Our journal "Nanosystems: Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics" is devoted to fundamental problems of physics, chemistry and mathematics concerning all aspects of nanosystems science. It considers both theoretical and experimental problems of physics and chemistry of nanosystems, including methods of their design and creation, studies of their structure and properties, behavior under external influences, and the possibility of use. We accept papers directly or conceptually related to the key properties of nanosystems. Nanotechnology has required the creation of new methods of mathematical modeling and mathematical physics, as well as the development of existing methods for their extension to the study of new objects, many of which were previously simply absent. The corresponding mathematical problems will be covered in our journal. The scope of the journal includes all areas of nano-sciences. Papers devoted to basic problems of physics, chemistry and mathematics inspired by nanosystems investigations are welcomed. Both theoretical and experimental works concerning the properties and behavior of nanosystems, problems of their creation and application, mathematical methods of nanosystem studies are considered. The journal publishes scientific reviews (up to 30 journal pages), research papers (up to 15 pages) and letters (up to 5 pages). All manuscripts are peer-reviewed. Authors are informed about the referee opinions and the Editorial decisions.
Current issue
MATHEMATICS
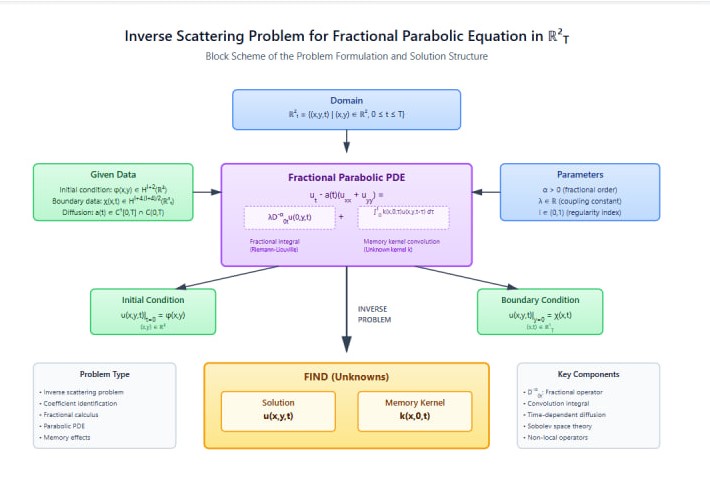
This work considers an inverse problem for a heat conduction equation that includes fractional loaded terms and coefficients varying with spatial coordinates. By reformulating the original equation into a system of equivalent loaded integro-differential equations, we establish sufficient conditions ensuring the existence and uniqueness of the solution. The study focuses on determining the multidimensional kernel associated with the fractional heat conduction operator. The approach is based on the contraction mapping principle and the use of Riemann-Liouville fractional integrals, providing a mathematical framework applicable to diffusion processes with spatial heterogeneity and memory effects.
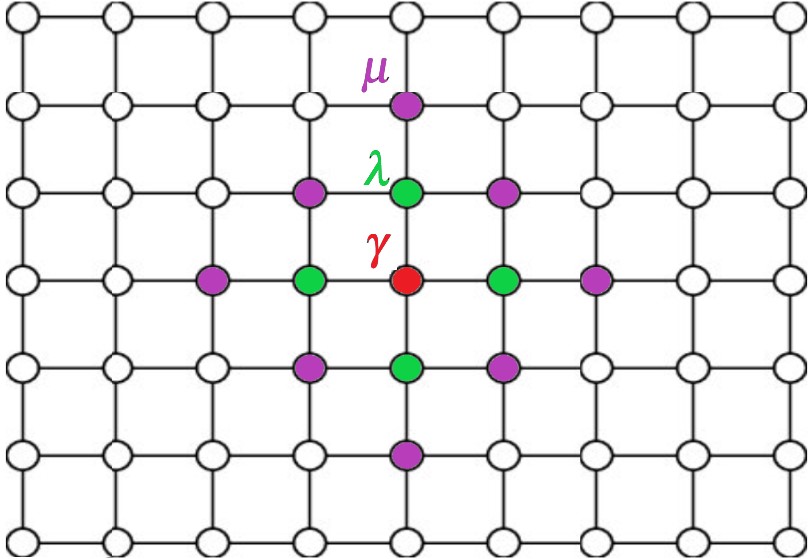
This paper presents a detailed spectral analysis of the discrete Schrodinger operator Hγλµ(K), which describes a system of two identical bosons on a two-dimensional lattice, Z2 . The operator’s family is parameterized by the quasi-momentum K ∈ T2 and real interaction strengths: γ for on-site, λ for nearestneighbor, and µ for next-nearest-neighbor interactions. A key finding of our study is that, under specific conditions on the interaction parameters, the operator Hγλµ(K) consistently possesses a total of seven eigenvalues that lie either below the bottom or above the top of its essential spectrum, over all K ∈ T2
This study proposes a mathematical model for ammonia synthesis based on nonlinear reactiondiffusion equations. The model integrates degenerate gas diffusion in the reactor with Haber-Bosch reaction kinetics to explore efficiency and environmental sustainability. A theoretical analysis is conducted to establish the existence and stability of global solutions for the underlying degenerate parabolic system. Numerical simulations were validated against industrial data from Navoiyazot facility in Uzbekistan, demonstrating 98.2% accuracy in concentration profiles and outperforming constant-diffusivity models by 12–15% in low-concentration regions.
PHYSICS
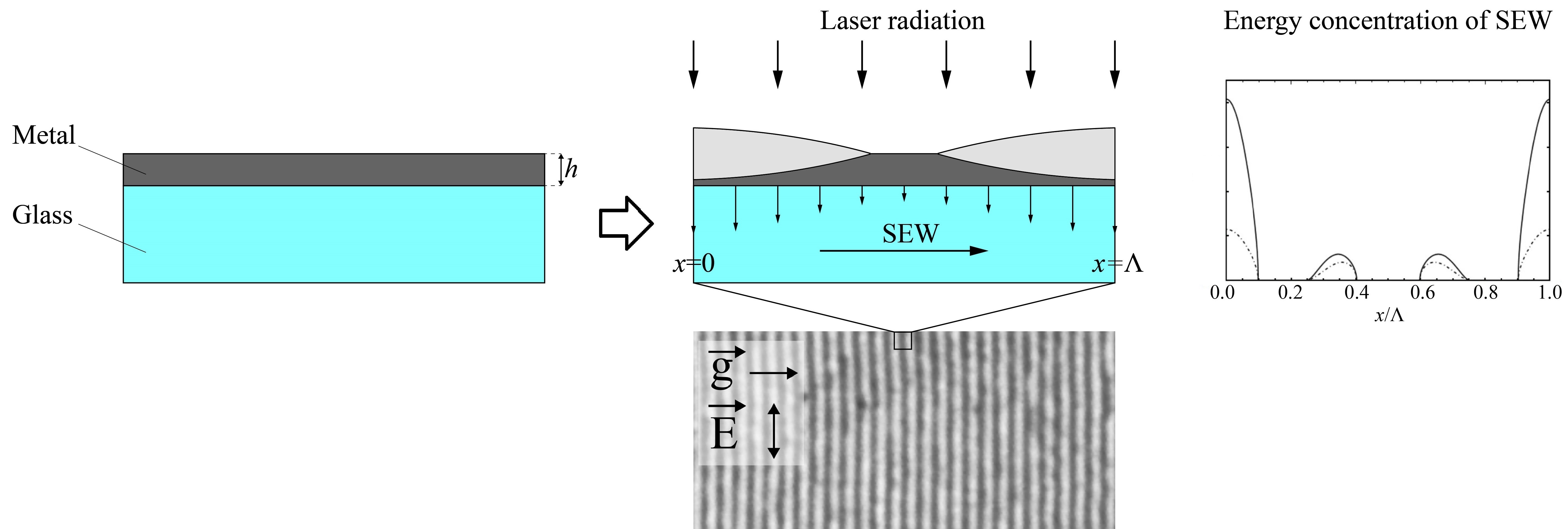
Precise nanopatterning of thin films is an important task in production of modern optoelectronics and photonics elements. Direct recording of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) is a promising tool for direct subwavelength nanopatterning. Recent studies show that the dynamics of LIPSS formation changes significantly if the film is relatively thin. Here we present a comprehensive analytical model aiming to bridge the gap between the expected dynamics of electromagnetic fields during LIPSS formation and experimentally obtainable nanopatterning results. The phenomenological model of surface electromagnetic wave (SEW) propagation at the film–substrate interface illustrates the mechanism of LIPSS formation using a periodic distribution of SEW energy concentration. SEW features are calculated depending on metal film thickness, and positive feedback between the local thickness of the growing oxide layer and the SEW energy concentration is unveiled. Changes in LIPPS formation mechanisms are confirmed experimentally on titanium films with different thickness. These findings shed light on the intrinsic physical mechanisms of LIPSS formation on thin metal films and ease the possibilities for LIPPS applications for nanopatterning.
