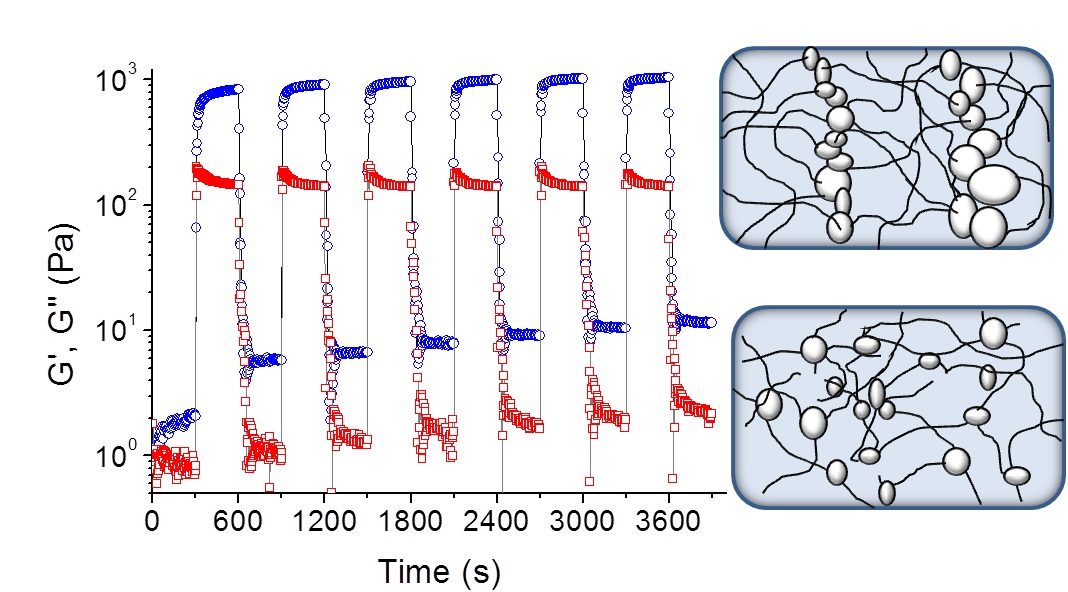
Magnetorheological effects in viscoelastic soft magnetic nanocomposites (SMNs) composed of submicron magnetite particles embedded in a network of wormlike micelles (WLMs) of surfactant were studied in a homogeneous magnetic field. In field, the SMNs showed rapid rise of storage and loss moduli by a few orders of magnitude as a result of the ordering of magnetized particles into chain-like or columnar structures. Moreover, solid-like behavior and yield stress of the SMNs were observed. Study of rheological response on periodic switching of field revealed that the initial viscoelasticity of SMNs did not recover completely after removing field, which was attributed to extremely long relaxation time of the WLM network. It was found that the variation of storage and moduli loss was associated with the stepwise change in magnetic field; this can be fitted by two-exponential functions, a characteristic time for the slower process being almost the same as the relaxation time of SMN without field, indicating that this process is essentially determined by the viscoelastic properties of the matrix.
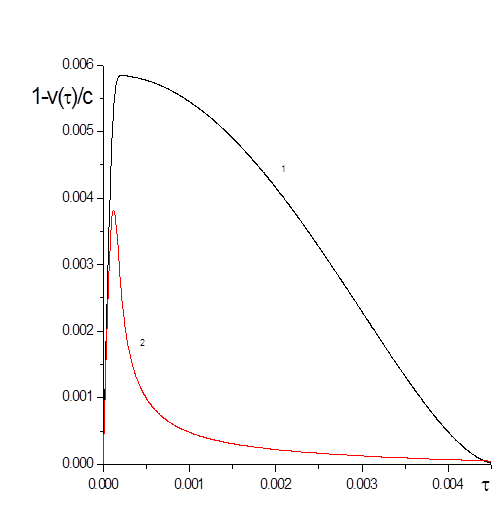
The problem of solving light was installed about thirty years ago and was widely considered in different approximations. In this paper, this process is investigated using both perturbation theory and numerical integration of the system of Liouville–Maxwell differential equations.
