NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2019, 10 (6), P. 711–719
A comparative study of the effect of solvents on the optical, structural and morphological properties of ZnO–GO nanocomposites synthesized by sol-gel method
Sudha Maurya – Department of Nanotechnology, Christian College of Engineering and Technology, Bhilai, Durg, Chhattisgarh, India; sudhamaurya1911@gmail.com
Sandhya Pillai – Department of Nanotechnology, Christian College of Engineering and Technology, Bhilai, Durg, Chhattisgarh, India
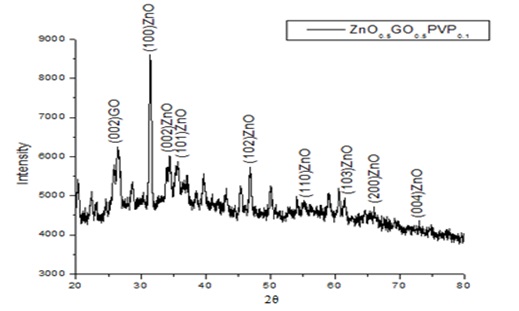
Zinc Oxide-Graphene Oxide (ZnO–GO) nanocomposites were prepared using solvents polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and N-Methyl-2 Pyrrolidone (NMP) by sol-gel technique and their optical, structural and morphological properties were investigated. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) studies show the presence of planes of GO and ZnO confirming the formation of composites. The particle sizes were calculated using Scherrer’s formula and were found to be in the nanometer range. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images show the formation of layered structures dispersed non-uniformly over clusters of particles. Energy Dispersive X-Ray (EDX) spectra confirm the presence of carbon, zinc and oxygen in the composites. The optical absorbance of ZnO–GO synthesized using PVP was higher than ZnO–GO with NMP with the absorption edge shifting to shorter wavelength in the presence of NMP. The band gap values were found to be in the range of 2.7–3.0 eV. The band gap of ZnO–GO synthesized using NMP was higher than ZnO–GO synthesized using PVP.
Keywords: GO, ZnO, ZnO–GO Nanocomposite, PVP, NMP.
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2019-10-6-711-719