Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2023, 14 (4), 454–466
Solution processed Ag-In-S nanoparticles as light adsorber in ZnO for photovoltaic application
K. Abinaya – London South Bank University, London, UK
P. Sharvanti – Research and Development, Saint Gobain, San Diego, California, USA
N. Rajeswari Yogamalar – Hindustan Institute of Technology and Science, Padur, Kelambakkam, Chennai, India; rajeswariyogamalar.n@gmail.com
Corresponding author: N. Rajeswari Yogamalar, rajeswariyogamalar.n@gmail.com
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2023-14-4-454-466
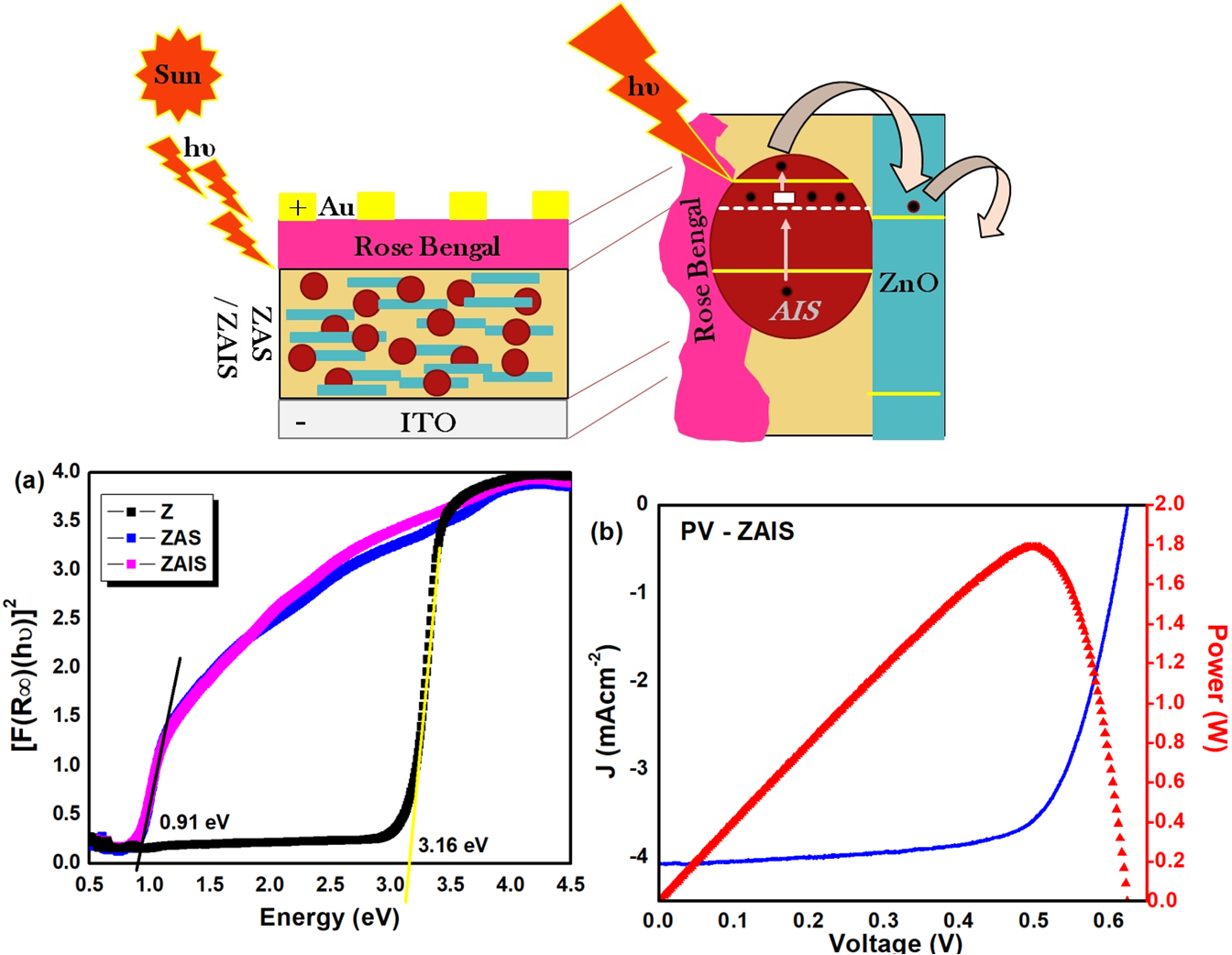
ABSTRACT Nano-sized indium incorporated silver sulphide (Ag-In-S) nanocomposites were synthesized by simple wet chemical method as an electron transport layer in zinc oxide (ZnO) for high efficient photovoltaic (PV) cell. The inclusion of high conductivity indium ions in Ag2S will improve the facile electron transfer and the assembled hetero-structure features the solar light harvesting in PV cell. The powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies confirmed the formation of indium incorporated Ag2S (AIS) nanocomposites and ZnO/AIS (ZAIS) compound nanocomposites crystallizing in pure monoclinic phase and mixed wurtzite hexagonal, monoclinic and tertiary phases respectively. The wide particle size distributions in ZAIS clearly revealed the adherence of AIS nanocomposites in ZnO lattice thus, promoting the light adsorption property. In addition, the tuning of the optical bandgap covering the entire solar spectrum (UV, visible, and infra-red regions), multiple-band electron transitions and hence, promoting the fast electron transportation are effectively achieved in ZAIS compound nanocomposites. With this simple positive approach, the PV cell efficiency is pushed forward with the In3+ metal ion incorporation however; enhanced, enriched solar cell efficiency can be later tuned up with the detailed optimization studies.
KEYWORDS Electron transport layer, nanocomposites, hetero-structure, nano-confinement, light adsorption.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We acknowledge Hindustan Institute of Technology and Science for the financial assistance through HITS Seed Money Grant 2023 SEED/CRC/HITS/2022-23/0013. We owe a deep sense of gratitude to Prof. Dr. R. Jayavel, Former Dean, ACT campus and all the research scholars, Centre for Nanoscience and Technology, Anna University, Chennai for ensuring the facilities and instruments available in the laboratory.