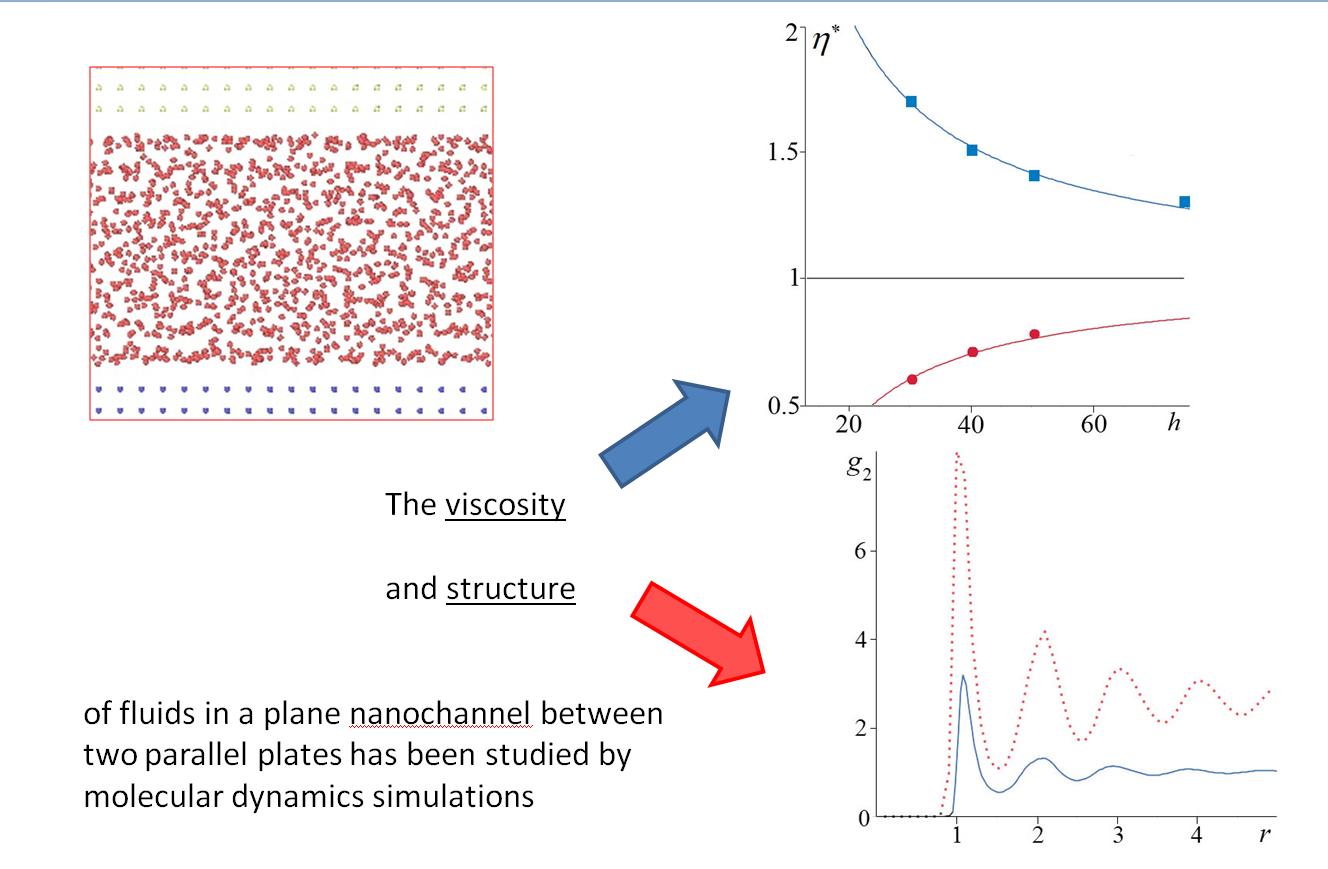
The viscosity of fluids in a plane nanochannel has been studied by molecular dynamics method. The effective viscosity coefficient was determined using the fluctuation-dissipation theorem derived previously by the authors from the nonequilibrium statistical theory of fluid transport in confined conditions. It has been found that the fluid viscosity in a nanochannel is strongly dependent on the interaction potential between the fluid and channel wall molecules. In particular, increasing the depth of the potential well of this interaction leads to an increase in the viscosity. At the same time, if the depth of the potential well is small, the fluid viscosity in a nanochannel may be even lower than its viscosity in an unconfined (bulk) system. Thus, the fluid viscosity in a nanochannel and hence the channel flow resistance can be varied by changing the material of the nanochannel walls.
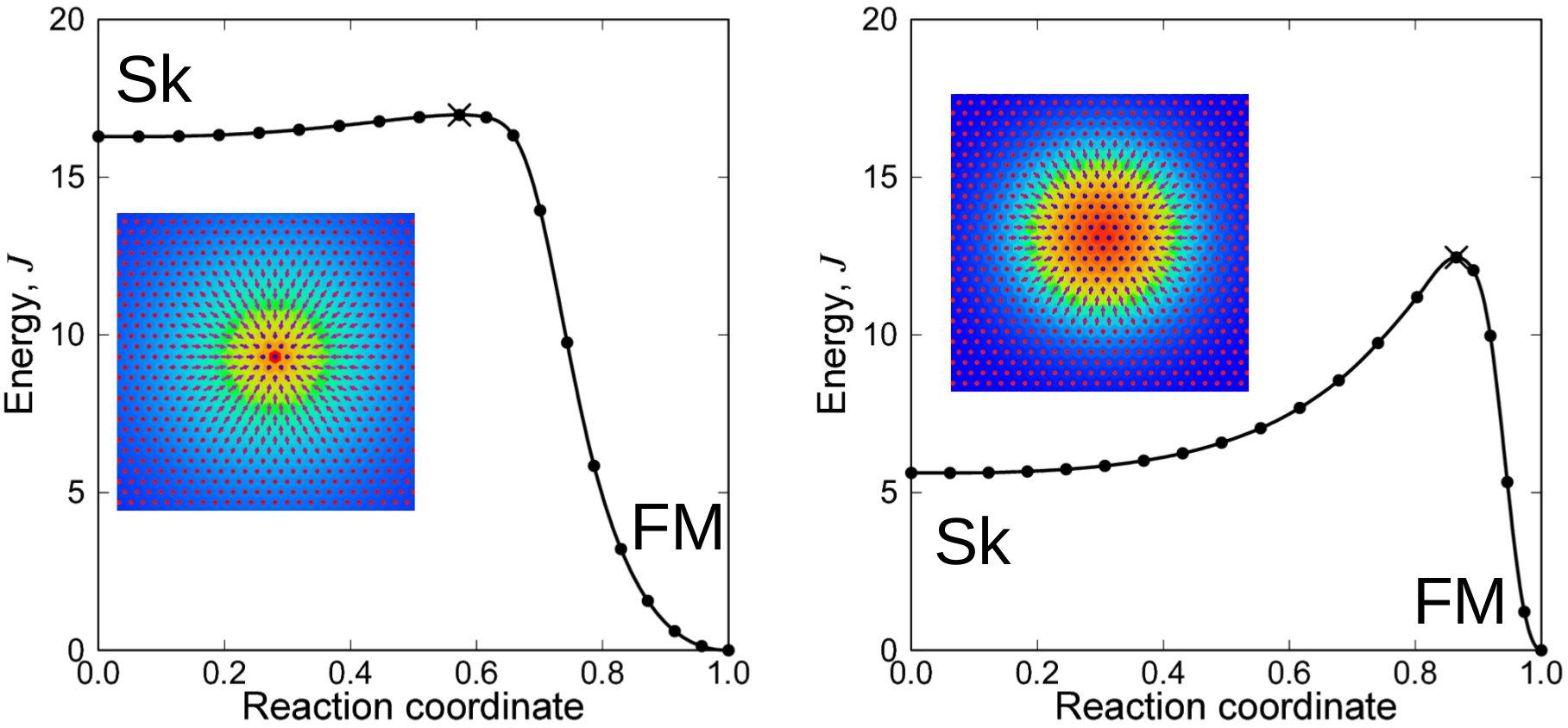
The relationship between the size and stability of isolated skyrmions in a magnetic monolayer is analyzed based on minimum energy path calculations and atomistic spin Hamiltonian. It is demonstrated that the energy barrier protecting the skyrmion from collapse to the ferromagnetic state is not uniquely defined by the skyrmion size, although these two properties as