MATHEMATICS
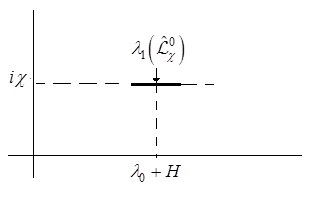
Scattering problem on an infinite chain of zero-range potentials with internal structure in the stochastic magnetic field is investigated. Model operator is constructed using the perturbation theory for the self-adjoint operators. The relations with the scattering problem without stochasticity are investigated.
PHYSICS
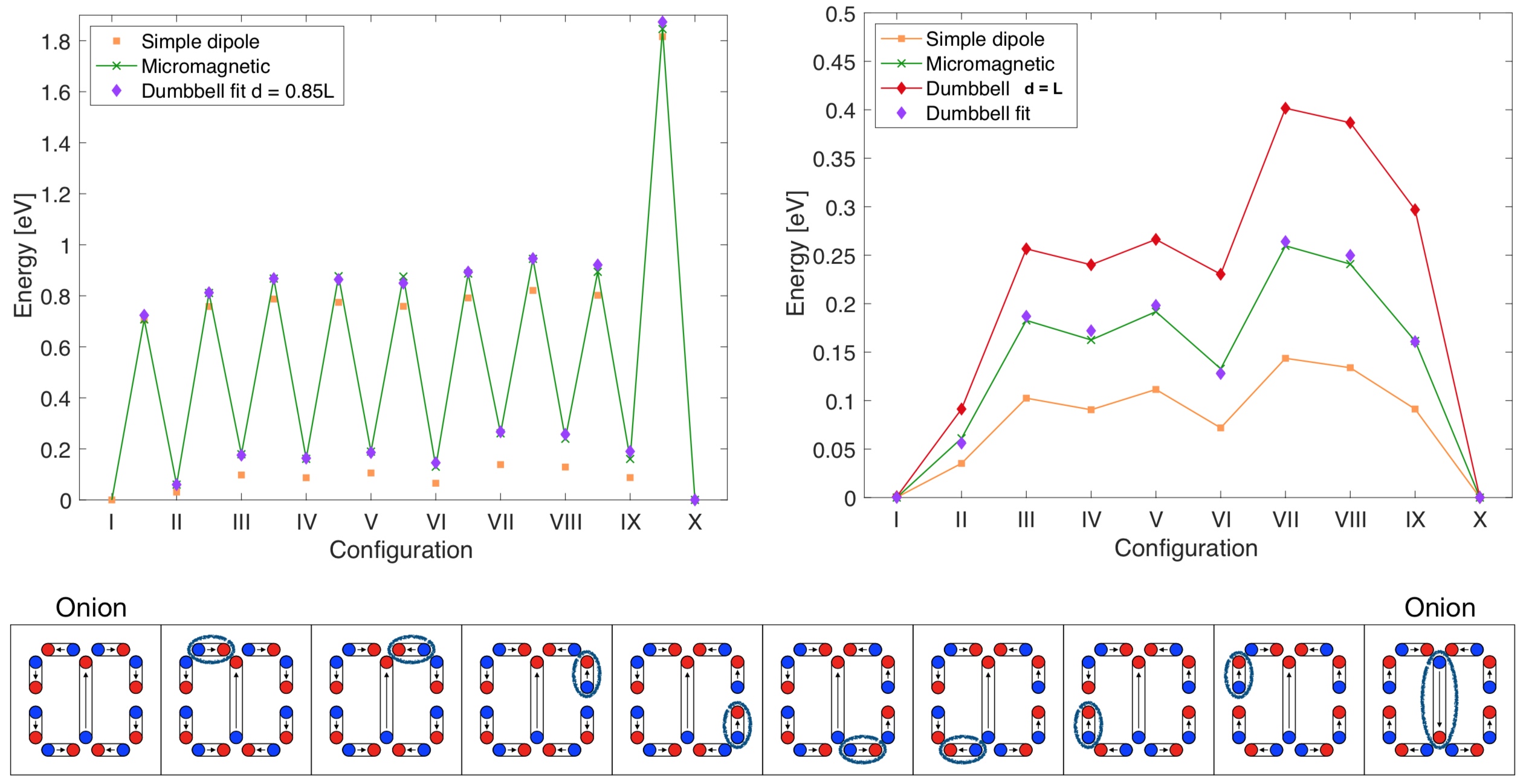
Micromagnetic calculations are compared with faster model calculations of interacting nanoscopic magnetic islands representing an element of a shakti spin ice lattice. Several pathways for transitions between equivalent ground states are studied. The model calculations describe the interaction between the islands either with the point dipole approximation, or with a dumbbell approximation where the distance between the two poles is optimized to match the micromagnetic results. The closest agreement in the energy of both local minima as well as transition state configurations where one macrospin has rotated by 90◦ is obtained with a dumbbell model where the distance between the poles is ca. 20 % smaller than the island length.
