NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2019, 10 (4), P. 466–474
Photoelectrochemical cell performance Cu doped ZnO photoanode sensitized by xanthene dyes
Deepak Kumbhar – Department of Chemistry, Raje Ramrao Mahavidyalaya, Jath, 416 404, affiliated to Shivaji University Kolhapur 416004; Department of Chemistry, Lal Bahadur Shastri College, Satara, 415 002, affiliated to Shivaji University Kolhapur 416004, MS, India
Sarita Kumbhar – Department of Physics, Rajashri Chhatrapati Shahu College, Kolhapur, 416 005, affiliated to Shivaji University Kolhapur 416004, MS, India
Sagar Delekar – Department of Chemistry, Shivaji University, Kolhapur, 416 004, MS, India
Rekha Nalawade – Department of Chemistry, Shivaji University, Kolhapur, 416 004, MS, India
Avinash Nalawade – Department of Chemistry, Lal Bahadur Shastri College, Satara, 415 002, affiliated to Shivaji University Kolhapur 416004, MS, India; avinashnalawaderes@gmail.com
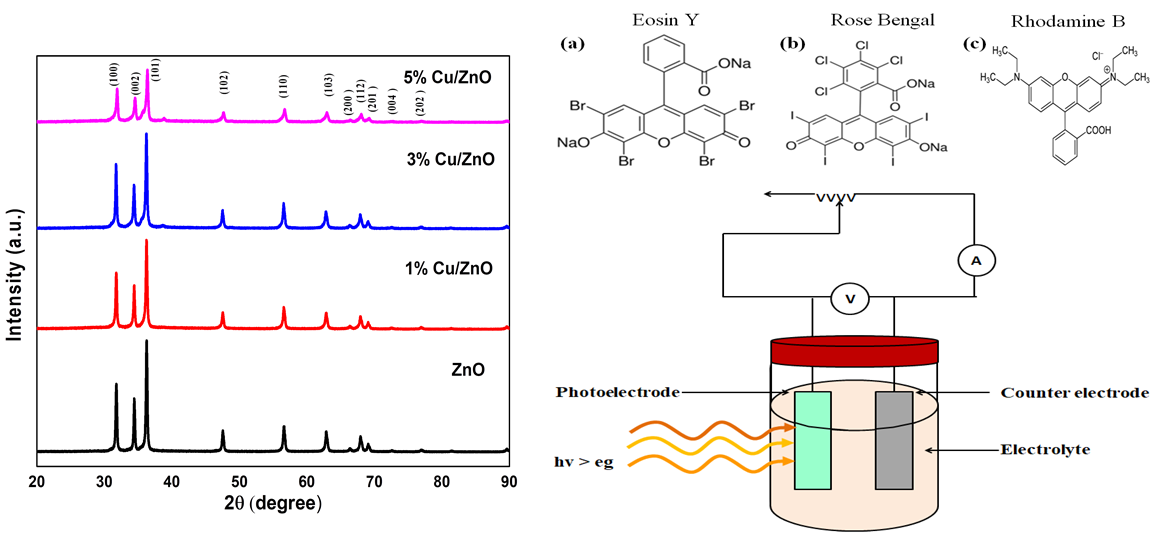
In this study transition metal Cu is doped into ZnO framework at 1, 3 and 5 mol% concentrations by sol-gel method and Photoelectrochemical performance under sensitization is recorded. Structural analysis XRD and Raman gives information of wurtzite structure formation without any mislaid peaks. It also informs decrement in crystalline size and lattice parameters as doping level increases. SEM and EDAX provide nono structure formation with appropriate compositions. Optical analysis by FTIR and PL gives peaks at expected positions while DRS UV-visible peaks show humps with red shift due to effect of Cu doping. After structural and morphological study NPs are deposited on conducting glass surface of FTO substrate by doctor blade method and sensitized with mixed xanthene dyes (Eosine Y., Rhodamine B., and Rose Bengal) for 12 h and photoelectrochemical cell performance are recorded under solar simulator under standard AM 1.5 one sun illumination in that 1 % Cu/ZnO photoanode shows good performance as compared to other.
Keywords: Sol-gel, Cu doped ZnO NPs, xanthene dyes, sensitization, photoelectrochemical cell.
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2019-10-4-466-474