functions of relevant material parameters follow similar trends. Stability of nanoscale skyrmions can be enhanced by a concerted adjustment of material parameters. The proposed parameter transformation conserves the skyrmion size, but does not conserve the skyrmion shape which changes from an arrow-like pattern to a profile that resembles magnetic bubbles. This transformation of the skyrmion shape is accompanied by an increase in the collapse energy barrier and thus enhancement of skyrmion stability.
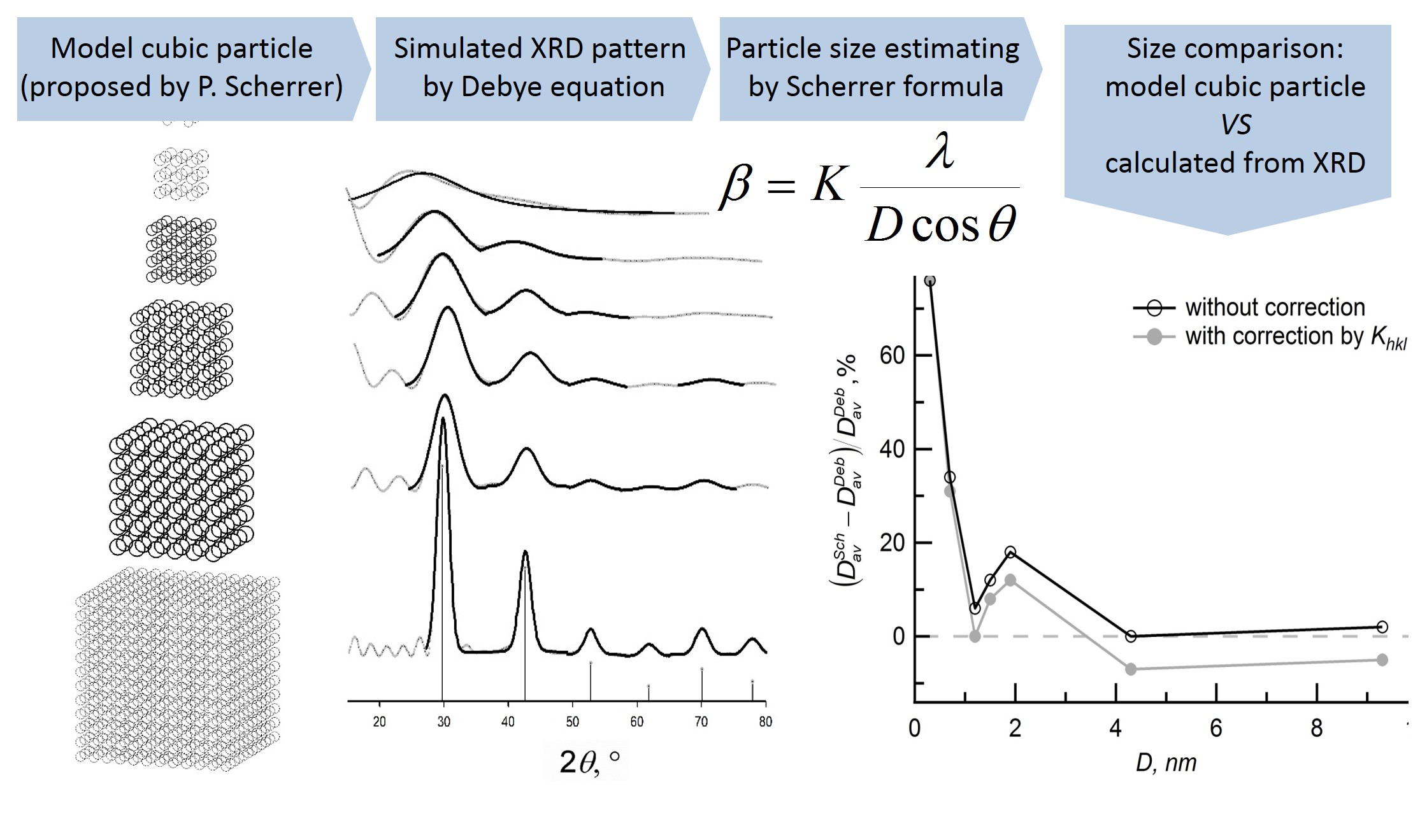
The lower limit of the applicability of the Scherrer formula has been established by calculating the diffraction patterns from model nanoparticles by the Debye formula. Particle size was calculated using the Scherrer formula for different hkl-peaks. The obtained data of particle sizes were compared with “real” sizes of model particles in the same hkl-directions. The form-factor Khkl was analyzed as main correction of Scherrer formula. It was shown that the Scherrer formula error increases nonlinearly at particle sizes less than 4 nm. For any hkl direction, the absolute error of average particle size determination using formula does not exceed 0.3 nm. Analysis shows that average particle size can be determined by Scherrer formula from single diffraction peak of experimental pattern for center-symmetrical particles.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE