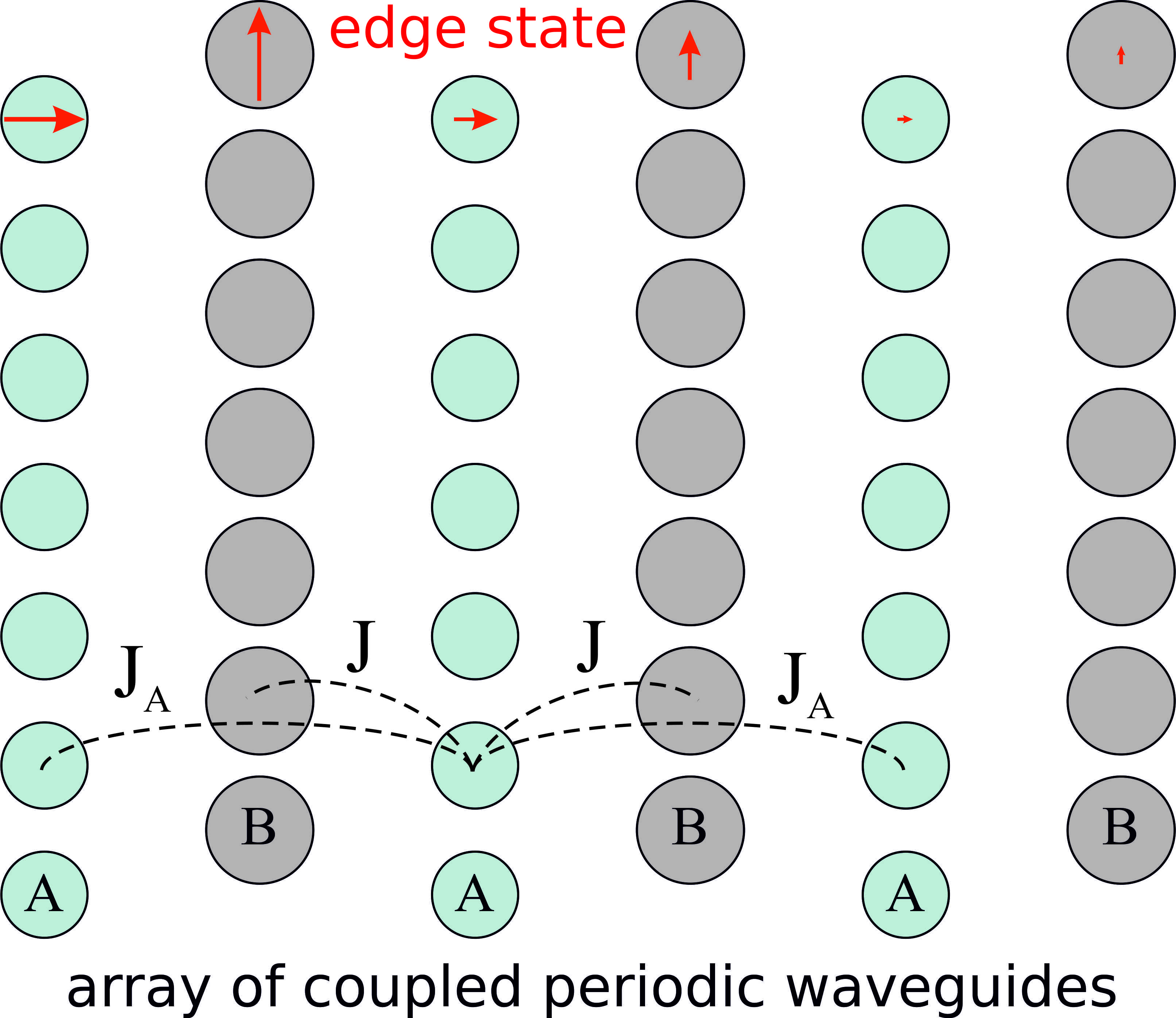
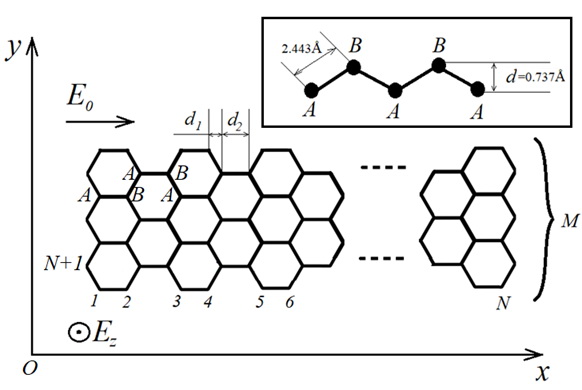
We study the properties of coupled periodic dielectric nanowaveguides and reveal that finite arrays of equally spaced waveguides with certain parameters support edge modes, which originate due to the presence of the long-range interactions between the waveguides. We provide a simple model of the coupled waveguides with next-to-nearest neighbors interaction that captures the main properties of the considered system including the formation of the edge states. The predicted results suggest that the arrays of periodic dielectric nanowaveguides may serve as a fruitful system for studying the discrete coupled systems with long-range interaction and realizing optical metasurfaces with novel functionalities for guiding surface waves.