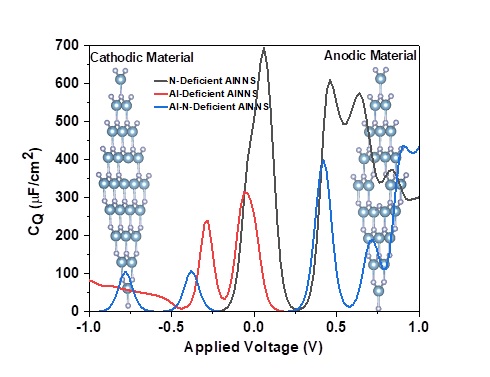
This paper analyzes the quantum capacitance properties of aluminum nitride nanosheets (AlNNS) with defects focusing on their potential use in supercapacitors. We validated the structural stability of the primitive cell through cohesive energy calculations and phonon spectrum analysis. Our findings indicate that monolayers containing aluminum (Al), nitrogen (N), or with Al–N deficiencies exhibit p-type/n-type or wide bandgap semiconducting state. Calculations of defect formation energy indicate that N-deficient AlNNS is the least favorable option. The presence of under-coordinated atoms near the defect leads to the emergence of new impurity state in the forbidden energy bad gap region. This prompted us for a detailed examination of their quantum capacitance, which is heavily influenced by the density of states around the Fermi energy. Our study reveals that Al-deficient AlNNS achieves a maximum quantum capacitance (CQMax) of 690 µF/cm2 in the positively biased region, making it a suitable candidate for anodic material in supercapacitor applications. In comparison, the nitrogen-deficient AlNNS reaches a CQMax of 313 µF/cm2 and a maximum surface charge capacity (QMax) of −91 µC/cm2 , highlighting its potential as a cathodic material. The Al-N-deficient AlNNS shows intermediate behavior with prominent quantum capacitance peaks in both biased regions, offering additional flexibility for potential applications.
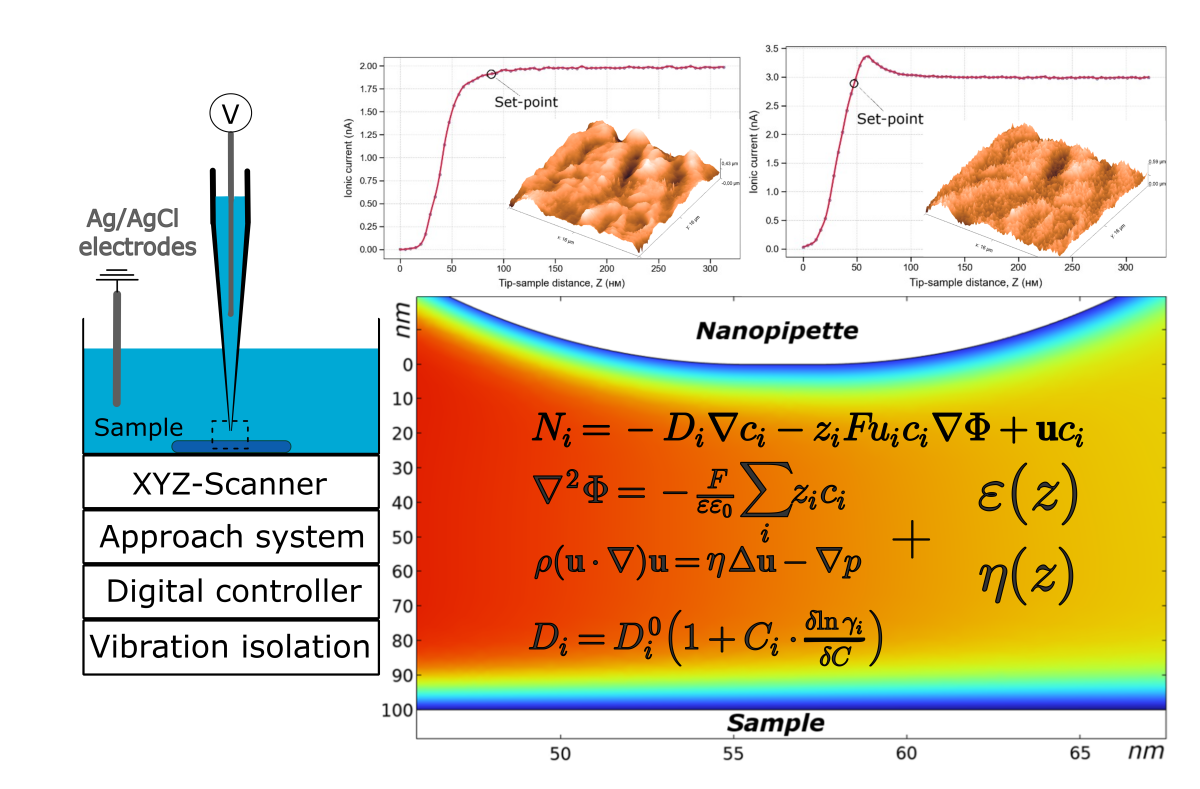
The features of the ion current dependence on distance when a glass nanopipette with an aperture diameter of ∼100 nm approaches the surface of a solid dielectric in a scanning ion conductivity microscope have been studied. A characteristic peak in the approach curve has been observed when the electrode in the nanopipette with an electrolyte is negatively biased relative to electrode in the bath, while a monotonic current decline occurs with a positive bias. To explain this unusual behavior of the ion current, the model accounting for the overlap of electric double layers and water confinement phenomenon in nanochannels and nanogaps have been proposed. The model demonstrates good agreement with the experimental data and provides a basis for quantitative assessment of surface charge at electrolyte–solid interfaces with nanometer-scale spatial sensitivity.
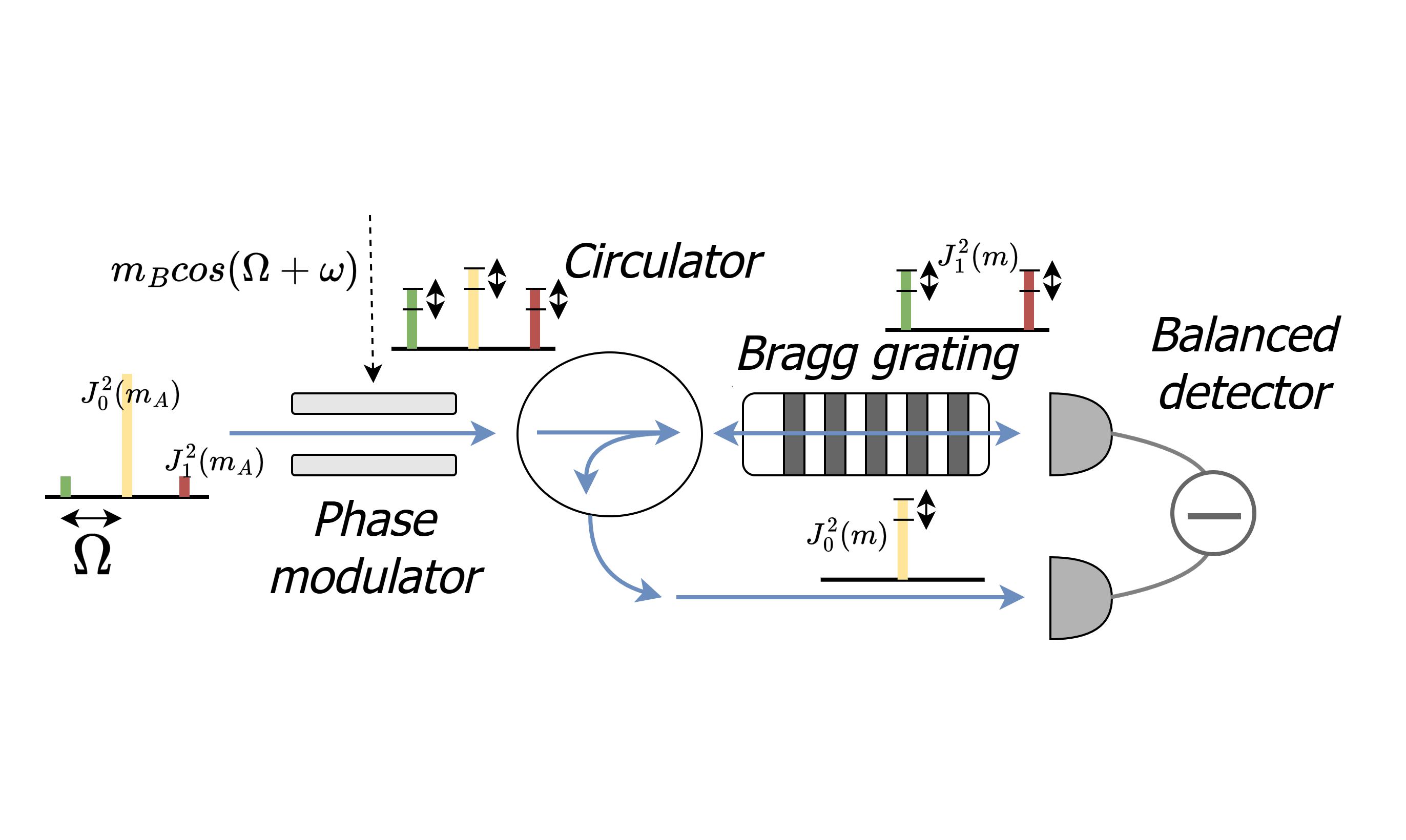
A novel coherent detection method for subcarrier wave (SCW) quantum states applied to continuousvariable quantum key distribution (CV-QKD) is presented. The proposed approach relies on repeated phase modulation at the receiver and spatial separation of the carrier and subcarrier frequency components. The resulting output is an intermediate frequency determined by the difference between the sender’s and receiver’s modulation frequencies. An analytical model of the detection output is developed through time-varying modulation using a classical method based on Bessel functions, and a comparative analysis with alternative heterodyne detection methods is provided. Experimental validation confirms the linear dependence of the output signal on the receiver’s modulation frequency and the sender’s modulation index in the small-modulation regime. Furthermore, the feasibility of the proposed method is demonstrated through the detection of discretely modulated signals using quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK).