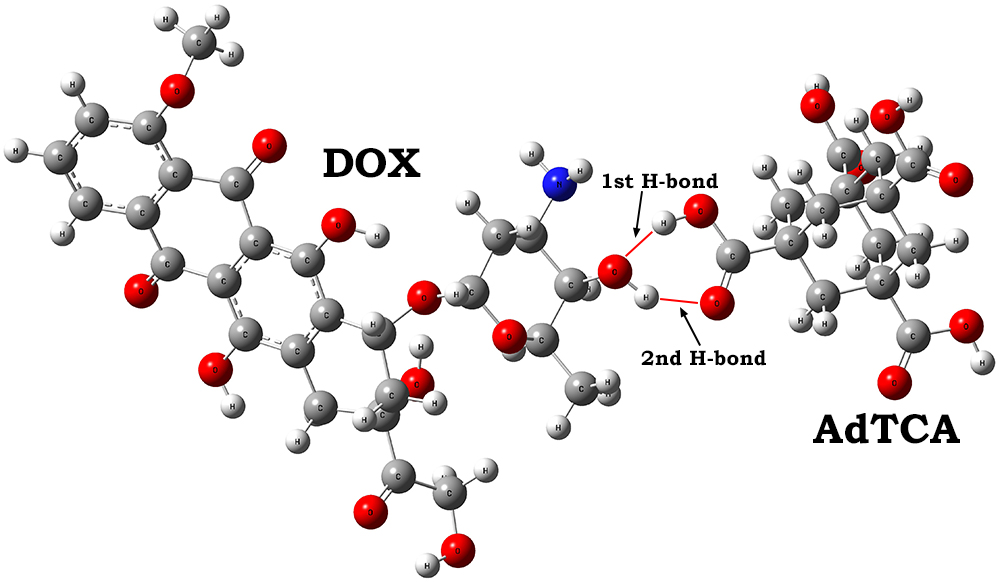
The possibility of drug delivery and retention in cells due to hydrogen bond formation between enriched nanodiamonds and highly toxic drugs (for example doxorubicin), is investigated by numerical simulation. Using molecular modeling by the density functional theory method with the B3LYP functional and the 6-31G(d) basic set, we analyze hydrogen bond formation and their influence on IR-spectra and structure of molecular complex which is formed due to interaction between doxorubicin and nanodiamonds enriched by carboxylic groups. Numerical modeling of carboxylated nanodiamonds and doxorubicin interaction is based on nanodiamond representation by a diamond-like nanoparticle with simpler structure. Enriched adamantane (1,3,5,7-adamantanetetracarboxylic acid) is used as an example of carboxylated diamond-like nanoparticle. Combined IR spectrum as imposing of IR spectra for doxorubicin and 1,3,5,7-adamantanetetracarboxylic acid various interaction positions is obtained. The combined IR spectrum demonstrates good agreement with experimental data. The obtained results demonstrate that there can be strong hydrogen bonds between doxorubicin and nanodiamond as one of basic mechanism for drug delivery and retention in cells.