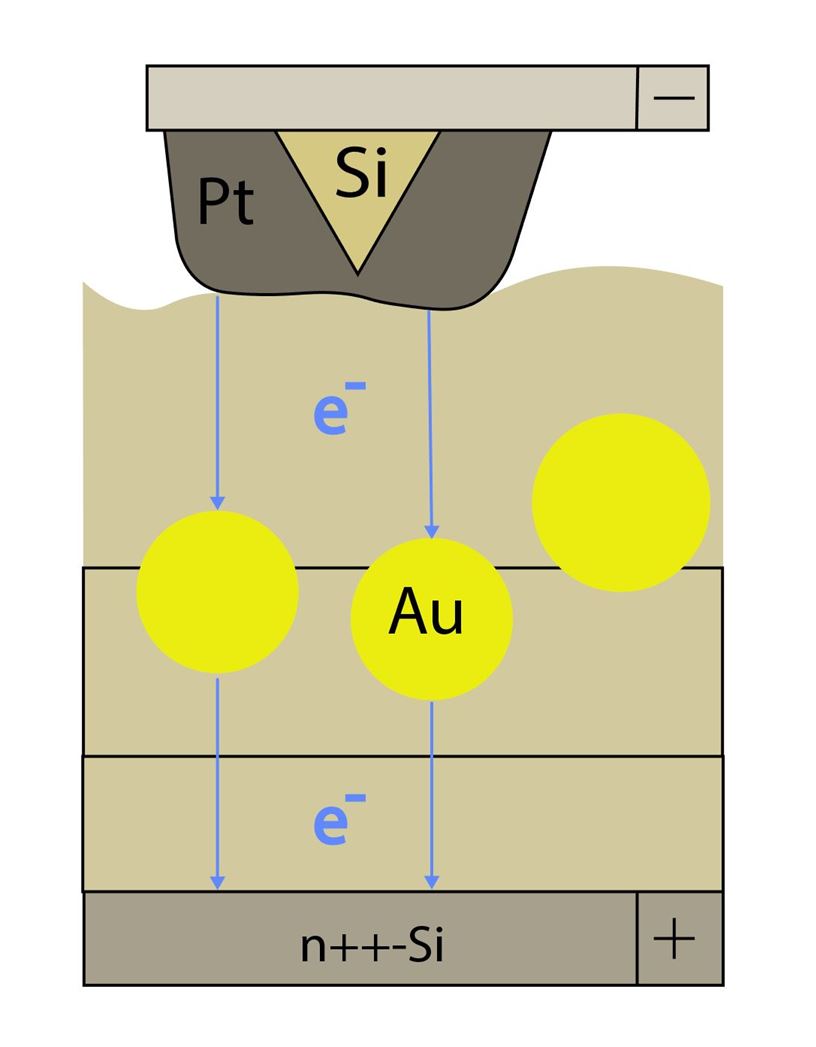
The effects of 2D tunneling bifurcations for quasi-one-dimensional and quasi-two-dimensional Au-quantum dot (QD) arrays in thin dielectric films in an external electric field have been studied theoretically and experimentally by Conductive Atomic Force Microscopy (CAFM). In the case of quasi-one-dimensional Au–QD structures (with the QD size ∼ 5 nm), in a dielectric film, a single break under positive bias polarity, corresponding to the effect of 2D tunneling bifurcation, previously predicted theoretically by our team [1], has been detected in experimental I—V curves of the CAFM probe-to-sample contact. A convincing qualitative agreement between the obtained experimental I—V curves and the theoretical field dependence for the 2D-dissipative tunneling probability in the model 2D-oscillator potential has been obtained for the case of parallel tunneling in the weak-dissipation limit at a finite temperature in an external electric field. In the case of quasi-two-dimensional structures with Au QD (with the QD sizes of 2 to 5 nm), possessing metamaterial properties, a pair of kinks corresponding to the double effect of 2D-tunneling bifurcations has been detected on the experimental I—V curves. A qualitative agreement between the experimental I—V curves and the theoretical field dependence for the 2D-dissipative tunneling probability has been obtained for a situation with an effectively “negative” permittivity of the heat bath.
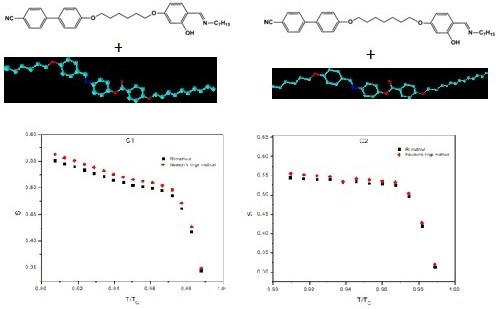
The orientational order parameter is one of the most important material parameters of nematic phase. In the present work, the phase transition temperatures of the mesogenic mixtures are measured by using a polarizing optical microscope. The birefringence in nematic phase is estimated by measuring ordinary and extraordinary refractive indices. The birefringence is also measured by measuring the diameter of Newton’s rings at various temperatures in nematic phase. The orientational order parameter is evaluated by using the birefringence data obtained in the above two methods. The orientation order parameter can be enhanced by the dispersion of different nanoparticles in the liquid crystal matrix.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
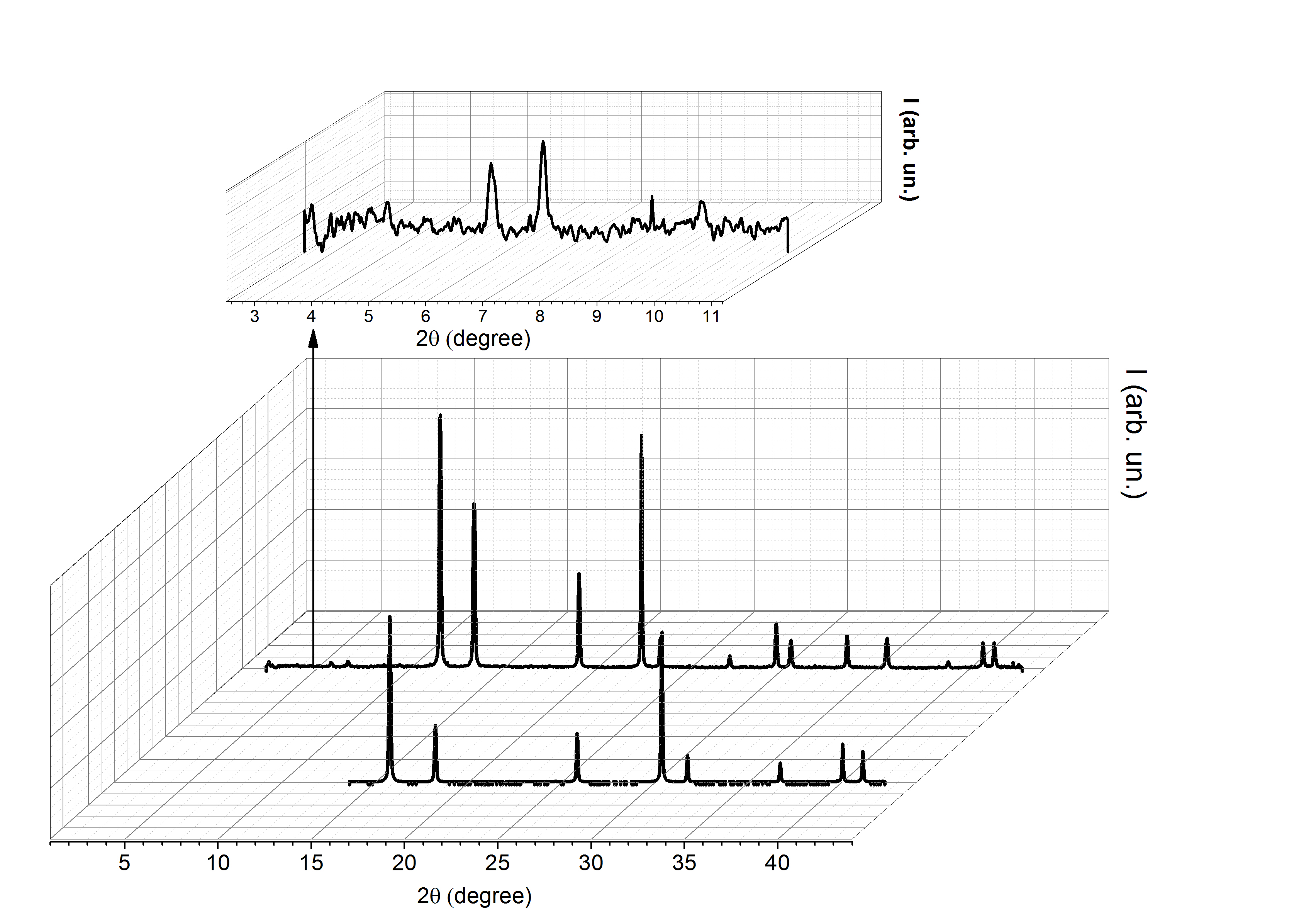
