Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (4), 487–497
Colloidal chemical properties of the sol V2O5 · nH2O
Hein Myat Lwin – D. I. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia, Moscow, Russia; heinmyatlwin2468@gmail.com
Oksana V. Yarovaya – D. I. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia, Moscow, Russia; iarovaia.o.v@muctr.ru
Corresponding author: Oksana V. Yarovaya, iarovaia.o.v@muctr.ru
PACS 82.70.Dd
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2024-15-4-487-497
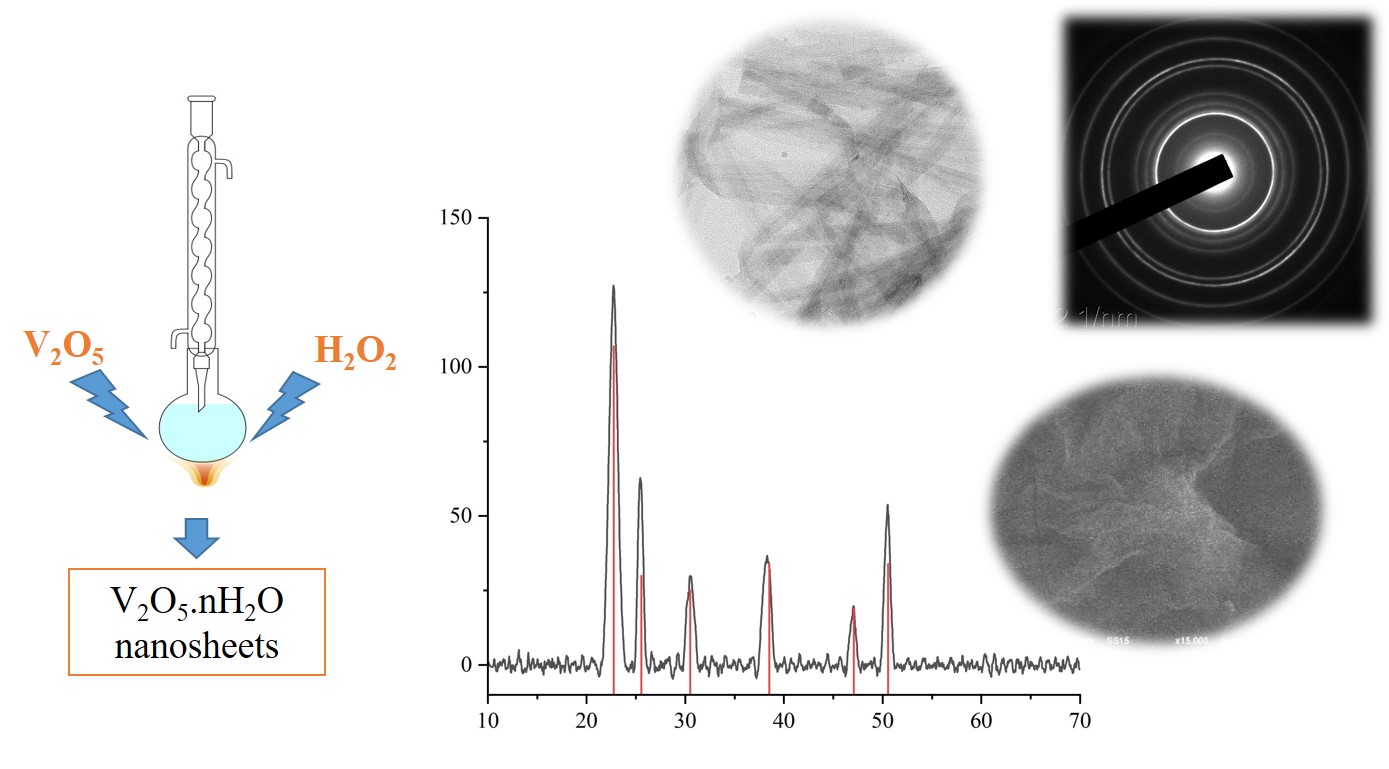
ABSTRACT The colloidal properties of the lyophilic dispersion system V2O5 · nH2O sol studied in this work was obtained by the thermolysis of V2O5 powder with hydrogen peroxide. The dispersion phase exists in the form of nanorods. The optimal mole ratio of V2O5 and H2O2 for synthesizing the sol is 1:30, and the possible concentration of V2O5 in the entire colloidal system ranges between 0.3 to 1.6 mass percent. The existence of nanoparticles in this colloidal system and the pH range that maintains the stability of the sol conform to the phase diagram of vanadium (V) in an aqueous medium. The absolute value of the zeta potential of the sol increases when the initial concentration of the sol during synthesis increases and the ionic strength of the dispersion medium decreases. Potential curves of pair interaction between nanoparticles were also constructed according to the DLVO theory.
KEYWORDS V2O5 · nH2O, thermolysis, nanorods, lyophilic colloidal system, stability, DLVO theory
FOR CITATION Lwin H.M., Yarovaya O.V. Colloidal chemical properties of the sol V2O5 · nH2O. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (4), 487–497.
[In Russian] Хеин Мьят Лвин, Яровая О. В.
Коллоидно-химические свойства золя V2O5 · nH2O
АННОТАЦИЯ В данной работе были изучены коллоидные свойства лиофильной дисперсной системы V2O5 · nH2O золя, полученной путем термолиза порошка V2O5 пероксидом водорода. Дисперсионная фаза существует в виде нанолистов. Оптимальное мольное соотношение V2O5 и H2O2 для синтеза золя составляет [1]:[30], а возможная концентрация V2O5 во всей коллоидной системе составляет от 0,3 до 1,6 мас.%. Существование наночастиц в этой дисперсной системе и диапазон pH, обеспечивающий стабильность золя, соответствуют фазовой диаграмме ванадия (V) в водной среде. Абсолютная величина дзета-потенциала частиц увеличивается с увеличением исходной концентрации при синтезе золя и уменьшением ионной силы дисперсионной среды. Фактор формы частицы, определяемый формулой Эйнштейна, имеет значение 9,608. По теории ДЛФО также были построены потенциальные кривые парного взаимодействия между наночастицами.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА V2O5 · nH2O, термолиз, нанолисты, лиофильная коллоидная система, стабильность, теория ДЛФО.