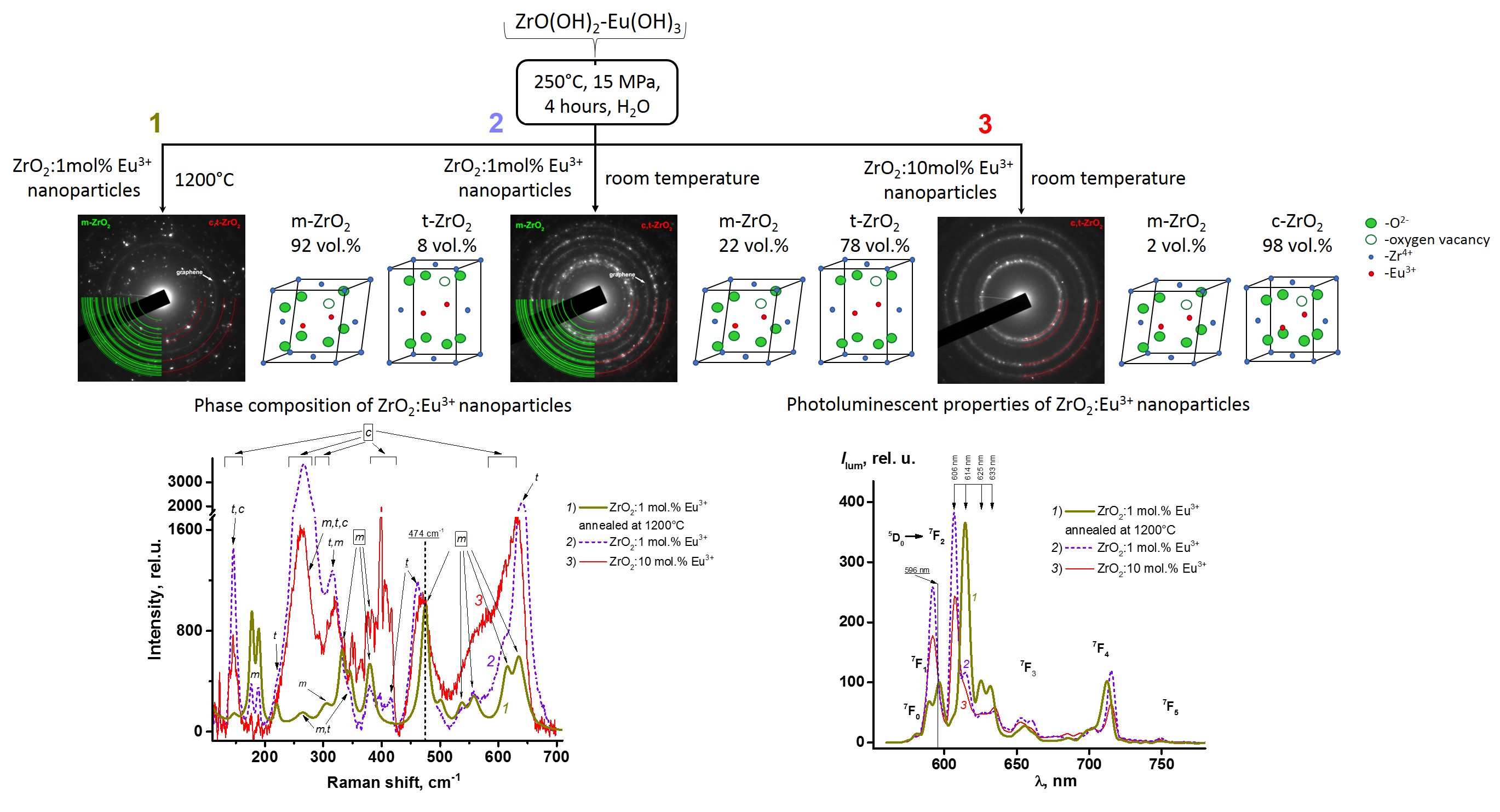
Luminescent zirconia nanoparticles with europium ion content 1 and 10 mol.% were synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. Annealing of ZrO2: 1 mol. Eu3+ nanoparticles made it possible to obtain a sample with a high monoclinic phase content up to 92 %. An increase in the concentration of Eu3+ ions introduced into the zirconia crystal lattice has made it possible to almost completely convert its monoclinic and tetragonal phases into cubic modification. The phase composition of the synthesized samples was determined by powder X-ray diffraction, electron microdiffraction, and Raman spectroscopy. Analysis of the crystallographic data and the luminescent spectra helped to reveal correlations between the ZrO2:Eu3+ nanophosphor structure and the energy redistribution of Eu3+ optical transitions at 614 – 626 nm and 606 –633 nm wavelengths. In addition, a relationship was established between the phase composition of nanoparticles based on zirconia and the luminescence lifetime of Eu3+ ions.