The paper presents X-ray diffraction studies of diffusion filters-membranes based on palladium. Information on the structural state of membranes was obtained using synchrotron radiation (SR) of Kurchatov Synchrotron Radiation Source. A comparison was made between states of the prolonged membrane relaxation after hydrogenation and that exposed to additional applied load by the method of electrolytic hydrogenation (EH). In addition to the structural maxima determining the face-centered lattice of the alloy matrix, reflections were revealed on the diffraction patterns, indicating the presence of long-range ordering in the structure.
The results for the sol-gel synthesis of acylate gels are reported in the titanium tetra-n-butoxide – barium hydroxide – acetic acid system at a molar ratio of Ba:Ti components of 1:1 and 2:1. The thermal decomposition of these gels over temperatures ranging from 85 –1200 ◦C was investigated using thermal analysis methods, XRD, FTIR spectroscopy, electron microscopy, and dielectrometry at frequencies from 25 – 106 Hz. The electrorheological effect in suspensions of powders synthesized at different temperatures with a stoichiometric Ba:Ti ratio = 1:1 and 2:1, in polydimethylsiloxane was studied. The influence of thermal gel treatment was analyzed on their dielectric properties as fillers of electrorheological fluids and on the magnitude of the electrorheological effect.
A set of nanocomposite film materials based on bacterial cellulose containing nanoparticles of cerium dioxide was prepared. An investigation into the structural and morphological characteristics of the films has been performed, their thermal, mechanical and tribological properties were determined. A protocol of the nanocomposite materials formation used in the work was shown to provide a homogeneous distribution of ceria nanoparticles in the matrix polymer volume in addition to the presence of certain amount of broadly size-dispersed cerium oxide aggregates in the bulk film. The increase of nanoparticles concentration in the composite provokes a progressive growth of the Young’s modulus and strength of the film material. Introduction of nanoparticles into the polymer causes the stabilization of sliding friction processes in the tribocontact with steel as well as the decrease of intensity in the wear rate of the film. An increase of the nanoparticles concentration results in a decrease of the material thermal stability.
