Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2022, 13 (6), 640–648
The characteristics of TiO2 anatase from tulungagung sand as an antibacterial material
L. Rohmawati – Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Ketintang, Gayungan, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia
Istiqomah – Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Negeri Malang, Semarang 5, Malang 65145, Indonesia
A. A. Pratama – Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Ketintang, Gayungan, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia
W. Setyarsih – Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Ketintang, Gayungan, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia
N. P. Putri – Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Ketintang, Gayungan, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia
Munasir – Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Negeri Surabaya, Ketintang, Gayungan, Surabaya 60231, Indonesia
Darminto – Physics Department, Faculty of Science and Data Analytics, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember (ITS), Keputih, Sukolilo, Surabaya 60111, Indonesia
Corresponding author: L. Rohmawati, lydiarohmawati@unesa.ac.id
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2022-13-6-640-648
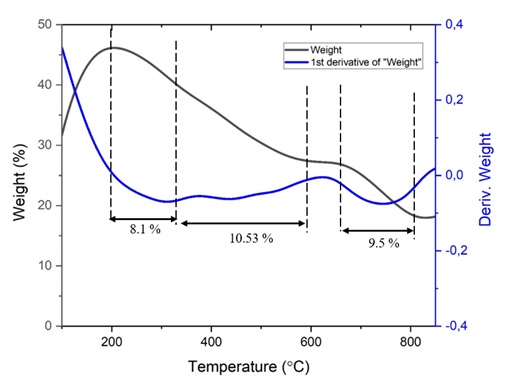
ABSTRACT TiO2 anatase is a material that has good photocatalytic properties. The synthesis of TiO2 anatase from Tulungagung natural sand used the leaching method. The synthesized samples were characterized by TGA, XRD, FTIR, BET, SEM, UV-DRS and tested for antibacterial effect. In this study, the TiO2 anatase phase was already formed and experiencing three stages of weight loss. It had stretching vibration of the OH group, had a bending mode of water Ti–OH, and Ti–O–Ti at wavenumbers 4000 to 400 cm-1. It also had a mesoporous size, was spherical with a grain size of 58 nm and had an energy gap of 3.42 eV. TiO2 anatase with a 600 μg/mL concentration could reduce Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria. Therefore, TiO2 anatase has the potential in an antibacterial agent.
KEYWORDS TiO2 anatase, natural sand, antibacterial
FOR CITATION Rohmawati L., Istiqomah, Pratama A.A., Setyarsih W., Putri N.P., Munasir, Darminto The characteristics of TiO2 anatase from tulungagung sand as an antibacterial material. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2022, 13 (6), 640–648.
[In Russian] Л. Рохмавати, Истикомах, А.А. Пратама, В. Сетьярсих, Н.П. Путри, Мунасир, Дарминто
Характеристики анатаза TiO2 из песка Тулунгагунг как антибактериального материала
АННОТАЦИЯ Анатаз TiO2 является материалом, обладающим хорошими фотокаталитическими свойствами. Для синтеза анатаза TiO2 из природного песка Тулунгагунг использовали метод выщелачивания. Синтезированные образцы были охарактеризованы методами TGA, XRD, FTIR, BET, SEM, UV-DRS и протестированы на антибактериальное действие. В этом исследовании фаза анатаза TiO2 уже сформировалась и испытывает три стадии потери массы. По данным ИК-спектроскопии фиксировались валентное колебание группы ОН, деформационная мода воды Ti-OH и Ti-O-Ti при волновых числах от 4000 до 400 см-1. Полученный TiO2 представлял собой мезопористый материал, сферическую форму с размером кристаллитов 58 нм и ширину запрещенной зоны 3.42 эВ. Суспензия анатаз TiO2 с концентрацией 600 мкг/мл может уменьшить количество бактерий Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus и Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Таким образом, анатаз TiO2 имеет потенциал в качестве антибактериального агента.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА анатаз TiO2, природный песок, антибактериальный