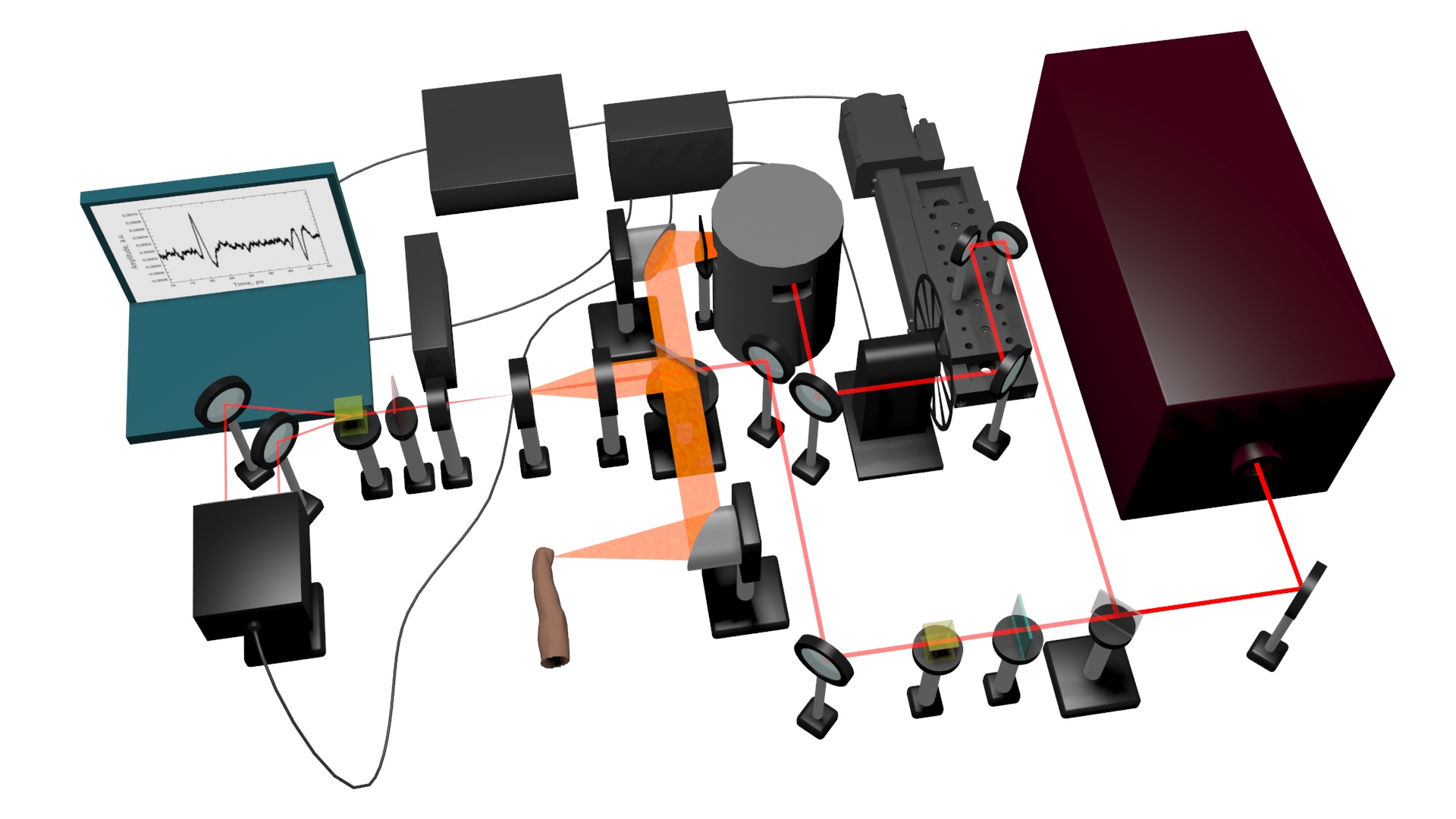
The optical properties of whole human blood with the different glucose level were studied by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy at frequencies ranging from 0.3 – 0.5 THz. The increasing of refractive index of blood at the glucose level growth was shown for series of experiments. The dispersion of complex refractive index of human nails was obtained. Based on these data, the non-invasive glucose measuring technique was proposed which utilizes the reflection of the THz pulse from nail plate/nail bed interface.
