NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2020, 11 (1), P. 78–85
Comparative assessment of antibacterial efficacy for cobalt nanoparticles, bulk cobalt and standard antibiotics: A concentration dependant study
V. Gupta – Department of Chemistry, University of Jammu, J&K, India; vijayta1gupta@gmail.com
V. Kant – Department of Veterinary Pharmacology & Toxicology, LUVAS, Hisar, India
A. K. Sharma – Department of Chemistry, University of Jammu, J&K, India
M. Sharma – Department of Chemistry, University of Jammu, J&K, India
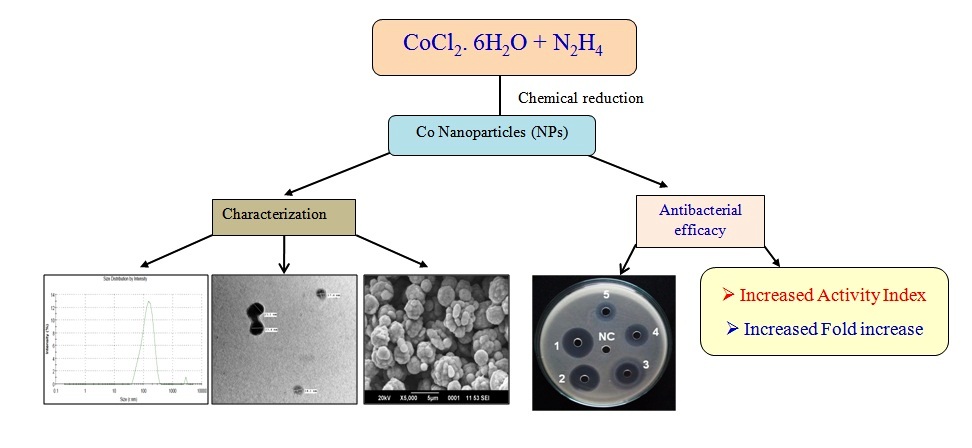
Synthesis of compounds that can prevent bacterial resistance is of huge interest and gaining immense popularity. Cobalt (Co) is one of the cheaper transition metals and its nano form has not been studied in details for antibacterial actions. Comparative analysis of Co nanoparticles with bulk Co and standard antibacterials are also lacking. In our study, concentration dependent action of Co nanoparticles was observed from 0.125 to 128.0 μg/ml against S. aureus and E. coli. Zone of inhibition of Co nanoparticles was better against E. coli than S. aureus. Co nanoparticles were markedly betterthan bulk Co, oxytetracycline and gentamicin. Activity index and fold increase of Co nanoparticles were higher at most of the concentrations. In conclusion, Co nanoparticles showed better antibacterial action than other tested compounds against S. aureus and E. coli particularly at lower concentrations, and their use may be extended in different biomedical fields in future.
Keywords: Cobalt nanoparticles, S. aureus, E. coli, antibacterial activity, activity index, fold increase.
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2020-11-1-78-85