Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (2), 240–254
Pyrochlore phase in the Bi2O3-Fe2O3-WO3-(H2O) system: its stability field in the low-temperature region of the phase diagram and thermal stability
Makariy S. Lomakin – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg; St. Petersburg Electrotechnical University “LETI”, St. Petersburg, Russia; lomakinmakariy@gmail.com
Olga V. Proskurina – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, St. Petersburg, Russia; proskurinaov@mail.ru
Aleksandr A. Levin – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; aleksandr.a.levin@mail.ioffe.ru
Vladimir N. Nevedomskiy – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; nevedom@mail.ioffe.ru
Corresponding author: M. S. Lomakin, lomakinmakariy@gmail.com
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2024-15-2-240-254
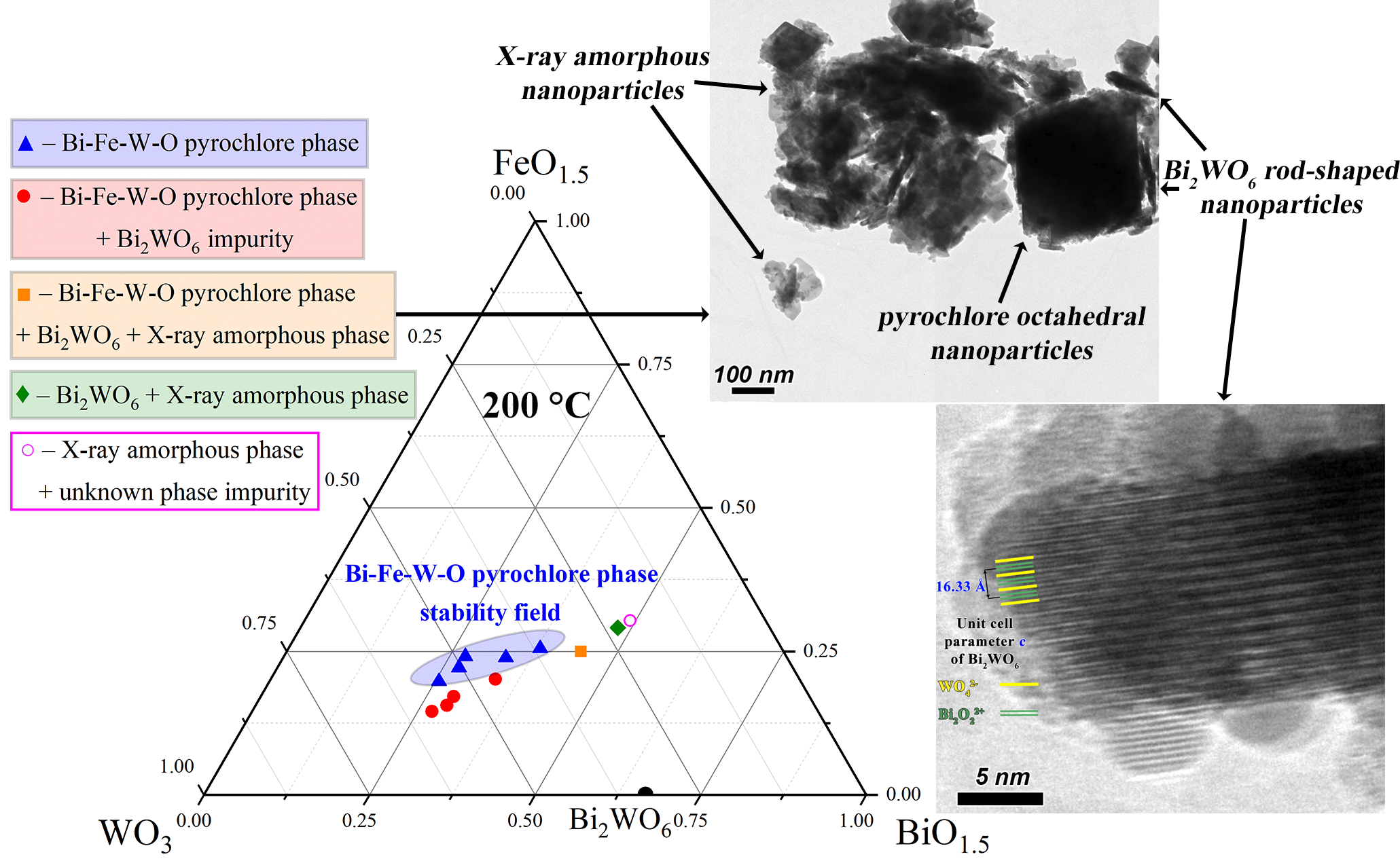
ABSTRACT The concentration stability field localization of the pyrochlore-structured compounds of variable composition formed in the Bi2O3-Fe2O3-WO3 system under hydrothermal conditions at a temperature of T = 200 °C and a pressure of P = 7 MPa was determined. It was found that the pyrochlore-structured compounds stability field is longitudinally limited within the atomic ratios 0.47 < Bi/W < 1.25, and in the transverse direction within 1.14 < Bi/Fe < 1.87. It was shown that the pyrochlore phase cubic unit cell parameter a depends on the compound chemical composition as follows: it increases linearly from ∼ 10.3319 Å to ∼ 10.4199 Å with an increase in the Bi/W atomic ratio from ∼ 0.47 to ∼ 1.25. It was established that from the Bi2O3–WO3 system side, there is a region of two-phase equilibrium, in which a pyrochlore phase of variable composition coexists with the Bi2WO6 compound, which is formed in the form of plate-like (thickness h ∼ 50–100 nm) nanoparticles. It was shown that from the Bi2O3–Fe2O3 system side, there is a region of compositions, in which the pyrochlore phase of the most enriched in bismuth oxide composition coexists with the Bi2WO6 compound, which is formed in the form of rod-shaped (h ∼ 10–30 nm) nanoparticles, and with the X-ray amorphous phase composition, formed in the form of nanocrystalline particles about 10 nm in size. It was found that the higher temperature point of the pyrochlore-structured compounds stability field does not exceed 725 °C, which allows them to be synthesized only by “soft chemistry” methods.
KEYWORDS pyrochlore-structured phase, hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure, phase diagram, thermal stability