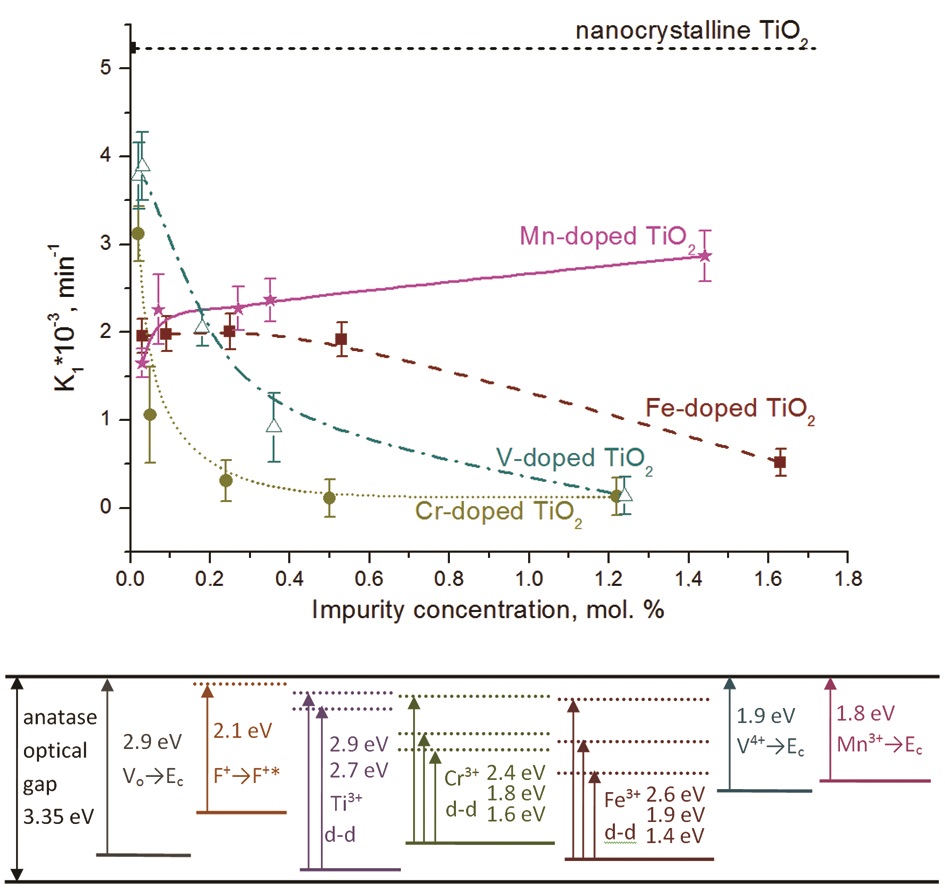
The influence of impurities on optical and photocatalytic properties was studied in a series of nanocrystalline TiO2 with similar coherent scattering region sizes, phase compositions, surface areas and lattice parameters doped by Fe, Cr, Mn and V ions. Doping leads to an increase of absorption in the visible part of the spectrum due to the formation of additional levels in the band gap. In the case of Fe and Cr ions, d-d transitions are observed, whereas in the case of Mn and V ions, an additional band is associated with the transition from impurity level to Ec. The presence of impurities effectively suppresses photocatalytic activity in the methyl orange decoloration reaction.
Here, we study a performance of nanotubular Mg3Si2O5(OH)4/TiO2 hybrid adsorbent/photocatalyst in the process of decolorizing an aqueous solution of crystal violet. The composite material was produced by hydrothermal treatment with one or more subsequent cycles of TiCl4 treatment and vapor-phase hydrolysis according to the molecular layering technique. Decolorization was observed in situ by UV-VIS spectroscopy. It was found that TiO2 deposition yields 2 to 3 times improvement of decolorization performance. Depending on TiO2 phase type – amorphous or crystalline – this rise is related with either enhancement of adsorption rate either appearance of photocatalytic activity. Finally, fitting procedure issues in case of complex decolorization process were discussed.
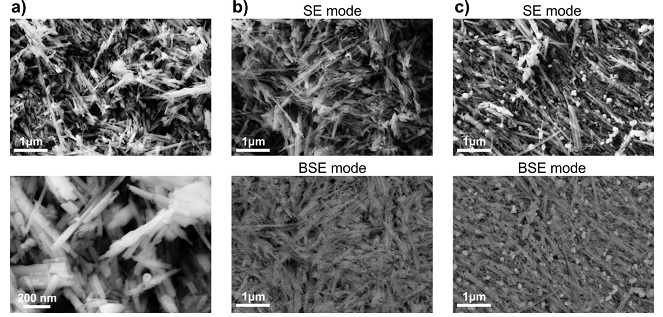
Thin films of the Y2O3–Fe2O3/Si system with nanometer-scale thicknesses were synthesized by centrifugation with application of sol and gel of YFeO3. It was found that the samples formed from the gel are characterized by the following composition: Fe2O3, Fe3O4, and Y2O3, YFeO3, which is not consistent with the data, obtained for powder products, and can indicate that the thermal annealing conditions were insufficient for the formation of a single-phase product. For the first time, the magnetic properties of thin ferrite films of yttrium on the surface of the silicon formed from the gel were measure. The nature of the hysteresis loop of nanofilms of yttrium ferrite with different parameters of time and speed of centrifugation suggests that the samples exhibit soft magnetic properties of a ferromagnet. The correlation between the value of specific magnetization and thickness of nanofilms was established.