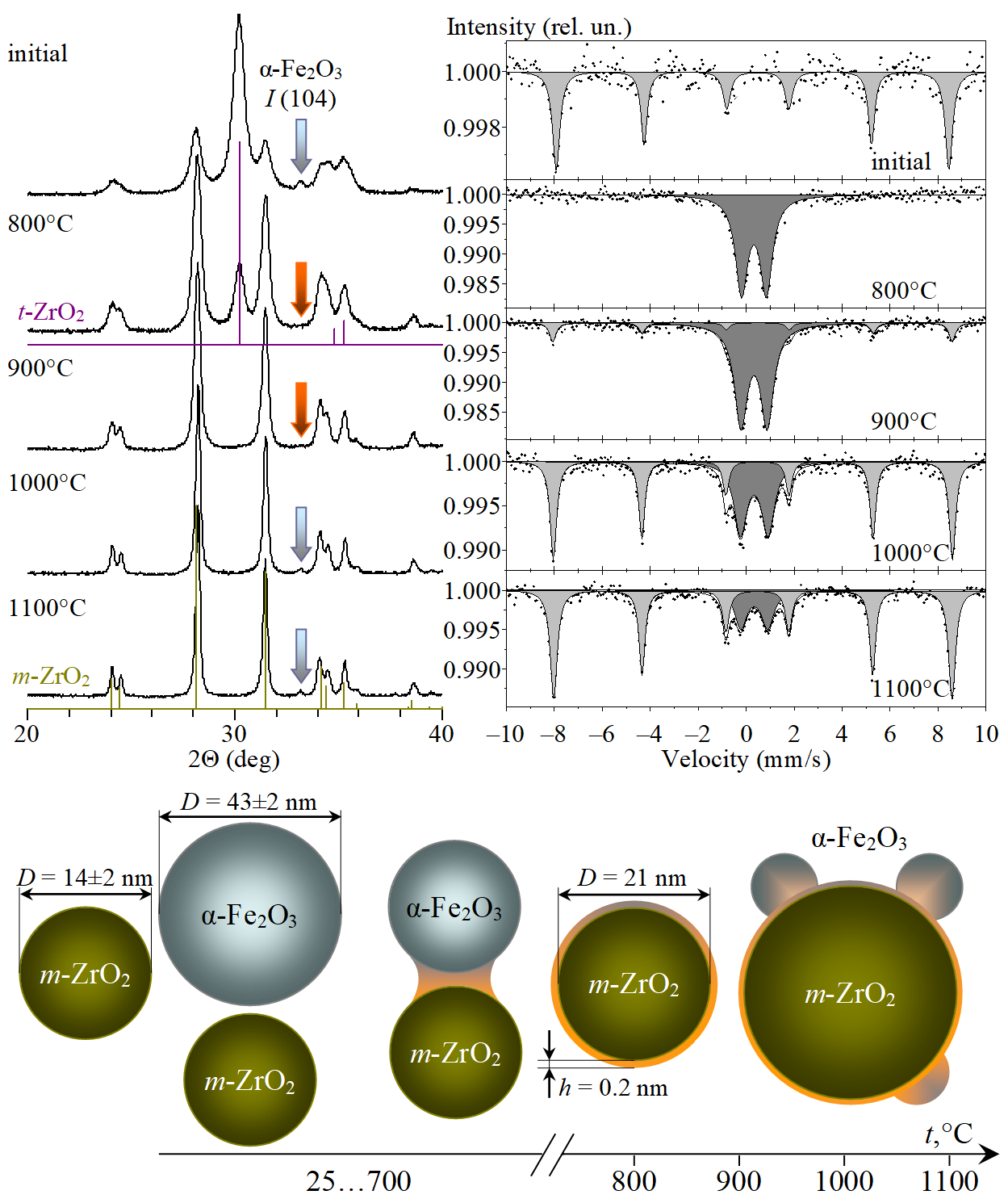
Based on the results of X-ray phase analysis and Mossbauer spectroscopy, it was demonstrated that in the ZrO¨ 2–Fe2O3 system, represented by the mechanical mixture of m–ZrO2 (14±2 nm) and α-Fe2O3 (43±2 nm) nanoparticles, being heated above the temperature corresponding to the melting temperature of the two-dimensional nonautonomous phase, transformation of α-Fe2O3 occurs resulting in appearing of the X-ray amorphous magnetically disordered state localized on the surface of ZrO2 nanoparticles in the form of a thin layer. Transformation pattern in ZrO2–Fe2O3 nanocrystalline system has been introduced.
In this paper, we investigate a sensitivity characteristics of germanene based on the tunneling current in the contact of a germanene with a metal or a superlattice. It is shown, that the sensitivity of the considered system to impurity molecules increases when a constant electric field is applied to it along the germanene plane.
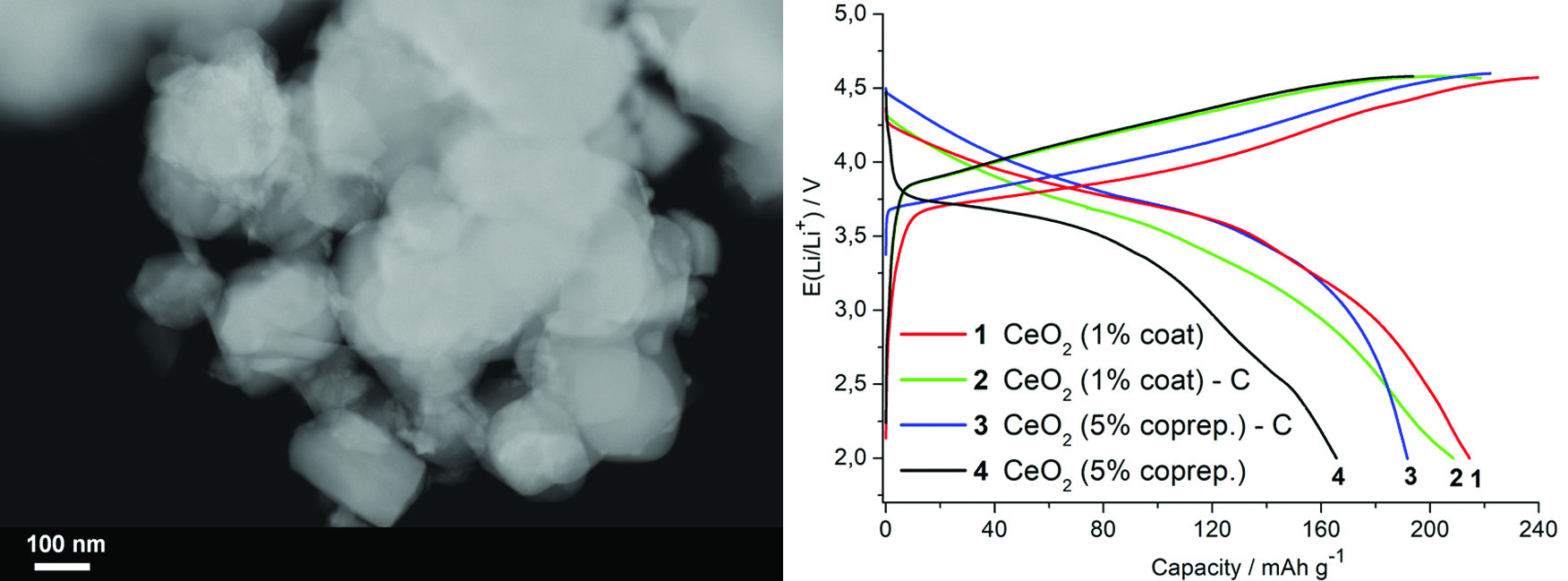
Li[Li0.13Ni0.2Mn0.47Co0.2]O2–CeO2 composites have been obtained by coprecipitation with CeO2 and by coating with ceria followed by coating with carbon film. STEM analysis revealed the formation of 20 – 30 nm ceria particles on the surface of LLNMC grains in all cases. Both carbon-coated LLNMC-CeO2 composites and carbon-free LLNMC coated with 1 % CeO2 demonstrated enhanced capacity values that could not be explained by the charge compensation via redox of nickel and cobalt. 5 % CeO2-coprecipitated sample demonstrated the most intense anomaly in CV at U = 4.1 – 4.5 V associated with redox processes in the anionic sublattice of LLNMC and a larger charge transfer resistance compared to other composites. The maximum values of Li+ diffusion coefficient have been observed for the samples coated with 1 % CeO2. The different electrochemical behavior of these samples could be explained by the different intensity of anionic redox processes in the samples with different amount of nanocrystalline ceria.
