Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (3), 369–379
Magnetic and photocatalytic properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles formed during the heat treatment of hydroxides coprecipitated in a microreactor with intense swirling flows
Olga V. Proskurina – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, St. Petersburg, Russia; proskurinaov@mail.ru
Ksenia I. Babich – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, St. Petersburg, Russia; babich3111@gmail.com
Sofia M. Tikhanova – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, St. Petersburg, Russia; tihanova.sof@gmail.com
Kirill D. Martinson – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, St. Petersburg, Russia; martinsonkirill@mail.ru
Vladimir N. Nevedomskiy – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; nevedom@mail.ioffe.ru
Valentin G. Semenov – St. Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg, Russia; val_sem@mail.ru
Rufat Sh. Abiev – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg; St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology, St. Petersburg, Russia; abiev.rufat@gmail.com
Victor V. Gusarov – Ioffe Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia; victor.v.gusarov@gmail.com
Corresponding author: O. V. Proskurina, proskurinaov@mail.ru
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2024-15-3-369-379
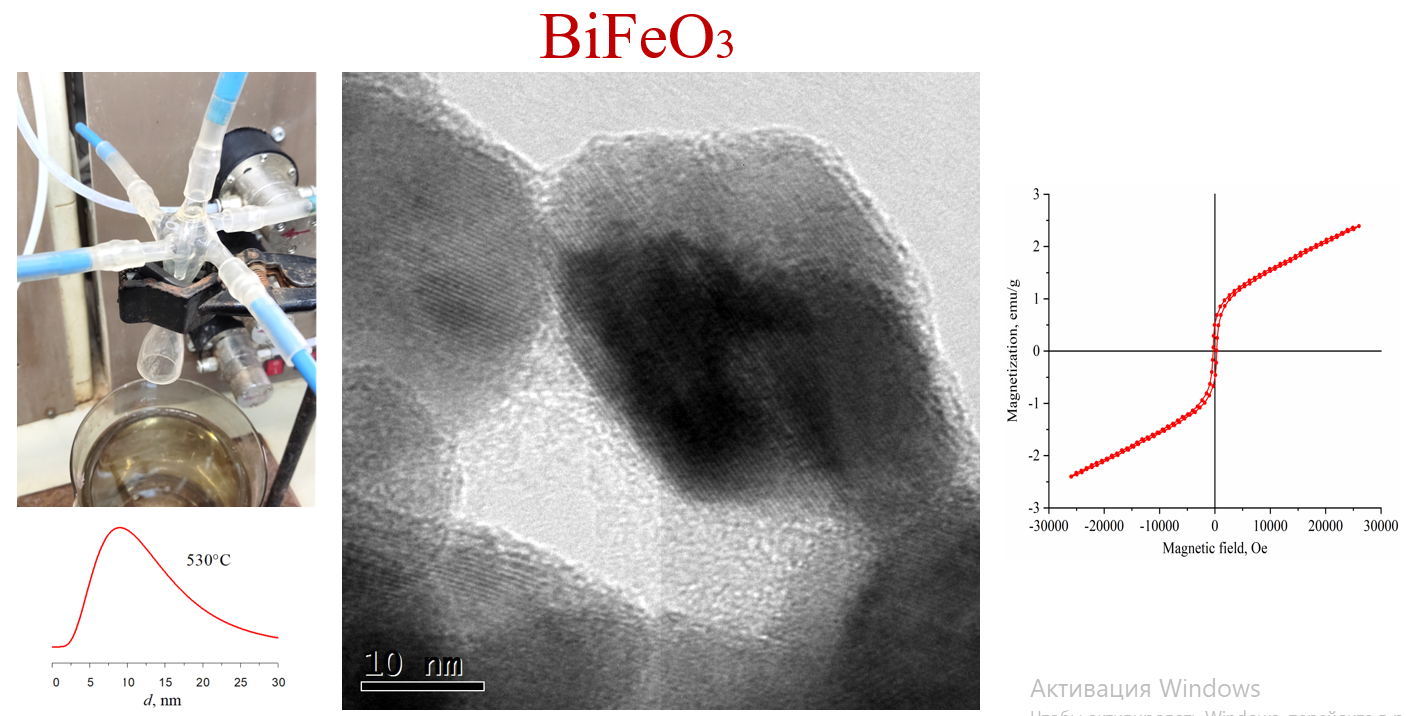
ABSTRACT In this work, hydroxide deposition in a microreactor with intensively swirling flows was used to obtain BiFeO3, followed by heat treatment of co-precipitated bismuth and iron hydroxides. The study of the formation of nanocrystalline bismuth orthoferrite was carried out using a set of methods: EDXMA, TEM, XRD, 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy, DRS, etc. The photocatalytic activity and magnetic characteristics of the material were determined. It is shown that during heat treatment of hydroxide precipitation for 1 minute at a temperature of 530 °, BiFeO3 nanocrystals with an average crystallite size of 14±7 nm are formed. It was found that the resulting BiFeO3 nanopowder is represented by agglomerates of individual nanoparticles. The saturation magnetization and residual magnetization values of these bismuth orthoferrite nanoparticles are 2.31 and 0.48 emu/g, respectively. According to the DRS results, band gap energy for the samples calculated at 530, 515, and 500 °C were 1.82, 1.86, and 1.91 eV, respectively, which ensures strong absorption of visible light by the samples. The sample showed higher photocatalytic activity in the X-ray amorphous state compared with nanocrystalline BiFeO3 in the process of Fenton-like discoloration of methyl violet under the action of visible light with reaction rate constants of the pseudo-first order 0.0256 and 0.0072 min-1, respectively.