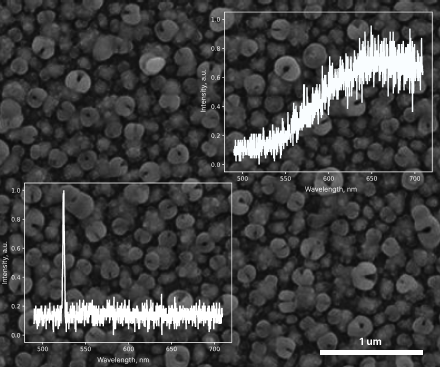
We present an optical physical unclonable function (PUF) based on silver nanostructures randomly formed on a crystalline silicon wafer through galvanic displacement and thermal annealing. The process produces nanostructures with stochastic spatial distribution and morphology, resulting in unpredictable nonlinear optical responses. The hybrid Ag–Si interface generates two independent signals: photoluminescence (PL) and second-harmonic generation (SHG). Spatial PL and SHG maps were binarized and analyzed using standard PUF metrics. SHG demonstrated higher entropy and more balanced bit distribution, making it the preferred encoding channel, while PL provides an additional verification layer. The fabrication method is scalable, lithography-free, and compatible with standard silicon processing.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
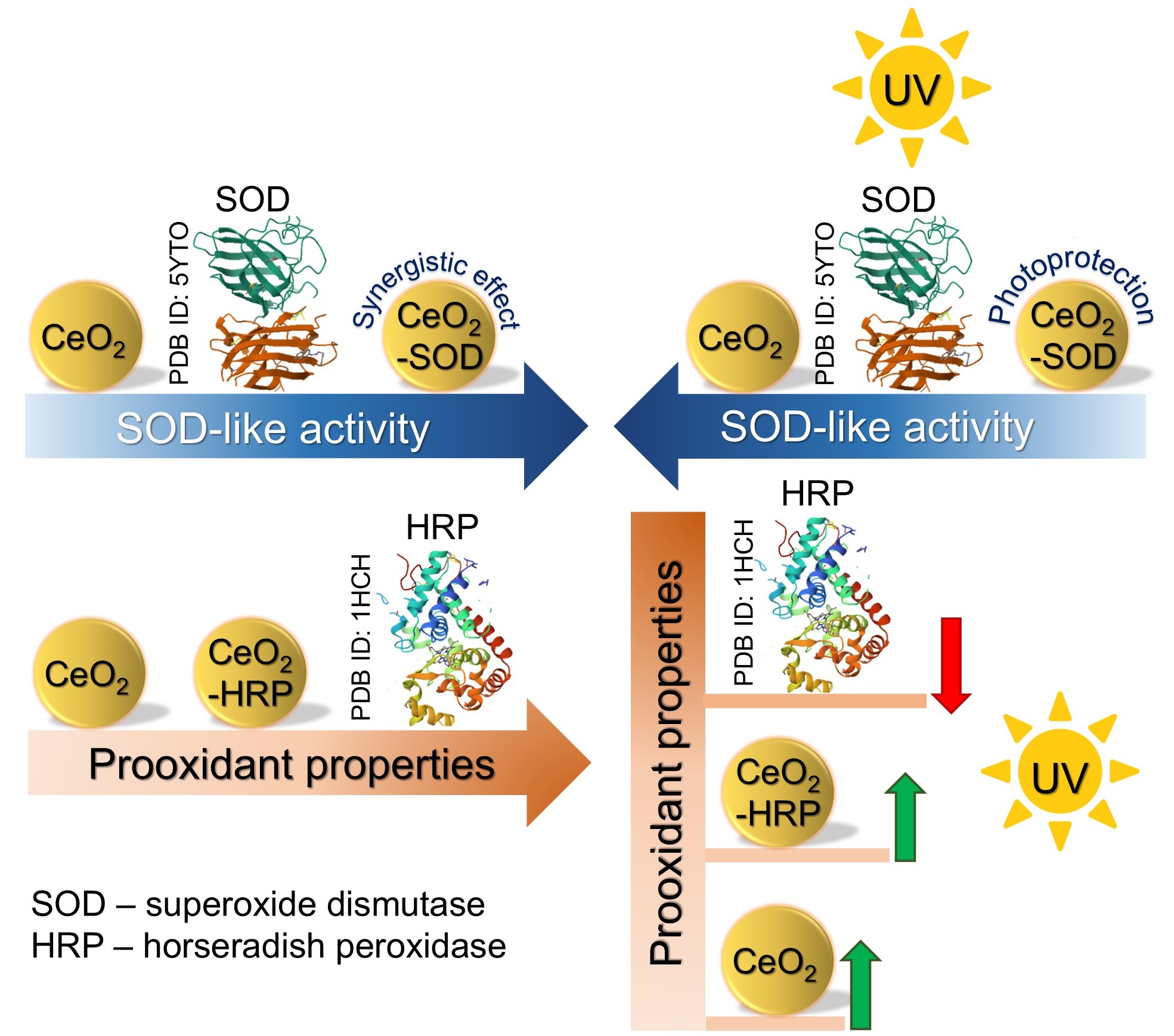
This study investigated the redox properties of cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) and their conjugates with superoxide dismutase (SOD) or horseradish peroxidase (HRP) as well as the UV-induced modulation of these properties. UV exposure non-monotonically decreased the SOD-like property of the bare CeO2 NPs. The CeO2 conjugates with enzymes were analyzed both immediately after preparation and after being aged for 3 h. Chemiluminescence assays showed the synergistic effect for the CeO2-SOD conjugates which showed high SOD activity. Additionally, CeO2 NPs enhanced the stability of the conjugated SOD under UV exposure thus demonstrating a photoprotective function. The CeO2-HRP conjugates demonstrated lower prooxidant activity compared to the bare enzyme, however higher stability under UV irradiation. The effect of UV radiation on CeO2-HRP conjugates was found to be multidirectional and depended on the incubation time f the CeO2 NPs with the enzyme. The results demonstrated that CeO2-enzyme conjugates offer tunable dual functionality and UV light could be an important parameter affecting their redox properties. The latter be taken into account for designing advanced cosmeceutical formulations.
