NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2019, 10 (2), P. 154–157
Effect of anodizing voltage and pore widening time on the effective refractive index of anodic titanium oxide
N. A. Sapoletova – Department of Chemistry, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119991, Moscow, Russia
S. E. Kushnir – Department of Chemistry, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119991, Moscow; Department of Materials Science, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119991, Moscow, Russia; kushnir@elch.chem.msu.ru
K. S. Napolskii – Department of Chemistry, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119991, Moscow; Department of Materials Science, Lomonosov Moscow State University, 119991, Moscow, Russia
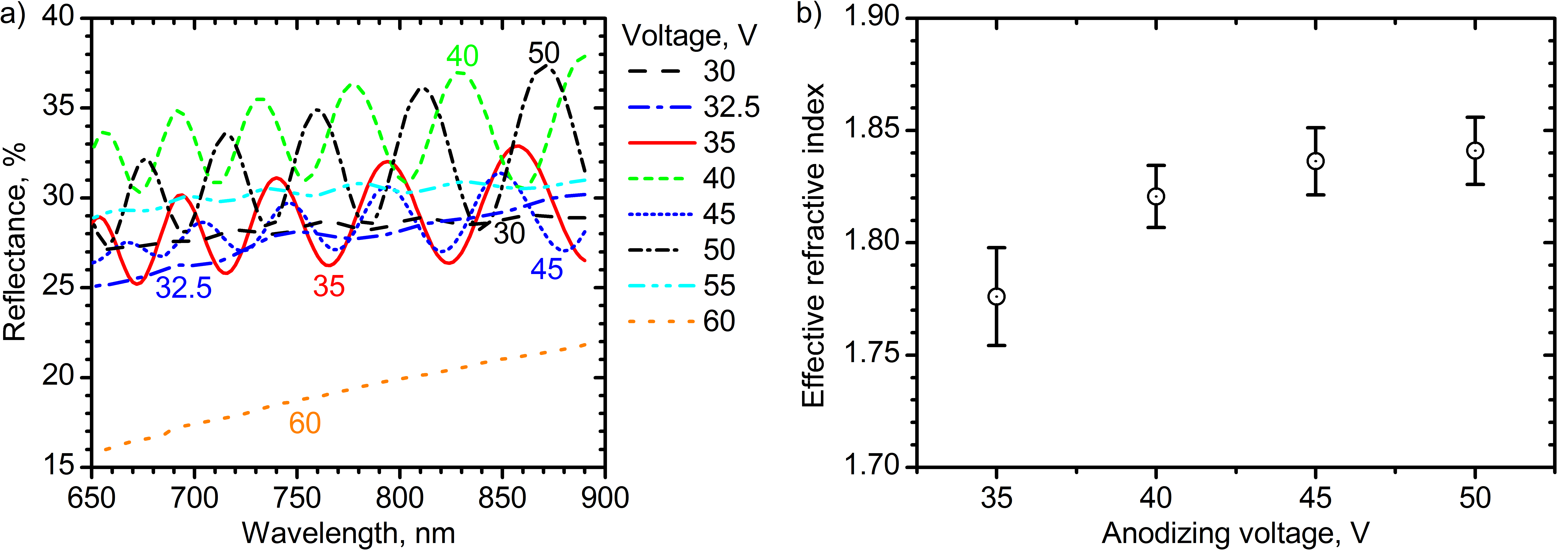
The unique optical properties of porous anodic titanium oxide (ATO) make it a promising material for solar energy conversion, sensorics, and optoelectronics. The optical path length and effective refractive index (neff) of ATO can be tuned by chemical etching of pore walls. However, precise control of these optical parameters is still challenging due to the lack of data on the effect of pore widening time on the neff. Here, a detailed study of the influence of anodizing voltage and pore widening time on the neff of the ATO films was performed. Analysis of reflectance spectra of ATO synthesized at 35 – 50 V shows that pore widening in 3 wt. % H2O2 aqueous solution allows one to control the neff at values ranging from 1.54 to 1.84. The data required for the prediction of the thickness, neff, and optical path length of the ATO films from anodizing and etching conditions are obtained.
Keywords: anodic titanium oxide, anodization, porous materials, film, refractive index, optical materials and properties.
PACS 42.25.Gy, 82.45.Aa, 82.45.Cc
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2019-10-2-154-157