FOR CITATION Abinaya K., Sharvanti P., N. Rajeswari Yogamalar Solution processed Ag-In-S nanoparticles as light adsorber in ZnO for photovoltaic application. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2023, 14 (4), 454–466.
[In Russian] К. Абинайя, П. Шарванти, Н. Раджешвари Йогамалар
Наночастицы в системе Ag-In-S, полученные методом осаждения, в качестве адсорбера света в ZnO для фотоэлектрических приложений
АННОТАЦИЯ Наноразмерные нанокомпозиты с сульфидом серебра (Ag-In-S) с включением индия были синтезированы простым мокрым химическим методом в качестве слоя переноса электронов в оксиде цинка (ZnO) для высокоэффективных фотоэлектрических (ФЭ) элементов. Включение ионов индия с высокой проводимостью в Ag2S улучшит легкий перенос электронов, а собранная гетероструктура обеспечит сбор солнечного света в фотоэлектрических элементах. Исследования порошковой рентгеновской дифракции (XRD) подтвердили образование нанокомпозитов Ag2S с включением индия (AIS) и нанокомпозитов (ZAIS) состоящих из ZnO и AIS, кристаллизующихся в чистой моноклинной фазе и смешанной гексагональной, моноклинной и фазах вюрцита. Широкое распределение частиц по размерам в ZAIS показало срастание нанокомпозитов AIS с решеткой ZnO, тем самым способствуя повышению светоадсорбционных характеристик. Кроме того, в составных нанокомпозитах ZAIS эффективно достигаются перестройка оптической запрещенной зоны, охватывающая весь солнечный спектр (УФ, видимую и инфракрасную области), многозонные электронные переходы и, следовательно, содействие транспортировке быстрых электронов. При таком простом положительном подходе, однако, эффективность фотоэлектрических элементов повышается за счет включения ионов металла In3+; дальнейшее повышение эффективности солнечных элементов может быть реализовано путем оптимизации процессов синтеза.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА электронно-транспортный слой, нанокомпозиты, гетероструктура, наноразмерная устойчивость, адсорбция света.