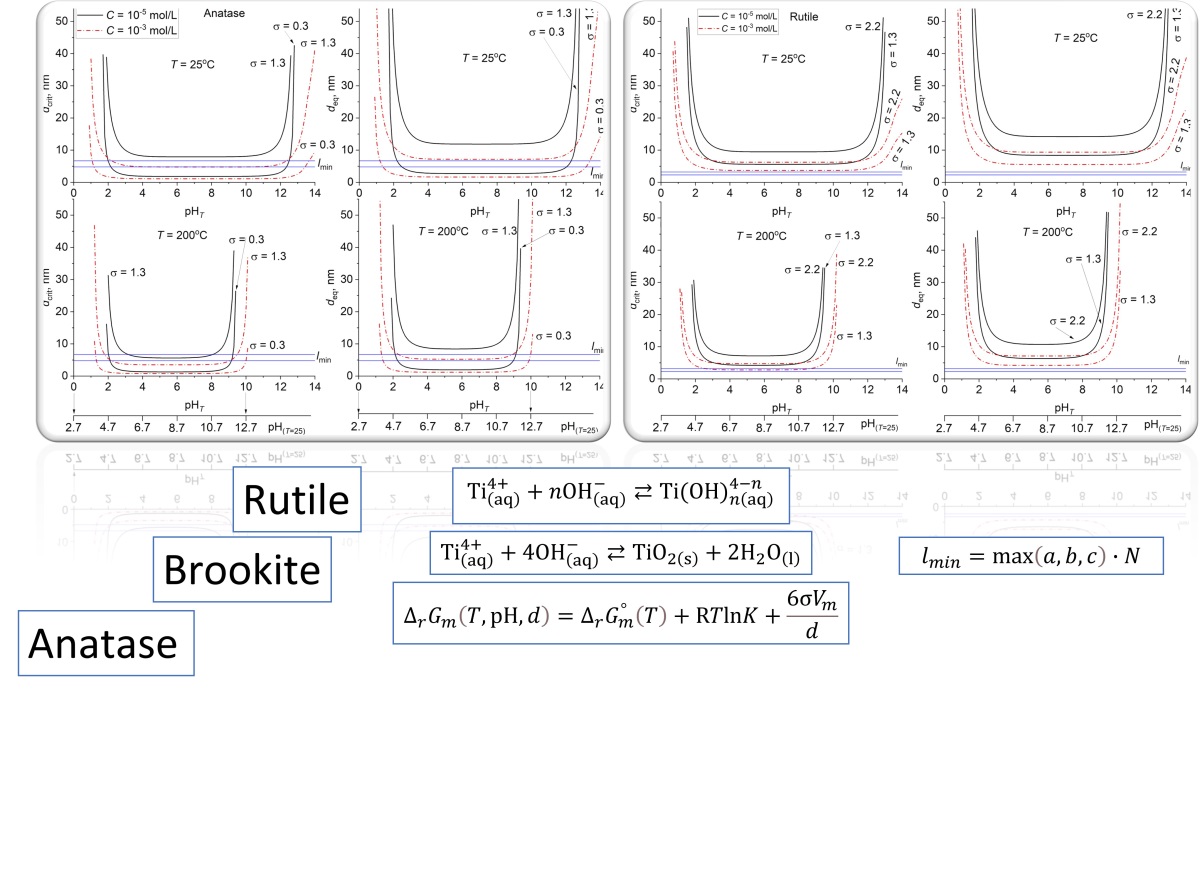
A thermodynamic analysis of the crystallization of titanium dioxide in the anatase, brookite, and rutile modifications from aqueous salt solutions was performed, taking into account the influence of medium pH, temperature, reagent concentration, and the specific surface energy (σ) of the phases. It was shown that the choice of the σ value for the thermodynamic analysis of anatase crystallization is decisive: at σA = 0.3 J/m2 , the minimum particle size is determined by the crystallochemical criterion (lmin ∼5–7 nm), while at σA = 1.3 J/m2 , it is determined by thermodynamic criteria (dcrit ∼8 nm, deq ∼12 nm). Using σ values most closely approximating the conditions of a hydrated TiO2 surface (σR = 1.79, σB = 1.0, σA = 1.13 J/m2 ), the regions of possible crystallization for each modification were determined. Rutile can crystallize in a relatively wide pH range of 0.8–14 (25 ◦C) and 1.1–10.2 (200 ◦C), and the minimum particle sizes of rutile under these conditions are determined by thermodynamic criteria – dcrit and deq. For brookite and anatase in acidic and alkaline conditions (pH ∼1–3 and 9–14), the minimum particle sizes, as for rutile, are also determined by thermodynamic criteria, whereas in the neutral region, they are determined by the crystallochemical criterion lmin. Based on the analysis of structural transitions, it was established that anatase can transform into rutile or brookite at particle sizes larger than ∼16 nm. The calculated size for the brookite → rutile transition is ∼712 nm.
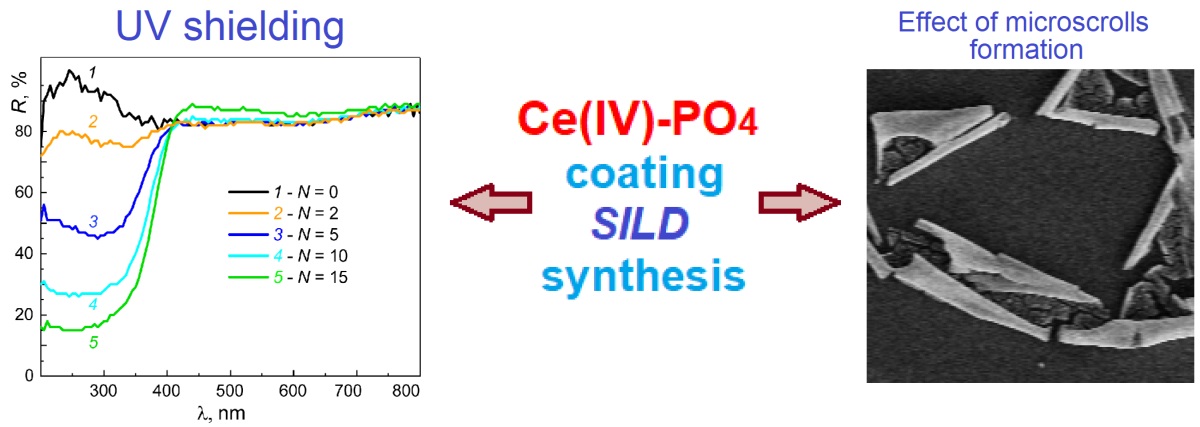
The article presents the conditions for obtaining Ce(IV) phosphate coatings on the surface of silicon and quartz by the successive ionic layer deposition (SILD) method. It has been shown that when using solutions of (NH4)4Ce(SO4)4 and NaH2PO4 as reagents, coatings of the composition Ce(OH)PO4 · nH2O are formed on the surface of the substrates, and when using solutions of (NH4)4Ce(SO4)4 and Na3PO4, coatings of the composition Na0.2Ce(OH)2.4(PO4)0.6 · nH2O are formed. These compounds have an amorphous structure. SEM analysis of Na0.2Ce(OH)2.4(PO4)0.6 · nH2O on the silicon surface showed that for the samples obtained as a result of 15 SILD cycles, the planar isotropic coatings are rolled into microtubules with a microscroll morphology of 3–5 µm in diameter and 30–100 µm in length. The composition of the noted Ce(IV) phosphates can be relatively easily doped during the synthesis process, for example, with Fe(II) cations and tungstate anions. It was found that Ce(OH)PO4 · nH2O coatings are characterized by intense absorption band in the UV region of the spectrum, and can be used as components in various types of absorbers. Moreover, the degree of absorption can be controlled by varying the number of synthesis conditions, for example, the number of SILD cycles.