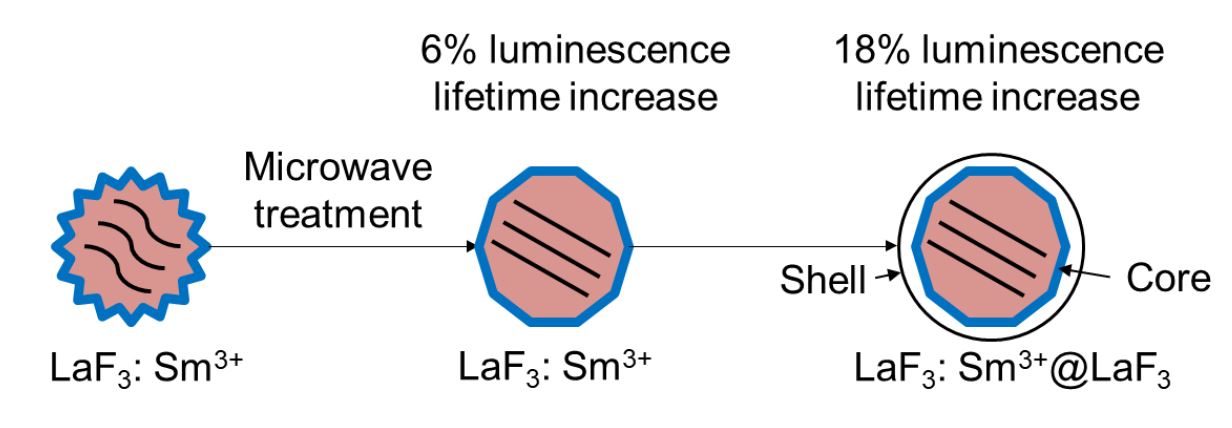
Crystalline LaF3:Sm3+ and LaF3:Ce3+ nanoparticles were fabricated via a co-precipitation method. The obtained nanoparticles were 15 – 20 nm and had good crystallinity. Spectral-kinetic properties of crystalline LaF3 nanoparticles activated with 5 % Sm3+ and 12 % Ce3+ ions were studied. Various duration of the microwave treatment as well as core-shell structure were studied as possible ways to control quenching in the nanoparticles. In case of the LaF3:Sm3+ nanoparticles, the additional microwave treatment increased the average luminescence lifetime by 6 % and addition of the LaF3 shell increased it by 18 %. In case of the LaF3:Ce3+ sample, microwave treatment increased the average lifetime by up to 20 %. The observed effects of varying the synthetic conditions and composite core-shell structure on luminescence properties of nanoparticles provide a means to manage the energy loss in the nanoparticles due to the quenching factors.
We report the results of research for the Pd/Ge/Au ohmic contact resistivity to n-GaAs thermally treated in various gas atmospheres at low temperature. The lowest contact resistivity of about 4 · 10−6 Ω·cm2 was obtained with annealing under a hydrogen atmosphere. The mechanism of the ohmic contact formation upon annealing under a hydrogen atmosphere has been proposed. The achieved results can be used for development of multi-junction solar cells, power semiconductor devices, lasers, and nanowire-based structures sensible to a high temperature treatment.
