Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (2), 255–259
Numerical model of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity in M1-xRxF2+x heterovalent solid solution nanocomposites where M stands for alkaline-earth metals and R for rare-earth metals
Pavel A. Popov – Petrovsky Bryansk State University, Bryansk, Russia
Alexander V. Shchelokov – Petrovsky Bryansk State University, Bryansk, Russia
Pavel P. Fedorov – Prokhorov General Physics Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia; ppfedorov@yandex.ru
Corresponding author: Pavel P. Fedorov, ppfedorov@yandex.ru
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2024-15-2-255-259
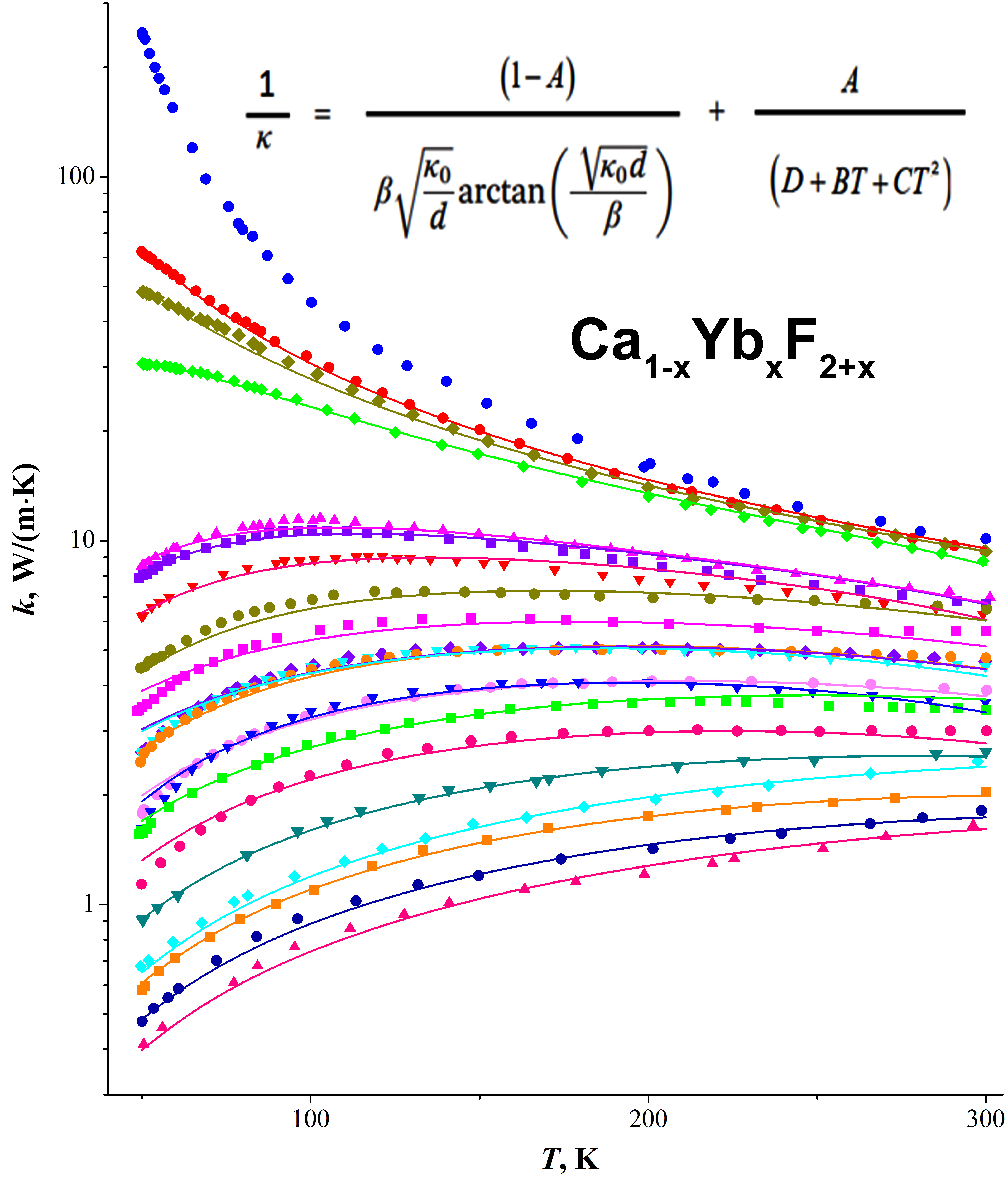
ABSTRACT We propose a mathematical model to fit the temperature-dependent thermal conductivity of M1-xRxF2+x heterovalent solid solutions where M stands for alkaline-earth metals and R for rare-earth metals. These solid solutions experience composition-driven transition from the crystal-like to glass-like behavior of thermal conductivity. When tested on Ca1-xYbxF2+x solid solutions, the model showed a potential for use with an option for further improvements.
KEYWORDS thermal conductivity, thermal resistance, temperature dependence, solid solution, mathematical model
FOR CITATION P. A. Popov, A. V. Shchelokov, P. P. Fedorov Numerical model of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity in M1-xRxF2+x heterovalent solid solution nanocomposites where M stands for alkaline-earth metals and R for rare-earth metals . Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (2), 255–259.
[In Russian] П.А. Попов, А.В. Щелоков, П.П. Федоров
Расчетная модель температурной зависимости теплопроводности нанокомпозитов – гетеровалентных твердых растворов M1-xRxF2+x, где М – щелочноземельные, R – редкоземельные элементы
УДК 661.48 + 546.161
АННОТАЦИЯ Предлагается математическое выражение для описания температурной зависимости теплопроводности гетеровалентных твердых растворов M1-xRxF2+x, где М – щелочноземельные, R -редкоземельные элементы в, демонстрирующих концентрационный переход теплопроводности от кристаллической к стеклоподобной. Апробация на примере твердого раствора Ca1-xYbxF2+x показывает перспективность предлагаемой модели с возможностью улучшающих модификаций.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА теплопроводность, тепловое сопротивление, температурная зависимость, твердый раствор, математическая модель.