Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2023, 14 (3), 372–379
Stable hydrosol prepared by deaggregation from laser synthesis nanodiamond
Aleksandr E. Aleksenskii – Division of Solid State Electronics, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; ORCID 0000-0002-5004-6993
Marina V. Baidakova – Division of Solid State Electronics, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; ORCID 0000-0002-5524-7233
Andrey D. Trofimuk – Division of Solid State Electronics, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; ORCID 0000-0003-3140-0245
Biligma B. Tudupova – Division of Solid State Electronics, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; ORCID 0000-0002-7655-294X
Anastasia S. Chizhikova – Division of Solid State Electronics, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; ORCID 0000-0002-5524-7233
Aleksandr V. Shvidchenko – Division of Solid State Electronics, Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; ORCID 0000-0002-5417-7472
Corresponding author: Aleksandr E. Aleksenskii, blin@mail.ioffe.ru
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2023-14-3-372-379
PACS 82.70.Dd, 76.30.-v
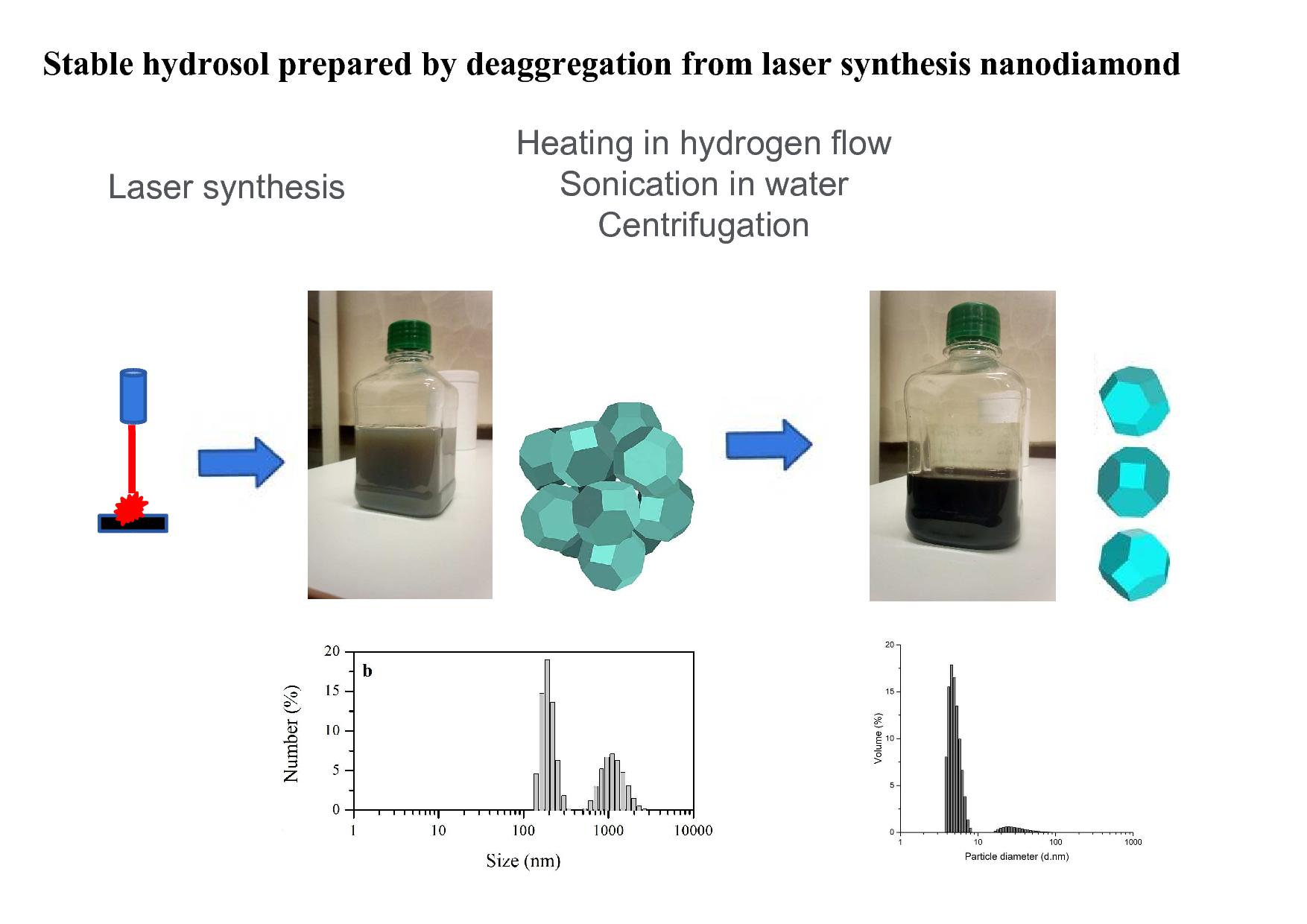
ABSTRACT The new applications of nanodiamond in biology and nuclear physics require the use of products with a low content of impurities. One of the possible methods for obtaining a high-purity nanodiamond is the recently developed laser synthesis method. The aim of this work was to study the state of aggregation of laser synthesis nanodiamond particles in aqueous suspensions and to test the possibility of deaggregation of laser nanodiamond. The process of deaggregation of a laser synthesis nanodiamond is investigated. It was shown that the previously described process of deaggregation by milling with baking soda and the usual process of deaggregation give almost the same results. A solid phase from a colloidal solution of a laser synthesis nanodiamond has been isolated and investigated. The low content of impurities in the studied product was
confirmed (less than 0.1% at.), the Raman, IR, and EPR spectra were studied.
KEYWORDS nanodiamonds, nanoparticles, optical properties, surface groups, EPR