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS XRD, SEM and EDXMA studies were performed employing the equipment of the Engineering Center of the St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology (Technical University). TEM studies and the analysis of XRD data have been carried out using the equipment and software of the Joint Research Center “Materials science and characterization in advanced technology” (Ioffe Institute). DSC/TG studies were performed employing the equipment of the First All-Russian Engineering Center for Molecular Layering Technology (St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology (Technical University)). HTXRD studies have been carried out using the equipment of the Center for X-Ray Diffraction Studies of the Research Park of St. Petersburg State University. The authors express their deep gratitude to Corr. Mem. RAS Victor Vladimirovich Gusarov for valuable comments and advice on improving the quality of the manuscript. The work was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Project No. 20-63-47016).
FOR CITATION Lomakin M.S., Proskurina O.V., Levin A.A., Nevedomskiy V.N. Pyrochlore phase in the Bi3O2-Fe2O3-WO3-(H2O) system: its stability field in the low-temperature region of the phase diagram and thermal stability. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (2), 240–254.
[In Russian] М.С. Ломакин, О.В. Проскурина, А.А. Левин, В.Н. Неведомский
Фаза пирохлора в системе Bi2O3-Fe2O3-WO3-(H2O): поле устойчивости в низкотемпературной области фазовой диаграммы и термическая устойчивость
АННОТАЦИЯ Определено положение концентрационной области устойчивости соединений переменного состава со структурой пирохлора, формирующихся в системе Bi3O2-Fe2O3-WO3 в гидротермальных условиях при температуре T = 200 °C и давлении P = 7 МПа. Установлено, что область устойчивости фазы пирохлора в продольном направлении ограничена в пределах атомных соотношений 0.47 < Bi/W < 1.25, а в поперечном направлении в пределах 1.14 < Bi/Fe < 1.87. Показано, что параметр a кубической элементарной ячейки фазы пирохлора зависит от химического состава соединения следующим образом: линейно возрастает от ~ 10.3319 Å до ~ 10.4199 Å с увеличением атомного соотношения Bi/W от ~ 0.47 до ~ 1.25. Установлено, что со стороны системы Bi2O3-WO3 имеется область двухфазного равновесия, в которой фаза пирохлора переменного состава сосуществует с соединением Bi2WO6, формирующемся в виде пластинчатых (толщиной h ~ 50‒100 нм) наночастиц. Показано, что со стороны системы Bi2O3-Fe2O3 имеется область составов, в которой фаза пирохлора наиболее обогащённого по оксиду висмута состава сосуществует с соединением Bi2WO6, формирующемся в виде стержневидных (h ~ 10‒30 нм) наночастиц, и с рентгеноаморфной фазой, формирующейся в виде нанокристаллических частиц размером около 10 нм. Показано, что верхний температурный предел области устойчивости полученных соединений со структурой пирохлора не превышает 725 °C, что позволяет синтезировать их только методами «мягкой химии».
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА Фаза со структурой пирохлора, гидротермальный синтез, кристаллическая структура, фазовые диаграммы, термическая устойчивость