KEYWORDS microreactor with intensively swirling flows, nanocrystals, nanoparticles, bismuth ferrite, photocatalysis, Fenton-like reactions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS EDXMA and X-ray diffraction studies were performed employing the equipment of the Engineering Center of the St. Petersburg State Institute of Technology. TEM characterization was performed using equipment owned by the Federal Joint Research Center “Material science and characterization in advanced technology”. The work was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Project No.
20-63-47016).
FOR CITATION Proskurina O.V., Babich K.I., Tikhanova S.M., Martinson K.D., Nevedomskiy V.N., Semenov V.G., Abiev R.Sh., Gusarov V.V. Magnetic and photocatalytic properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles formed during the heat treatment of hydroxides coprecipitated in a microreactor with intense swirling flows. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (3), 369–379.
[In Russian] О.В.Проскурина, К.И.Бабич, С.М.Тиханова, К.Д.Мартинсон, В.Н.Неведомский, В.Г.Семенов, Р.Ш.Абиев, В.В.Гусаров
Магнитные и фотокаталитические свойства наночастиц BiFeO3, формирующихся при термообработке соосаждённых в микрореакторе с закрученными потоками гидроксидов
АННОТАЦИЯ В работе для получения BiFeO3 использовалось осаждение гидроксидов в микрореакторе с закручивающимися потоками с последующей термообработкой соосажденных гидроксидов висмута и железа. Изучение процесса образования нанокристаллического ортоферрита висмута проводилось с использованием комплекса методов: EDXMA, TEM, XRD, 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy, DRS и др. Были определены фотокаталитическая активность и магнитные характеристики материала. Показано, что при термообработке осадков гидроксидов в течение 1 минуты при температуре 530 °C формируются нанокристаллы BiFeO3 со средним размером кристаллитов 14 ± 7 нм. Установлено, что полученный нанопорошок BiFeO3 представлен агломератами отдельных наночастиц. Значения намагниченности насыщения и остаточной намагниченности этих наночастиц ортоферрита висмута равны 2.31 и 0.48 emu/g, соответственно. По результатам DRS установлено, что band gap energy for the samples calcinated at 530 °C, 515 °C, and 500 °C were 1.82 eV, 1.86 eV, and 1.91 eV respectively, что обеспечивает сильное поглощение видимого света образцами. Более высокую фотокаталитическую активность проявил образец в рентгеноаморфном состоянии по сравнению с нанокристаллическим BiFeO3 в процессе фентоноподобного обесцвечивания метилового фиолетового под действием видимого света с константами скорости реакции псевдопервого порядка 0.0256 мин-1 и 0.0072 мин-1, соответственно.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА микрореактор с интенсивно закрученными потоками, нанокристаллы, наночастицы, феррит висмута, фотокатализ, фентоно-подобные реакции