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thanks O. Levinson and B. Zusman (Ray Techniques Ltd, Jerusalem, Israel) for providing the source material (LND) for this research. X-ray diffraction patterns were obtained on the equipment of the Joint Research Center “Material science and characterization in advanced technology” (Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia). EDS measurements were performed using equipment of Engineering Center of St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology. Authors sincerely thank D. P. Danilovich for the extremely useful help in carrying out measurements and comprehensive methodological assistance and A.Ya Vul for useful discussion and support of the research. This research was carried out in the frame of the Government Topical Program for Ioffe Institute (project FFUG-2022-0012).
FOR CITATION Aleksenskii A.E., Baidakova M.V., Trofimuk A.D, Tudupova B.B., Chizhikova A.S., Shvidchenko A.V. Stable hydrosol prepared by deaggregation from laser synthesis nanodiamond. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2023, 14 (3), 372–379.
[In Russian] Алексенский А.Е., Байдакова М.В., Трофимук А.Д., Тудупова Б.Б., Чижикова А.С., Швидченко А.В.
Получение и свойства деагломерированного золя наноалмаза лазерного синтеза
УДК 544.77.051.2
АННОТАЦИЯ В настоящее время активно исследуются возможности использования наноалмазов в биологии и ядерной физике. Эти области применения требуют использования продуктов с низким содержанием примесей. Одним из возможных методов получения наноалмаза высокой чистоты является недавно разработанный метод лазерного синтеза. Целью данной работы было изучение агрегатного состояния частиц наноалмаза лазерного синтеза в водных суспензиях и проверка возможности дезагрегации лазерного наноалмаза без использования дополнительных реагентов, являющихся потенциальными загрязнителями. Исследован процесс дезагрегации наноалмаза лазерного синтеза. Было показано, что описанный ранее процесс деагрегации путем измельчения с пищевой содой и обычный процесс деагрегации без использования каких-либо добавок дают почти одинаковые результаты. Выделена и исследована твердая фаза из коллоидного раствора наноалмаза лазерного синтеза. Было подтверждено низкое содержание примесей в исследуемом продукте (менее 0,1% ат.), изучены спектры комбинационного рассеяния света, ИК и ЭПР.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА наноалмазы, наночастицы, оптические свойства, поверхностные группы, ЭПР