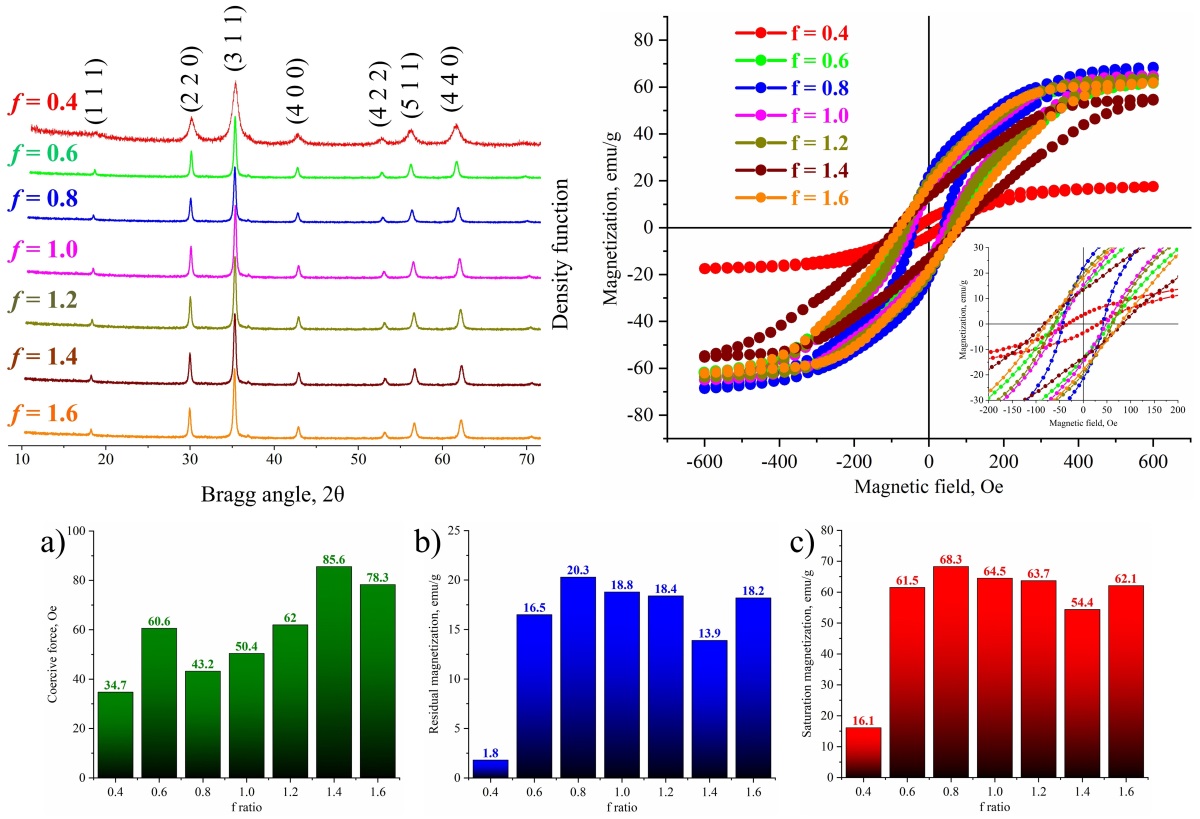
Nanostructured Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 ferrites were synthesized by the glycine–nitrate solution combustion method with the fuel-to-oxidizer ratio f varied from 0.4 to 1.6 in order to clarify the influence of redox conditions on structure and magnetic properties. X-ray diffraction confirms the formation of single-phase cubic spinel for all compositions, with the crystallite size changing from ∼ 8 to 108 nm and the minimum values of both crystallite size and lattice parameter (8.420 A) obtained under fuel-deficient conditions ( f = 0.4); the lattice microstrain does not exceed 0.5 %. SEM observations reveal 3 – 5 µm agglomerates composed of 30 – 190 nm particles, while EDX analysis shows cation ratios close to the nominal composition. Magnetic measurements at 300 K demonstrate typical soft-magnetic behavior with saturation magnetization ranging from 16.1 to 68.3 emu/g, residual magnetization from 1.8 to 20.3 emu/g and coercive force from 34.7 to 85.6 Oe, all efficiently tuned by the fuel content. The highest saturation magnetization is achieved near the stoichiometric regime (f ≈ 0.8 – 1.0), whereas fuel-rich mixtures result in increased coercivity due to microstructural refinement and lattice strain. The established correlations between combustion conditions, structural parameters and magnetic response show that controlled variation of the fuel ratio is an effective tool for tailoring Zn–Mn ferrite nanopowders for low-loss soft-magnetic applications.
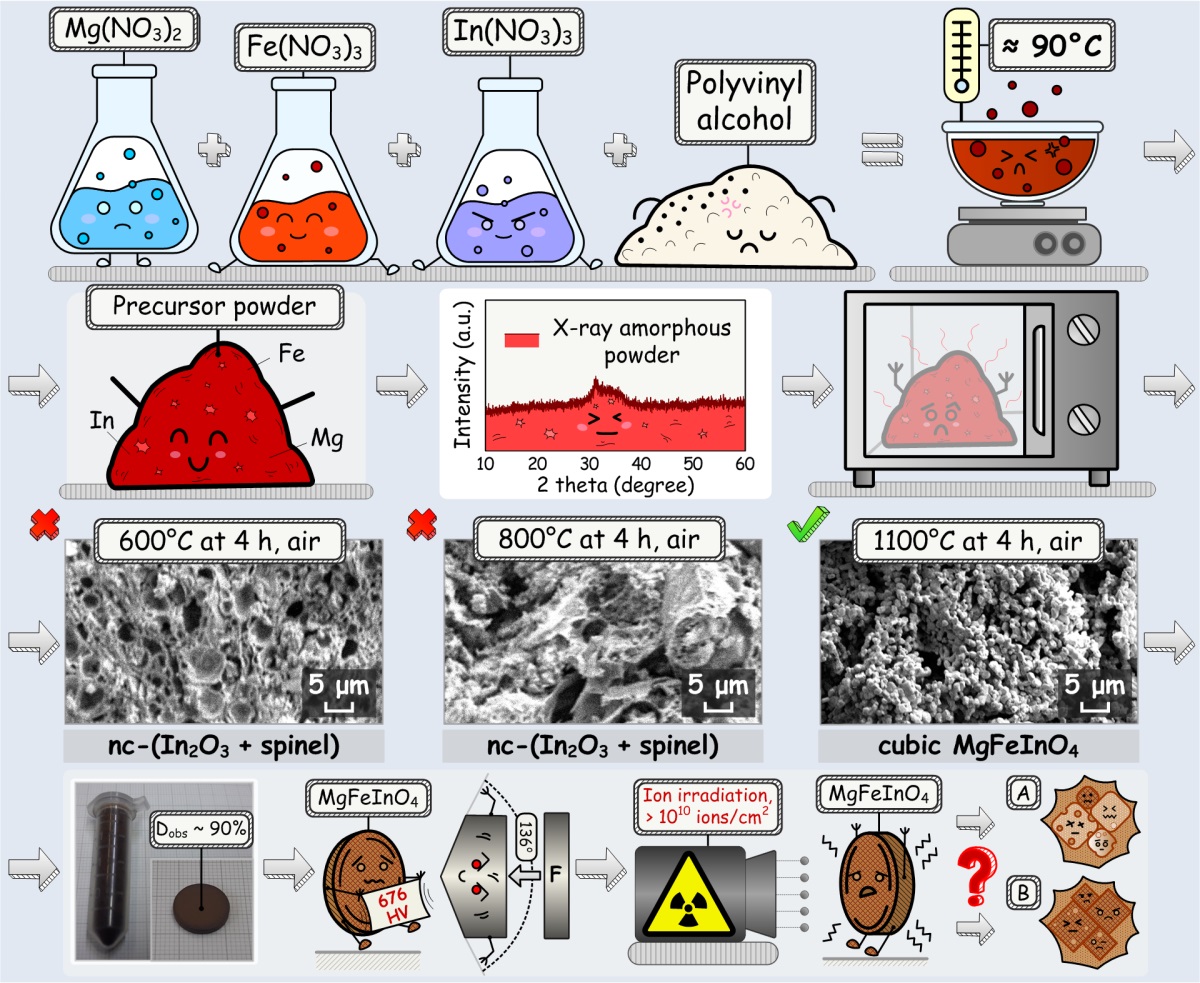
The paper discusses the features of polymer-nitrate synthesis of fine MgFeInO4 particles and presents experimental study results of the physico-mechanical properties of ceramics produced on their basis. According to powder XRD data, a single-phase ferrite-spinel powder can be obtained only as a result of hightemperature treatment of an X-ray amorphous precursor prepared by thermal decomposition of a mixture of polyvinyl alcohol and metal nitrates. Ceramics produced using submicron MgFeInO4 particles have a density close to the theoretical one. The results of microhardness measurements using the Vickers method showed that the resulting material has high hardness. The band gap energy of MgFeInO4 was determined from the DRS data. Based on the crystallographic and electrophysical characteristics of the synthesized material, its resistance to radiation-induced structural changes was predicted.