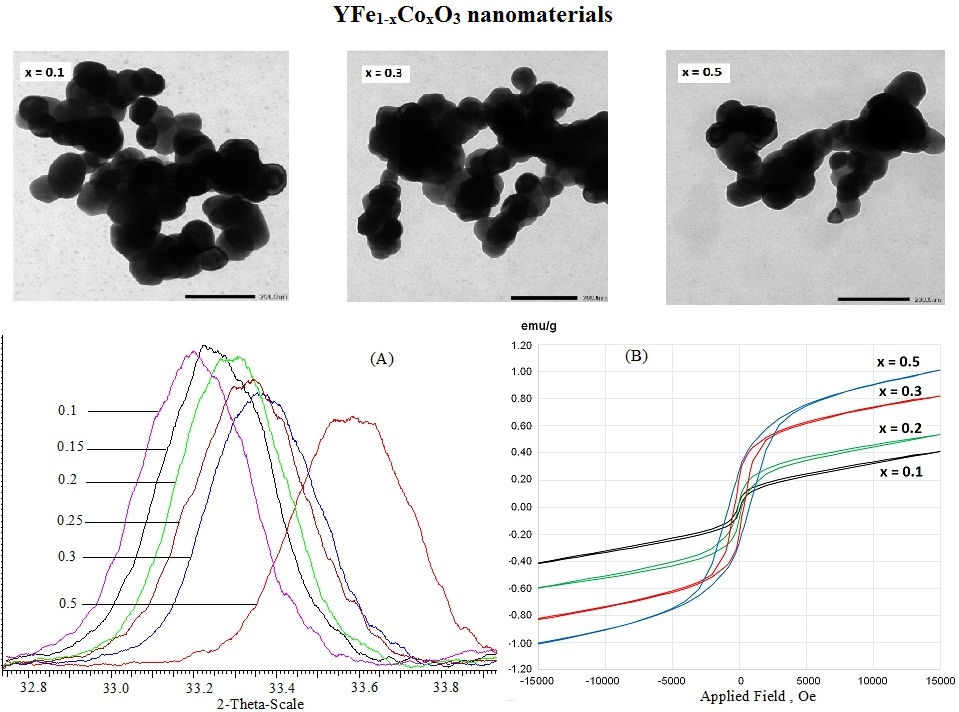
YFe1−xCoxO3 (0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) perovskite-type nanomaterials were successfully synthesized by the chemical co-precipitation method via the hydrolysis of Y(III), Fe(III) and Co(II) cations in boiling water using 5 % aqueous KOH solution as a precipitating agent. Along with the increase of cobalt ion concentration (x values, from 0.1 to 0,5), there was an decrease in the crystallite size nanomaterials (from 25.68 to 22.89 nm), as well as in the lattice constants (a = 5.5781 – 5.5217 ˚A; b = 5.2732 – 5.2177 ˚A, c = 7.5902 – 7.5009 ˚A; V = 223.26 – 216.11 ˚A), but there was an increase in the magnetic parameters including coercive force (Hc = 88.86 Oe), remnant magnetization (Mr = 0.031 – 0.268 emu/g), saturation magnetization (Ms = 0.413 – 1.006 emu/g) and maximum energy product ((BH)max = 0.413 – 1.006 emu/g).
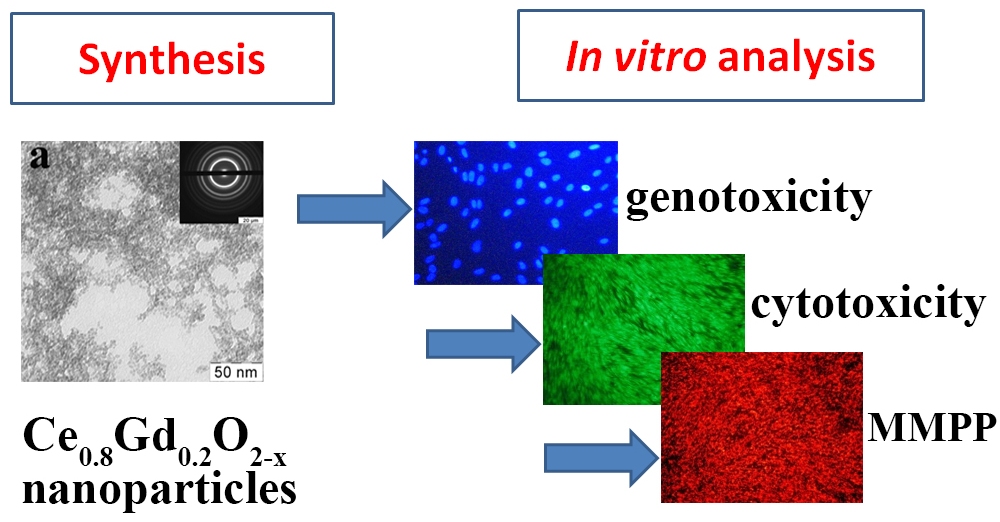
A complex analysis of cytotoxicity was performed for a nanodispersed sol of cerium dioxide doped with gadolinium (Ce0.8Gd0.2O2−x) using a culture of mesenchymal stem cells. The absence of cyto- and genotoxicity over a wide range of concentrations (10−5 – 10−9 M) was demonstrated. At that, the highest concentration of Ce0.8Gd0.2O2−x nanoparticles (10−4 M) was found to slightly reduce the activity of intracellular dehydrogenase, yet not leading to the development of apoptosis and further cell death. The obtained results confirm a high degree of Ce0.8Gd0.2O2−x nanoparticle biocompatibility, which opens prospects for their safe application as a contrasting agent in the magnetic resonance tomography.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)