NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2020, 11 (2), P. 246–251
Influence of hydrothermal synthesis conditions on the composition of the pyrochlore phase in the Bi2O3–Fe2O3–WO3 system
M. S. Lomakin – Ioffe Institute; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, 26, Moskovsky pr, 190013, St. Petersburg, Russia; lomakinmakariy@gmail.com
O.V. Proskurina – Ioffe Institute; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, 26, Moskovsky pr, 190013, St. Petersburg, Russia
V.V. Gusarov – Ioffe Institute, 26, Politekhnicheskaya St., 194021, St. Petersburg, Russia
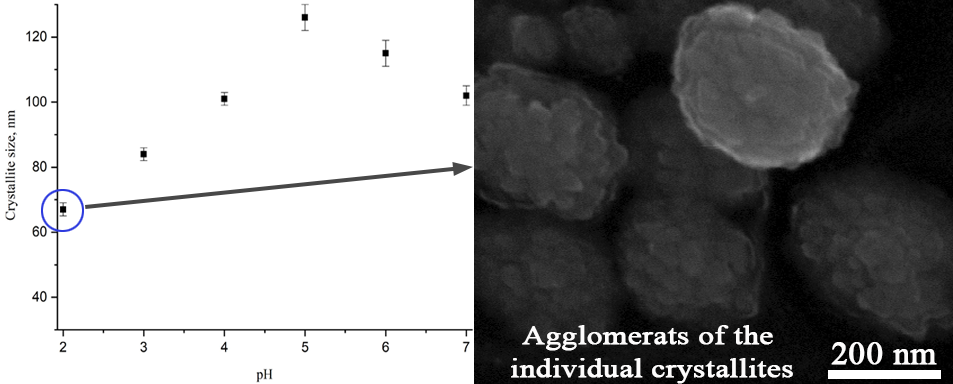
The paper deals with a study of the effect which the hydrothermal fluid pH has on the formation of a pyrochlore-structured phase in the Bi2O3–Fe2O3–WO3 system. It was shown that at pH of 1 and 8, the formation of pyrochlore-structured phase particles with crystallite sizes of 38 and 118 nm, respectively, is accompanied by the formation of the Bi2WO6 compound with the Aurivillius phase structure. At pH values from 2 to 7, only pyrochlore-structured nanocrystalline particles with a variable composition are formed. Under these conditions, the dependence of the average size of crystallites of the pyrochlore-structured phase particles on pH is extreme, as the size increases from ~67 nm at pH 2 up to ~126 nm at pH 5 and then decreases to ~102 nm at pH 7. The samples obtained at pH 3–4 have a composition that is the closest to that specified for the synthesis. When pH increases up to 10, there forms a non-single-phase product that contains the Bi2WO6 phase and δ-Bi2O3-based phase.
Keywords: hydrothermal synthesis, pyrochlore phase, nanocrystals, crystallite size.
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2020-11-2-246-251