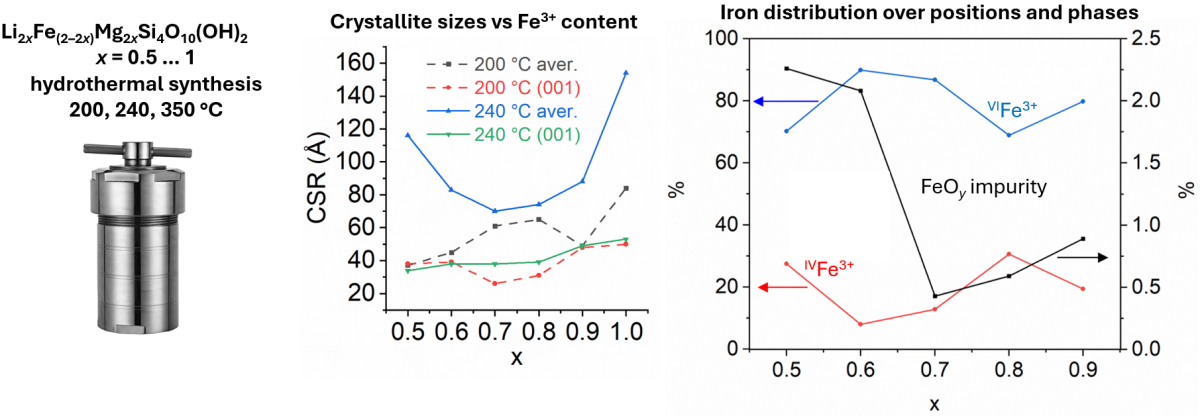
We report on hydrothermal synthesis and structural characterization of Li–Fe-montmorillonite (MMT). To date, this 2:1 type phyllosilicate attracts attention due to such properties as high ion mobility, hydrophilicity, electrical and thermal resistance. Due to that, various MMTs may serve as perspective components of Li-ion batteries (electrolyte and separator fillers, as well as protective buffer layer on top of Li metal anode). Scarce data on synthetic Li–Fe3+-MMTs motivated us to investigate formation process and structure features of such phyllosilicate by X-ray diffraction, UV-visible and Mossbauer spectroscopy, and other methods. We established critical Fe3+ content and temperature range needed for almost single-phase MMTs formation. Around 20 % of total Fe may occupy tetrahedral site of MMT layer. Thermal behavior of Li–Fe-MMT strongly depends on hydrothermal synthesis conditions because of different Li+ amount present in the interlayer space and in the layer vacancies.
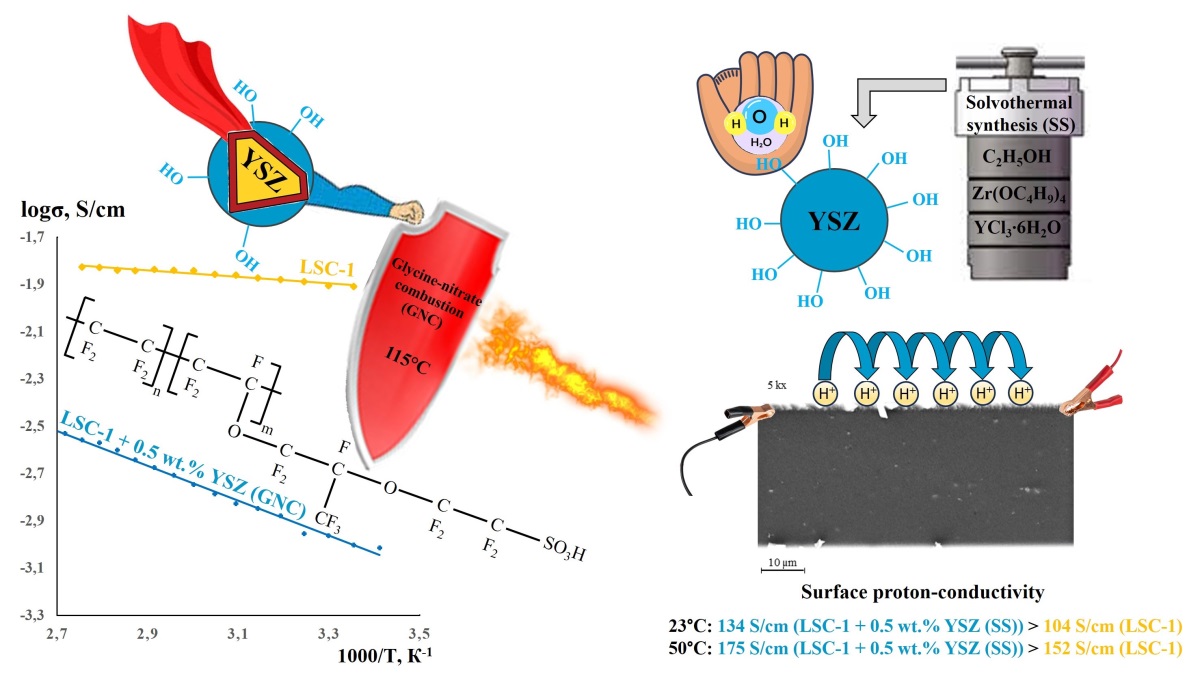
Zr1−xYxO2−0.5x nanoparticles were introduced into the sulfonic acid form of the Nafion-type perfluorinated copolymer prior to membrane formation to improve its water retention, thermal stability, and proton conductivity. Since the conditions under which nanoparticles are formed can significantly influence their size, phase composition, morphology, and surface chemistry, various approaches to filler synthesis were considered in this study. It was found that among the wet-chemical methods used to produce zirconia-based nanoparticles, solvothermal synthesis offers the most promise in terms of increasing the surface proton conductivity of composite membranes. This method ensures small size, large specific surface area, and high hydrophilicity of the nanoparticles. Consequently, their incorporation into a Nafion-type perfluorinated copolymer increases the membrane’s moisture retention and improves to its proton-conducting properties. In the case of Zr1−xYxO2−0.5x nanoparticles formed under solution combustion conditions, their more hydrophobic surface did not contribute to an increase in the moisture content of the perfluorinated copolymer, but did allow its maximum operating temperature to be increased by 20 ◦C.
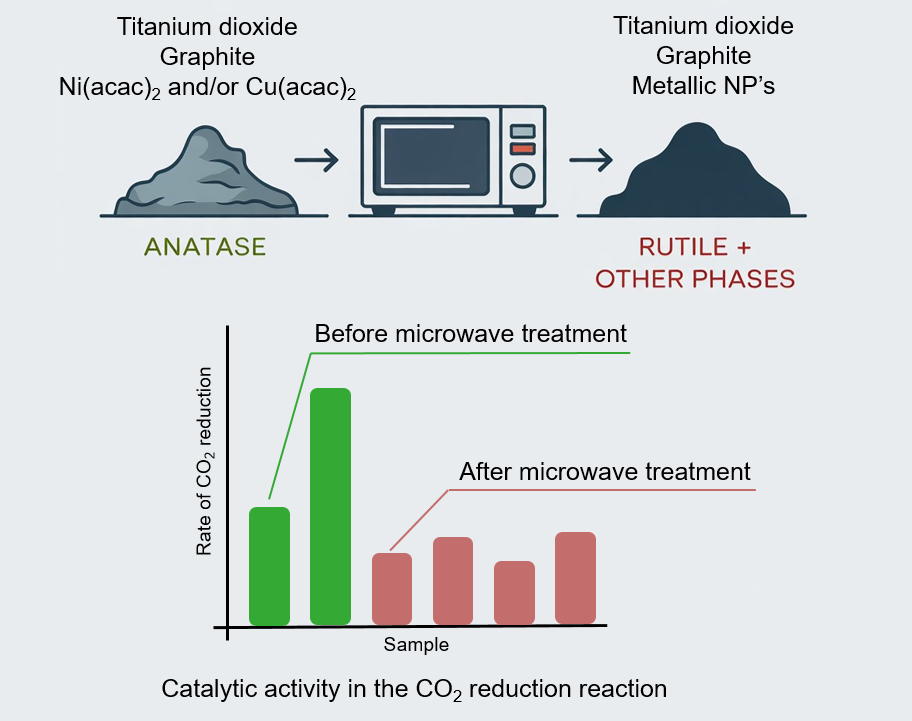
This study presents the synthesis of a TiO2-based composite material with transition metal (Ni, Cu) nanoparticles using microwave radiation. The obtained materials were characterised using X-ray powder diffraction, and the size of the nanoparticles was determined using the Scherrer equation. The photocatalytic activity of the synthesised composites was studied in reaction of CO2 reduction to CO and CH4 under the visible light with a wavelength of 400 nm. Microwave treatment of a mixture of TiO2 with transition metal salts (Ni, Cu) and graphite was founded to decrease a photocatalytic activity in CO2 reduction reaction, while a mechanical mixture of TiO2 and graphite, not subjected to microwave treatment, demonstrated increased catalytic activity compared to unmodified TiO2 Evonik P25. The decrease in catalytic activity of the case of microwave-treated samples is associated with an irreversible phase transition of the photoactive anatase phase into the catalytically inert rutile phase and formation of TiO2−x phases. This process is induced by overheating during microwave synthesis, where graphite (Cg) acts as an effective microwave absorber and a reducing agent for Ti4+ cations in TiO2. The obtained results are interesting for the development of efficient TiO2-based photocatalysts for CO2 reduction.
