NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2020, 11 (5), P. 578–589
High sensitive room temperature ammonia sensor based on dopant free m-WO3 nanoparticles: Effect of calcination temperature
M. S. Duraisami – PG & Research Department of Physics, Poompuhar College (Autonomous), Melaiyur – 609107, Tamilnadu, India; Affiliated to Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli; tharmamithran@gmail.com
K. Parasuraman – PG & Research Department of Physics, Poompuhar College (Autonomous), Melaiyur – 609107, Tamilnadu, India; Affiliated to Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli
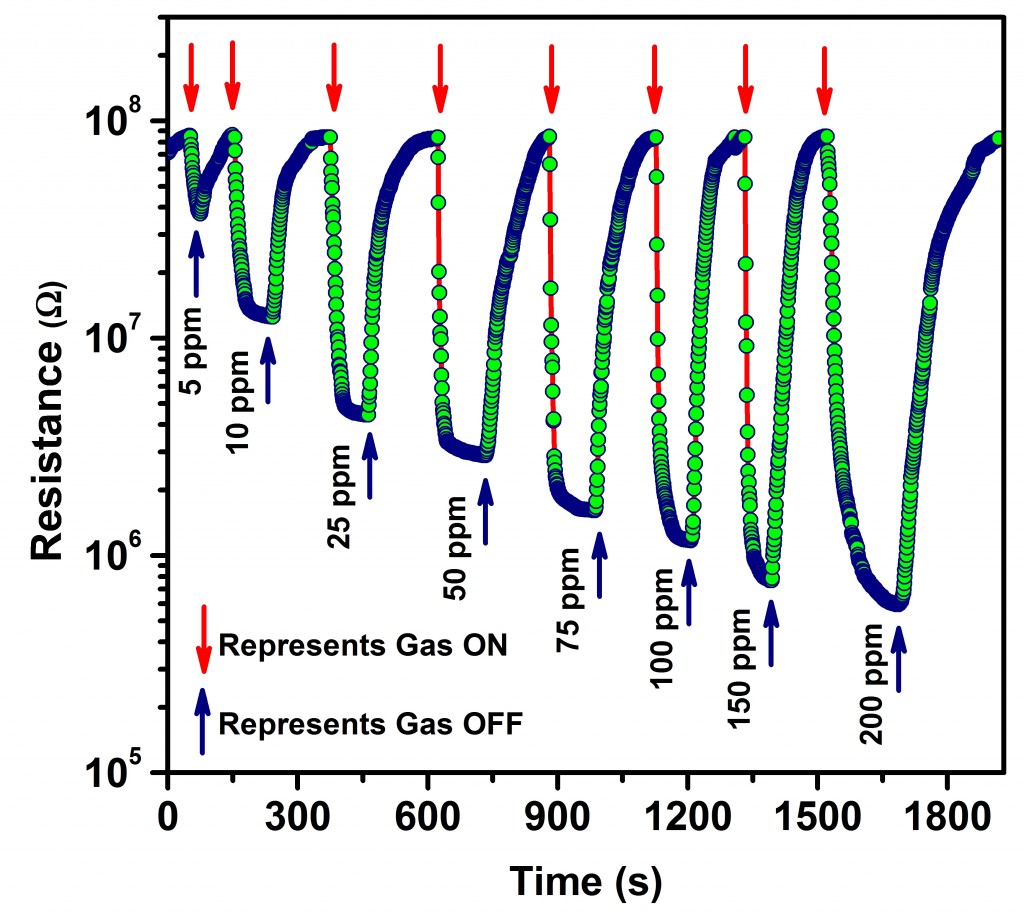
In this article, monoclinic tungsten tri-oxide (m-WO3) nanoparticles (hereafter NPs) were prepared by facile precipitation method and they were successfully examined as gas sensing materials for monitoring gaseous ammonia at room temperature have been reported. The effect of calcination temperature on structural and morphological properties of the prepared samples were also investigated. Physicochemical properties of the samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, XPS, UV-Vis and PL analysis. XRD studies confirmed the monoclinic structure of the prepared NPs. Optical studies disclosed that the obtained samples were having wider optical band gaps ranging from 2.48 to 2.76 eV. Sensing signatures such as selectivity, transient response along with performance indicators like repeatability and stability have also been investigated. Invitingly, the sample calcined at 823 K exhibited highly improved sensing response of 142 towards 200 ppm of ammonia with rapid response/recovery time of 26 / 79 s.
Keywords: ammonia sensor, tungsten trioxide, nanoparticles, calcination, precipitation.
PACS 07.07.Df, 81.07.b, 61.46-w, 61.46.Hk, 61.72Uj,61.82.Rx
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2020-11-5-578-589