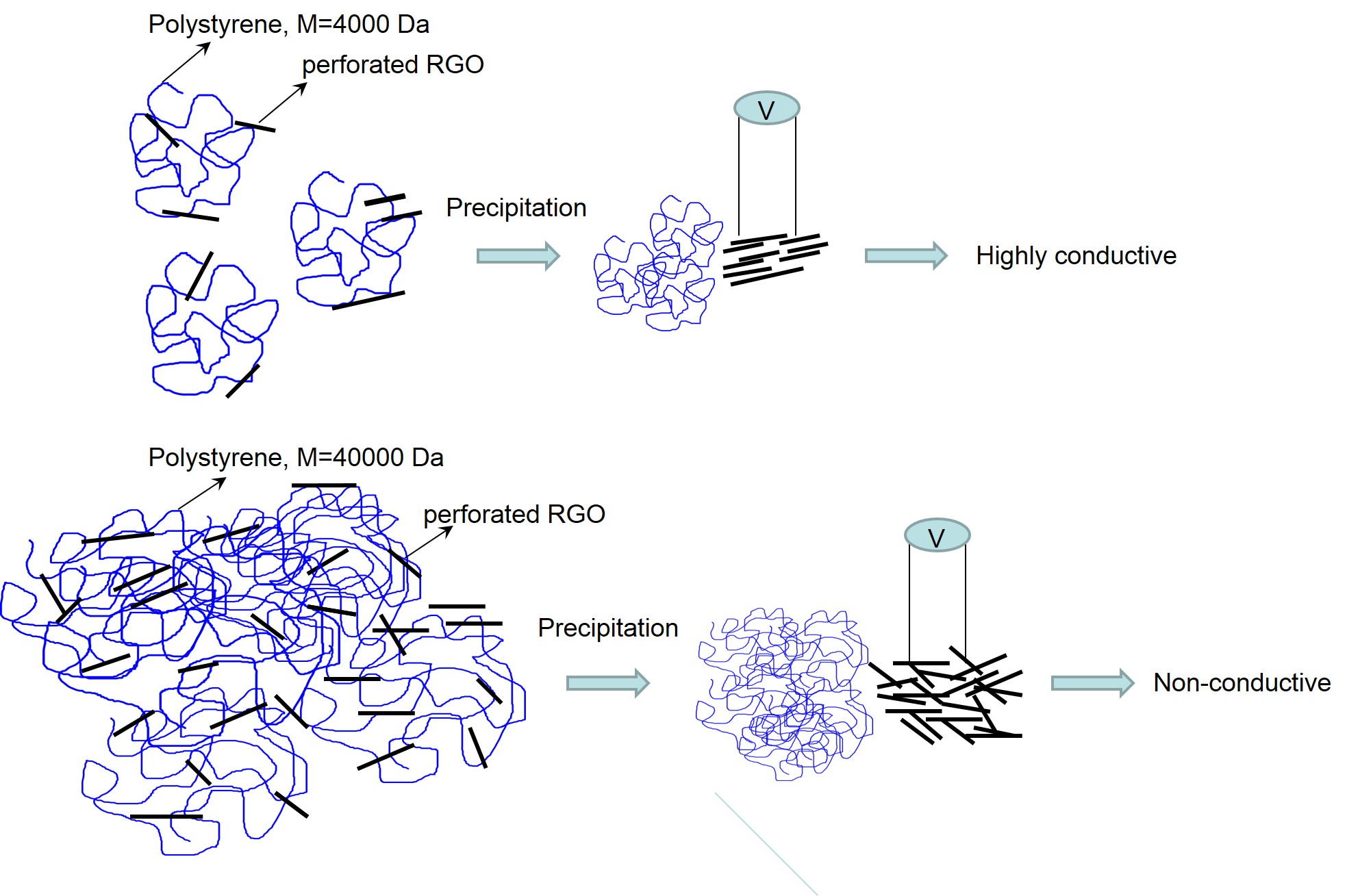
UV-perforated reduced graphene oxide flakes of large areas, some of them up to 500 µm in diameter, have been produced on polystyrene surface. These flakes were formed during precipitation of UV-reduced graphene oxide composites based on polystyrene from benzene solutions by petroleum ether. Two composites based on polystyrene with molecular weights of 9,000 Da and 45,000 Da were synthesized to compare their conductive properties. Conditions of the formation of planar structures from UV-perforated reduced graphene oxide flakes were varied. So, resistances were compared for composites deposited from solutions with different concentrations and at different temperatures. Very low resistances for some flakes precipitated from 5 wt.% solution of composite of 9,000 Da molecular mass at the room temperature were obtained. The absolute values of measured resistances were found to be 1.5 orders of magnitude lower than resistance of copper. At the same time some, regions of graphene inclusions from 12 wt.% solution of latter polystyrene composite demonstrated even lower resistance, almost 3 orders of magnitude lower than copper resistance. This result is explained by existence of superconducting component in the reduced graphene oxide inclusions. In the case of composites with graphene flakes produced from higher molecular weight polystyrene (45,000 Da) resistance was high and varied from semiconducting values to non-conductive state.
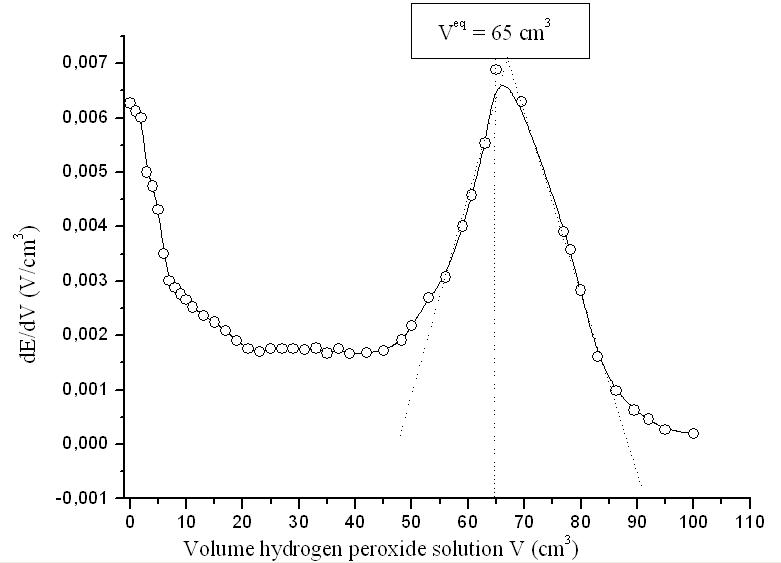
Fullerenol-d C60(OH)22−24 was synthesized by the method of direct heterogeneous oxidation of fullerene C60, dissolved in o-xylene, by NaOH, dissolved in water, in the presence of interphase catalyst OH. Identification of fullerenol-d was provided by: C–H–N elemental analysis, High performance liquid phase chromatography, IR – and Electronic spectroscopy, Mass-spectrometry. The antioxidant properties of aqueous fullerenol-d solutions were investigated against free radicals, generated by hydrogen peroxide and molecular I2. Measurement of fullerenol antioxidant activity was based on the potentiometric titration of fullerenol solutions by hydrogen peroxide and molecular I2 solutions and vice versa with compact Pt as working electrode. As a comparison, the very popular and strong anti-oxidant – ascorbic acid was used. Pourbaix Diagrams (pH −Eh) for hydrogen-oxygen and iodine forms were constructed. Fullerenol-d is a weaker antioxidant than ascorbic acid, but in contrast, fullerenols-d molecules are able to undergo multiply reversible absorption-desorption of some free radicals.