The nature of the interaction between metals and a catalyst support is a crucial factor in determining the dispersed state of active component phases. In this study, a series of Ni-Mo/ZSM-23 catalysts for the hydroprocessing of plant lipids was prepared by incipient wetness impregnation. The catalysts were prepared by a different sequence of metal deposition and using various complexing agents. The catalysts were investigated by a few physico-chemical methods (TPR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, XRD, TPD-NH3, Raman spectroscopy, HRTEM). It was found that the charge of the ZSM-23 zeolite surface (positive/negative) and the type of metal ions in the impregnation solution affect the formation of phases on the support surface. The use of ammonia impregnating solutions leads to the formation of phases NiO, α-NiMoO4 and β-NiMoO4. In the case of using aqueous and citrate impregnating solutions, only the formation of NiO and β-NiMoO4 phases is observed.
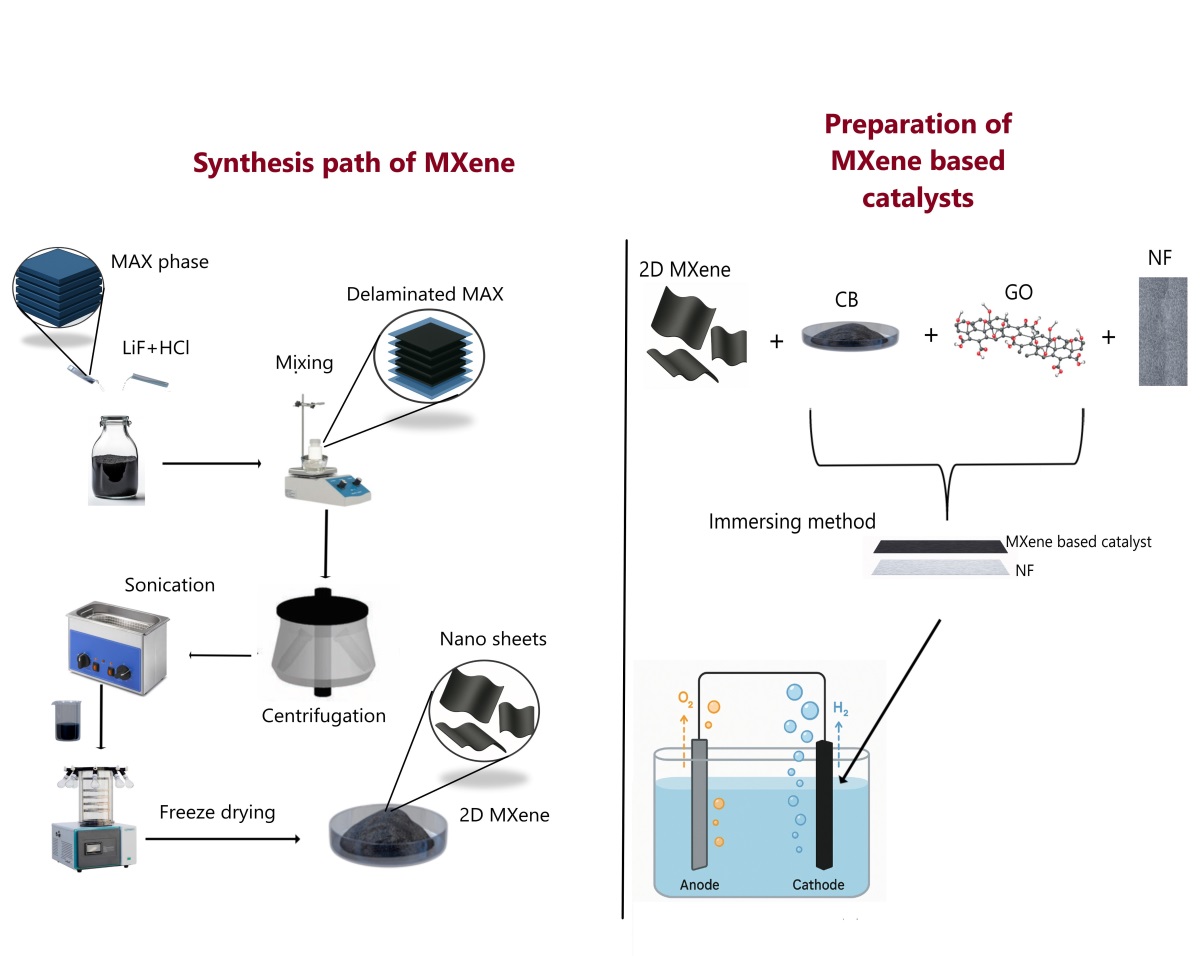
In this study, we modified Ni based electrodes with MXene and MXene-based composite catalysts for water splitting. The MXene based catalyst exhibited excellent electrochemical surface area (ECSA) of 1840 cm2 , highlighting its abundant active sites. To further enhance catalytic activity, MXene was modified with graphene oxide (GO) and carbon black (CB), which significantly reduced the overpotential from 300 mV to 196 mV at 10 mA cm−2 and improved the reaction kinetics, as evidenced by a low Tafel slope of 96.35 mV dec−1 . Moreover, the MXene–GO–CB composite demonstrated outstanding long-term durability, maintaining stable operation for 50 h at 100 mA cm−2 with only a 34 mV increase in overpotential at 10 mA cm−2 . These results confirm that the synergistic combination of MXene with GO and CB yields a highly active and durable electrocatalyst, offering strong potential for practical water electrolysis applications.
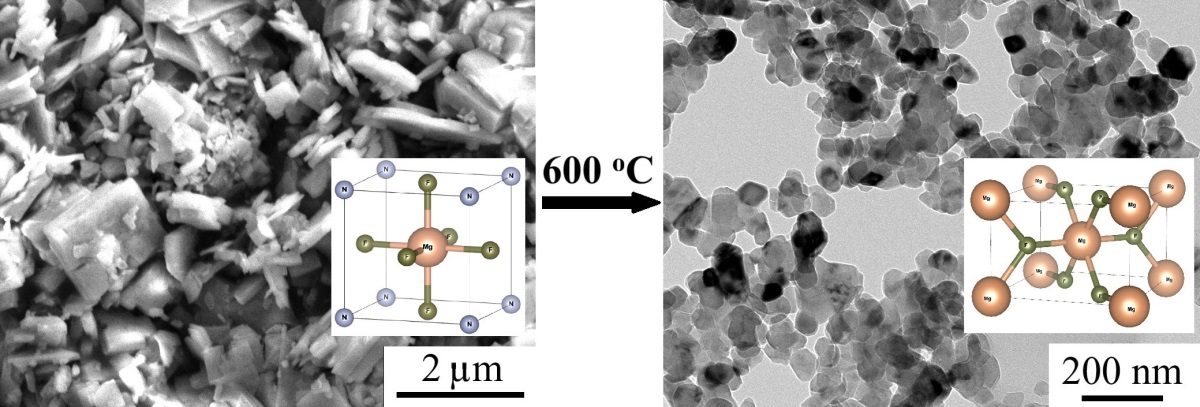
Ammonium fluorometalates with the perovskite structure NH4MF3 (M = 3d metals) are used for cathode materials and NH4MgF3 is used for solid electrolytes. There is only fragmentary information in the literature about the production of NH4MgF3 powder without available X-ray diffraction data. The conditions enable the synthesis of single-phase NH4MgF3 powder are proposed by reaction of magnesium hydroxycarbonate with ammonium hydrofluoride melt at a temperature of 220 ◦C. It has been established that the process is two-stage: the first reaction is the formation of the (NH4)2MgF4 compound and the second reaction is the decomposition of (NH4)2MgF4 at a temperature of 220 ◦C to NH4MgF3. Upon decomposition of NH4MgF3, anhydrous MgF2 nanoparticles (28 ± 7 nm) are formed. The proposed method for obtaining single-phase NH4MgF3 opens up opportunities for studying its functional properties.
