Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2022, 13 (6), 632–639
Photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide produced by high-energy milling
Ekaterina A. Kozlova – Institute of Metallurgy, UB RAS, Yekaterinburg, 620016; Boreskov Institute of Catalysis, SB RAS, Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia; kozlova@catalysis.ru
Albina A. Valeeva – Institute of Solid State Chemistry, UB RAS, Yekaterinburg, 620108, Russia; anibla v@mail.ru
Anna A. Sushnikova – Institute of Metallurgy, UB RAS, Yekaterinburg, 620016, Russia; sushnikova.ann@gmail.com
Angelina V. Zhurenok – Boreskov Institute of Catalysis, SB RAS, Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia; angelinazhurenok@gmail.com
Andrey A. Rempel – Institute of Metallurgy, UB RAS, Yekaterinburg, 620016, Russia; rempel.imet@mail.ru
Corresponding author: Ekaterina A. Kozlova, kozlova@catalysis.ru
PACS 82.65.+r, 68.43.-h
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2022-13-6-632-639
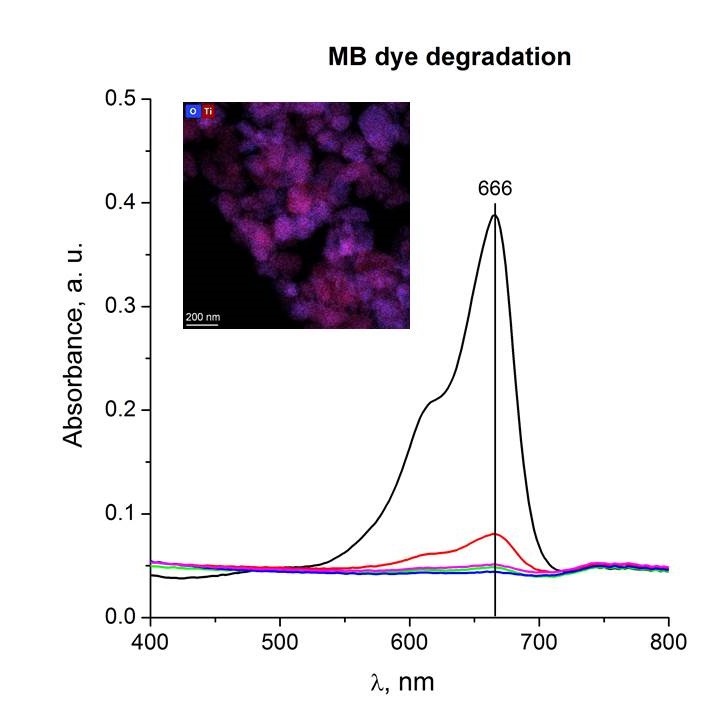
ABSTRACT In this work, photocatalysts based on titanium dioxide were synthesized by high-energy ball milling of commercial titanium dioxide in the anatase modification. Using a complex of physicochemical methods, including XRD, low-temperature nitrogen adsorption, XPS and TEM, it was shown that the milling of commercial anatase leads to phase transformations and the formation of several phases of titanium dioxide, namely the high-pressure phase, the monoclinic phase of anatase and rutile, except for in addition, there is a change in the crystalline size and the value of the specific surface area grows from 8 to 31 m2/g. It was found that defects are introduced into the system during ball milling. The photocatalysts obtained by milling showed an activity comparable to the commercial standard TiO2 Degussa P25 in the destruction of the methylene blue dye under the action of UV light, while the adsorption properties of the synthesized samples exceeded those of commercial P25.
KEYWORDS Titanium dioxide, high-energy ball milling, photocatalytic oxidation
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 21-73-20039. XPS and HRTEM investigations was performed using the facilities of the shared research center “National Center for the Investigation of Catalysts” at the Boreskov Institute of Catalysis. Authors thanks to I.D. Popov, A. A. Saraev, E.Yu. Gerasimov for DRS, XPS, and TEM experiments, respectively.
FOR CITATION Kozlova E.A., Valeeva A.A., Sushnikova A.A., Zhurenok A.V., Rempel A.A. Photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide produced by high-energy milling. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2022, 13 (6), 632–639.
[In Russian] Екатерина А. Козлова, Альбина А. Валеева, Анна А. Сушникова, Ангелина В. Журенок, Андрей А. Ремпель
Фотокаталитическая активность диоксида титана, полученного методом высокоэнергетического размола
АННОТАЦИЯ В данной работе фотокатализаторы на основе диоксида титана были синтезированы высокоэнергетическим размолом коммерческого TiO2 модификации анатаза. Характеризация образцов комплексом физико-химических методов, включая РФА, низкотемпературную адсорбцию азота, РФЭС и ПЭМ было показано, что размол анатаза приводит к фазовым превращениям и формированию нескольких фаз диоксида титана, в том числе фазы высокого давления, моноклинных фаз анатаза и рутила. Кроме того, были обнаружены изменения в размере кристаллитов и рост удельной поверхности образцов с 8 до 31 м2/г. Было показано, что размол приводит возникновению дефектов в структуре материалов. Фотокатализаторы, полученные методом размола, показали активность, сравнимую с коммерческим стандартом TiO2 Degussa P25, в фотокаталитической деструкции красителя метиленового синего под действием УФ-излучения, при этом, адсорбционные свойства синтезированных образцов были выше, чем у коммерческого P25.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА Диоксид титана, высокоэнергетический размол, фотокаталитическое окисление