NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2019, 10 (6), P. 666–673
Influence of nanoparticles of various types as fillers on resistance to hydrolysis of films of heat-resistant polyimide
E. N. Bykova – Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, Russian Academy of Sciences, 199004, Bolshoi prospect 31, Saint Petersburg, Russia; bykova.elena.n@gmail.com
I.V. Gofman – Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, Russian Academy of Sciences, 199004, Bolshoi prospect 31, Saint Petersburg, Russia; gofman@imc.macro.ru
E. M. Ivankova – Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, Russian Academy of Sciences, 199004, Bolshoi prospect 31, Saint Petersburg, Russia; ivelen@mail.ru
A. L. Nikolaeva – Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, Russian Academy of Sciences, 199004, Bolshoi prospect 31, Saint Petersburg, Russia; alexandra.l.nikolaeva@gmail.com
A.V. Yakimansky – Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, Russian Academy of Sciences, 199004, Bolshoi prospect 31, Saint Petersburg; Saint Petersburg State University, Institute of Chemistry, 198504, Universitetskii prospect 26, Peterhof, Saint Petersburg, Russia; yakimansky@yahoo.com
O. S. Ivanova – Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, 119991, Leninsky prospect 31, Moscow, Russia; runetta05@mail.ru
A. E. Baranchikov – Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, 119991, Leninsky prospect 31, Moscow, Russia; a.baranchikov@yandex.ru
V. K. Ivanov – Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, 119991, Leninsky prospect 31, Moscow; Lomonosov Moscow State University, Faculty of Materials Science, 119991, Leninskie gory 1, building 73, Moscow, Russia; van@igic.ras.ru
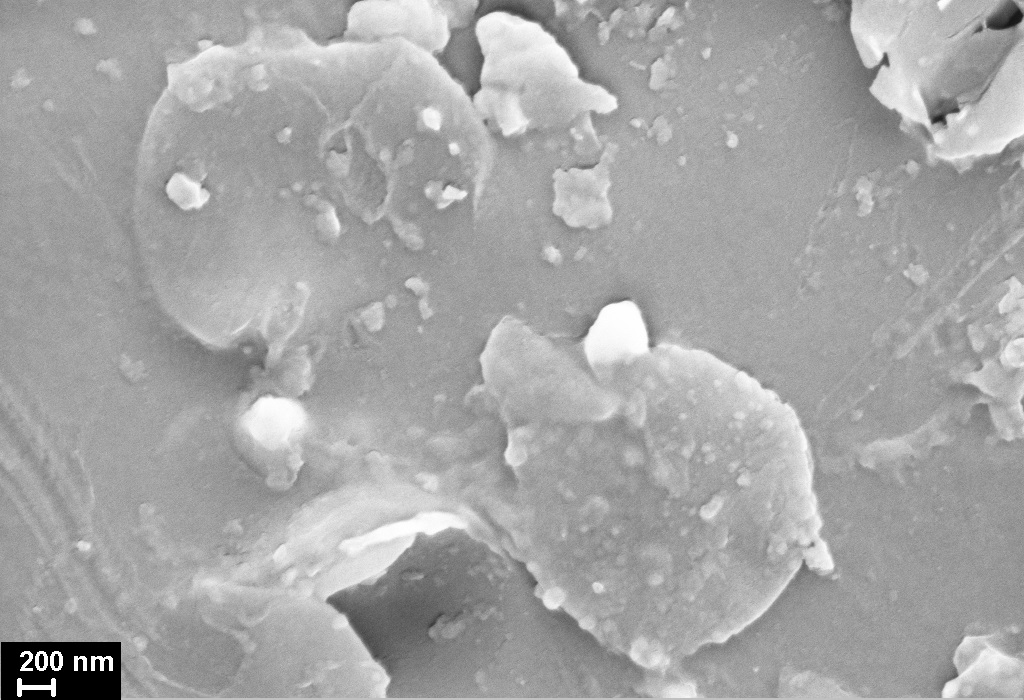
Impact of nanoparticles of various types as fillers on the stability of the poly(pyromellitimide)-based nanocomposite films’ properties in alkaline hydrolysis was studied. It was shown that the introduction of nanoparticles into the polymer can lead to an increase in excess free volume. This fact is evidenced by scanning electron microscopy and densitometric studies. The increase of the excess free volume was shown to provoke a rise of the diffusion intensity of the hydrolyzing agent in the films volume during their exposure to an alkaline medium. This effect leads to film swelling and, thereby, to increases of the intensity of the destructive action of hydrolysis on the material. Chemical surface pretreatment of the nanofiller allows one to obtain a composite with an increased packing density compared to that for a composite with unmodified nanoparticles. However, the hydrolytic stability of such a film still remains somewhat inferior to that of the pristine polyimide.
Keywords: polymer-inorganic nanocomposites, polyimides, hydrolysis, carbon nanoparticles, mechanical properties, thermal stability, packing
density.
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2019-10-6-666-673