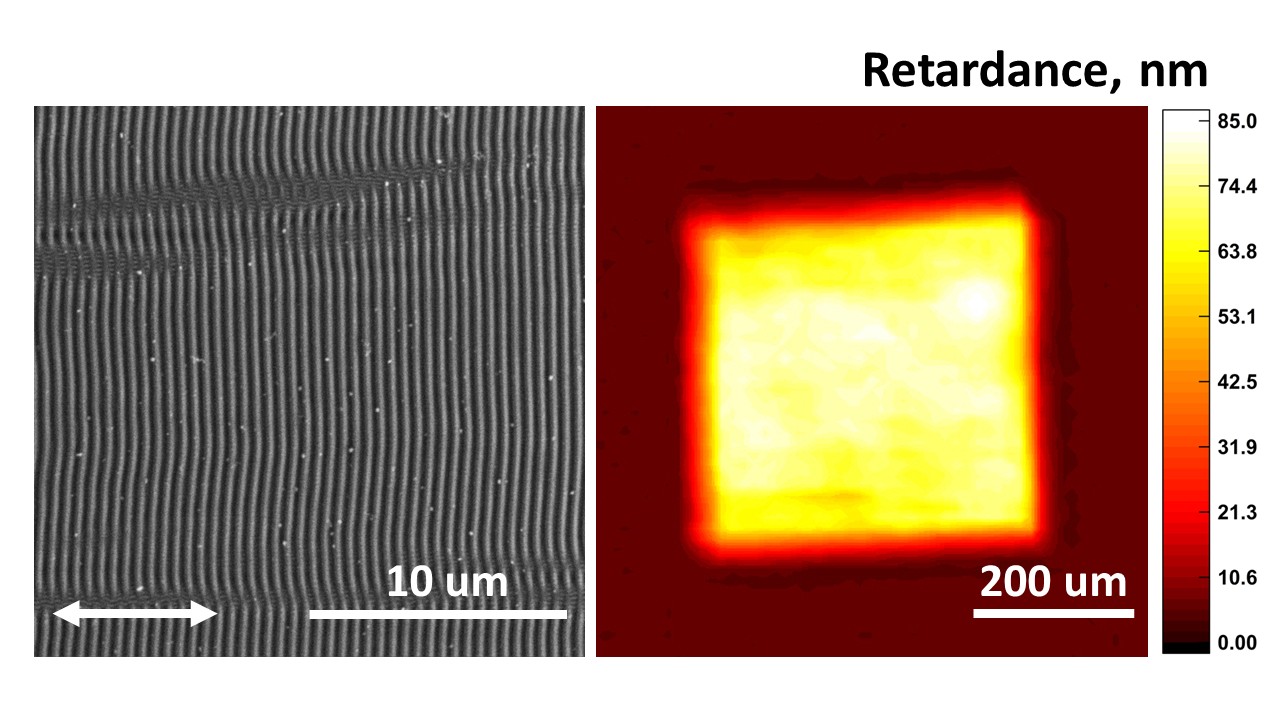
Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) on chalcogenide glassy semiconductors are of great interest in relation with creating polarization-sensitive optical elements. This study investigates the formation of LIPSS on the surface of As50Se50 amorphous film, fabricated by thermal vacuum deposition, under femtosecond laser irradiation in the wavelength range from 400 to 800 nm. The periods of various LIPSS types depend linearly on the laser wavelength. The measured birefringence of so-called low spatial frequency LIPSS, formed by different irradiation wavelengths, are in the 10–85 nm range. The maximum birefringence of 85 nm was obtained for structures irradiated at a 480 nm wavelength. A significant decrease in birefringence was observed at a wavelength of 800 nm, which may be due to the formation of a less pronounced and more disordered surface relief caused by less effective absorption of modifying laser radiation with photon energy lower than optical band gap of As50Se50. Decreased optical absorption observed in As50Se50 films with LIPSS is caused by increased light scattering on the surface relief.
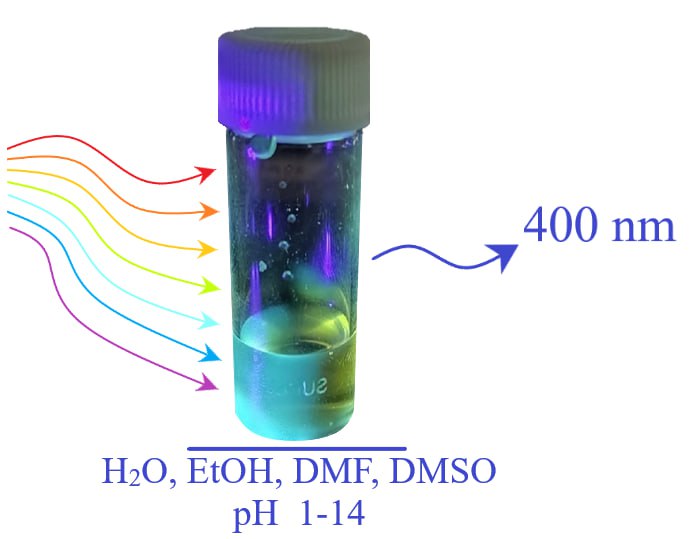
Since their discovery, carbon dots have been of great scientific interest due to their unique properties, including strong fluorescence and biocompatibility, which determine their potential application in biosensorics, bioimaging, drug delivery, and many other fields. This paper presents a new approach for the synthesis of high quantum yield carbon dots with media-independent fluorescence developed in the process of searching for solutions to the problem of carbon dot’s application in immunochromatographic analysis.
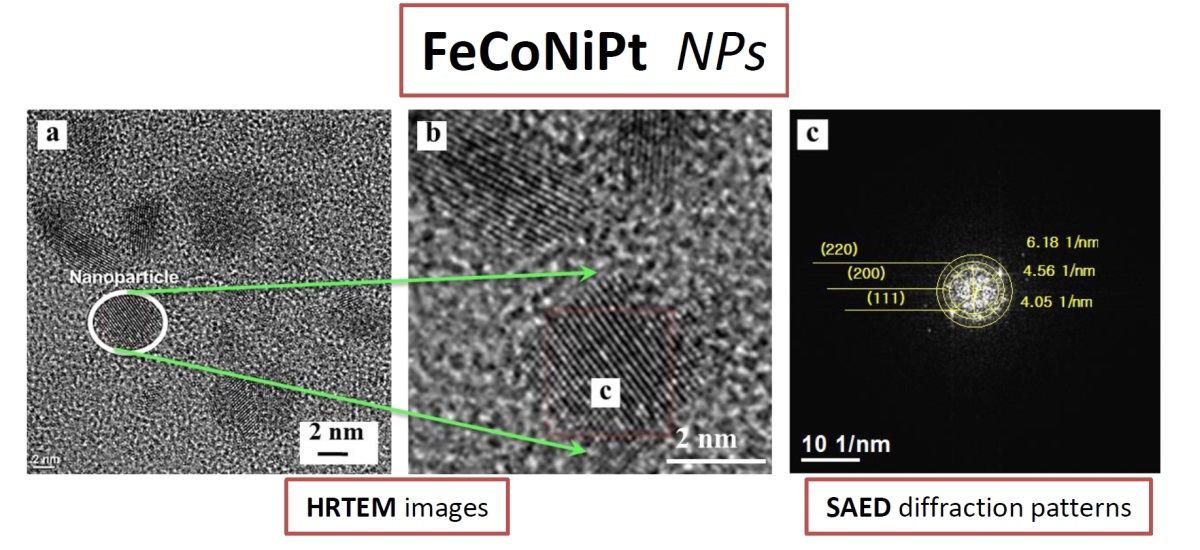
In this work, we present a facile synthesis of FeCoNiPt alloy nanoparticles (NPs) with tunable platinum content (10–30 at.%). The NPs were produced by medium-assisted solid-state reaction using acetylacetonate metal precursors. The structural characterization (TEM, HRTEM, STEM-EDS, and XRD) reveals that the obtained FeCoNiPt NPs exhibit a uniform morphology with an average diameter of 3–7 nm and crystallize in a single-phase face-centered cubic solid solution. Increasing the Pt content leads to lattice expansion and a systematic increase in crystallite size, consistent with the larger atomic radius of Pt. STEM-EDS elemental maps confirm homogeneous incorporation of Fe, Co, Ni, and Pt across individual nanoparticles, demonstrating the successful formation of a multicomponent alloy. This study demonstrates that tuning Pt content in FeCoNiPt multicomponent alloys enables precise modulation of d-band electronic structure. The proposed synthesis approach is simple, cost-effective, and scalable, offering a promising pathway for designing Pt-optimized electrocatalysts.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)