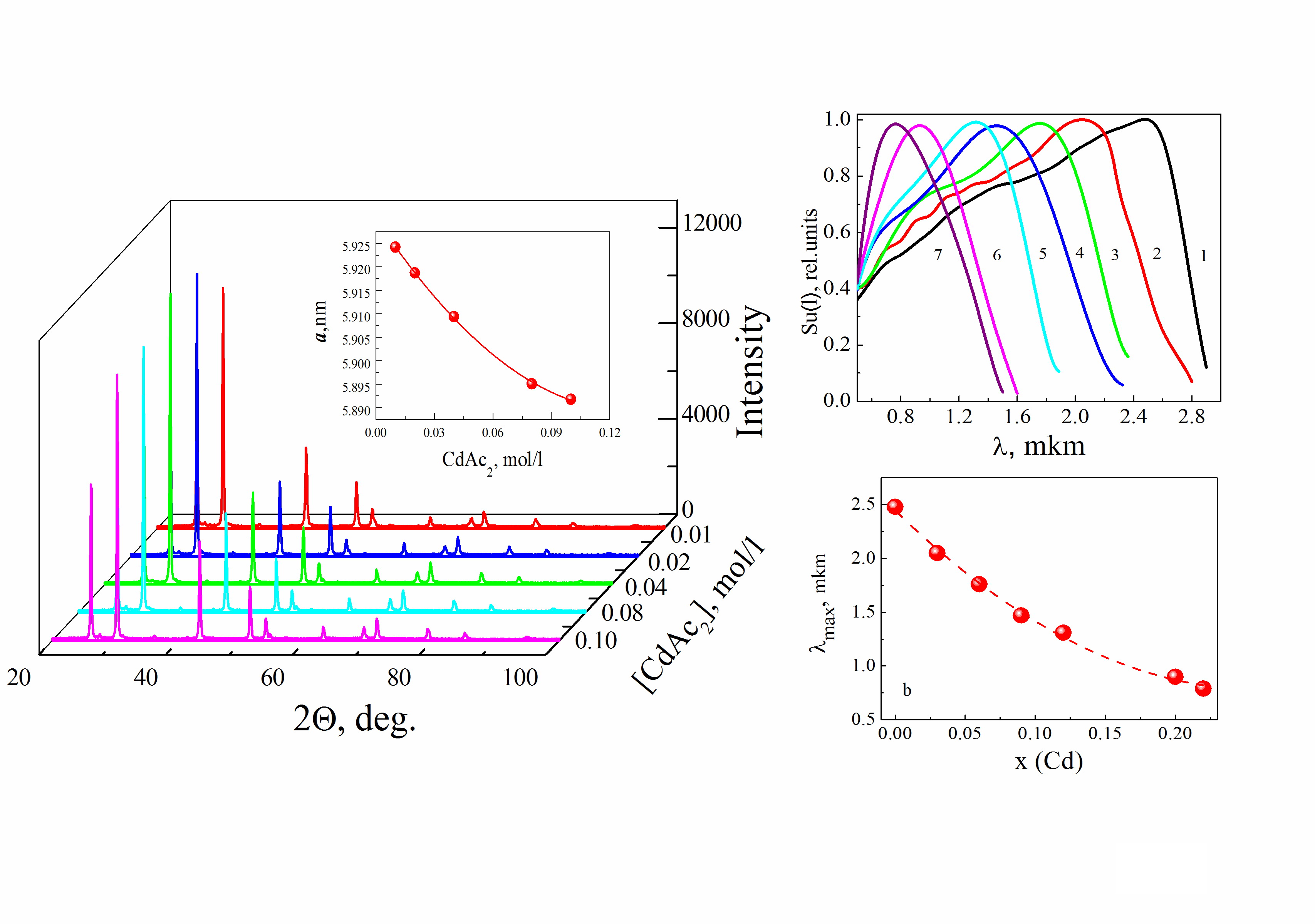
Films of supersaturated substitutional CdxPb1−xS (0.03 ≤ x ≤ 0.22) solutions with a B1-type structure based on lead sulfide cubic lattice were produced by chemical bath co-deposition of CdS and PbS with various concentrations of cadmium acetate in the ammonium citrate reaction mixtures. The results of X-ray measurements showed that with increasing cadmium acetate concentration the microstrains increase in the deposited layers and the crystallites have [200] preferred orientation and pronounced volume anisotropy. It is shown that the obtained films are nanostructured. Depending on the solid solution composition, the layers consist of crystallites with average sizes 200 – 1000 nm. These, in turn, are formed from initial nanoparticles with diameter 50 – 70 nm. The conductivity of the films decreases with increasing cadmium-sulfide content. The synthesized films are photosensitive without any special sensitization procedure in the visible and near-infrared spectral ranges. The maximum of spectral characteristic and the long-wave limit of the photo-response of CdxPb1−xS films move smoothly toward the short-wave spectral range from 3.1 to 1.6 µm and from 2.5 to 1.2 µm, respectively, with an increase in the substitution level of lead into cadmium in PbS lattice correspondently.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)