Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2022, 13 (3), 342–348
Evaluation of antibacterial potential of bilirubin nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli
Dhaval J. Kamothi – Department of Veterinary Pharmacology & Toxicology, COVS, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Hisar, Haryana, India
Vinay Kant – Department of Veterinary Pharmacology & Toxicology, COVS, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Hisar, Haryana, India; drvinaykantluvas@gmail.com
Vinod Kumar – Department of Veterinary Pharmacology & Toxicology, COVS, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Hisar, Haryana, India
Vinay G. Joshi – Department of Animal Biotechnology, COVS, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Hisar, Haryana, India
Rajesh Chhabra – College Central Laboratory, COVS, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Hisar, Haryana, India
Corresponding author: Vinay Kant, drvinaykantluvas@gmail.com
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2022-13-3-342-348
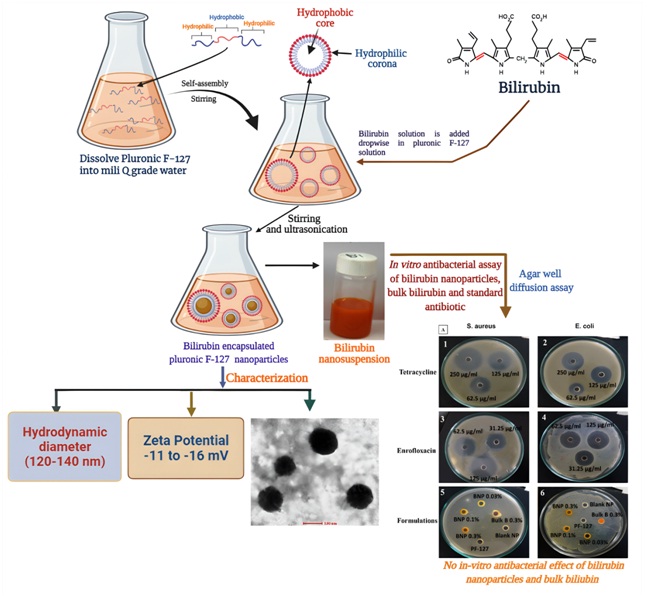
ABSTRACT Antimicrobial resistance is a major emerging clinical and public health issue across the globe. Nanotechnology is an emerging field and developing area of scientific interest in the world. Earlier reports showed in vivo antibacterial activity of bilirubin. Therefore, in present study, bilirubin nanoparticles (BNP) were synthesized of ~100 – 150 nm, spherical shape and negative charge. Antibacterial activity of BNPs at different concentrations (0.03, 0.1 and 0.3 %) was evaluated by agar well diffusion method against the gram-positive i.e. S. aureus and gram-negative i.e. E. coli bacteria. Tetracycline and enrofloxacin used as positive control. Tetracycline and Enrofloxacin at different concentrations exhibited zones of inhibition against both S. aureus and E. coli. However, BNPs as well as bulk bilirubin showed no in vitro antibacterial effect on S. aureus and E. coli, however, testing by broth method and at higher concentration as well as against other microorganisms can be explored in future.
KEYWORDS Bilirubin nanoparticles, S. aureus, E. coli, antibacterial activity
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS All the authors are highly thankful to the administration of Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences (LUVAS), Hisar, Haryana, India for providing essential facilities and support for carrying out present study. We also acknowledge the support of SAIF, AIIMS, New Delhi for providing the facilities for TEM studies.
FOR CITATION Kamothi D. J., Kant V., Kumar V., Joshi V. G., Chhabra R. Evaluation of antibacterial potential of bilirubin nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2022, 13 (3), 342–348.
[In Russian] Д.Дж. Камоти, В. Кант, В. Кумар, В.Г. Джоши, Р. Чабра
Оценка антибактериального потенциала наночастиц билирубина в отношении золотистого стафилококка и кишечной палочки
АННОТАЦИЯ Устойчивость к противомикробным препаратам является серьезной новой клинической проблемой общественного здравоохранения во всем мире. Нанотехнология – новая развивающаяся областью научных интересов в мире. Более ранние сообщения показали антибактериальную активность билирубина in vivo. Поэтому в настоящем исследовании были синтезированы наночастицы билирубина (БНЧ) размером ~100 – 150 нм, сферической формы и с отрицательным зарядом. Антибактериальную активность БНЧ в различных концентрациях (0.03, 0.1 и 0.3 %) оценивали методом диффузии в лунки агара в отношении золотистого стафилококка и кишечной палочки. Тетрациклин и энрофлоксацин использовали в качестве сравнения. Тетрациклин и энрофлоксацин в различных концентрациях проявляли зоны ингибирования как против золотистого стафилококка, так и против кишечной палочки. БНЧ, а также общий билирубин не показали антибактериального действия in vitro ни на золотистый стафилококк, ни на кишечную палочку, однако в будущем могут быть изучены испытания бульонным методом и в более высоких концентрациях, а также в отношении других микроорганизмов.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА наночастицы билирубина, золотистый стафилококк, кишечная палочка.