Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (6), 814–820
Solution combustion approach to the phase pure nanocrystalline lithium ferrite (Li0.5Fe2.5O4) with spinel structure and magnetically soft behavior
KirillD. Martinson – Ioffe Institute, Politekhnicheskaya st., 26, Saint Petersburg, 194064, Russia; martinsonkirill@mail.ru
Vadim I. Popkov – Ioffe Institute, Politekhnicheskaya st., 26, Saint Petersburg, 194064, Russia; vip-07@yandex.ru
Corresponding author: K.D. Martinson, martinsonkirill@mail.ru
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2024-15-6-814-820
PACS 61.46Df, 75.50.Gg, 75.75.Fk
ABSTRACT Lithium ferrite nanoparticles (Li0.5Fe2.5O4) were synthesized via the solution combustion method with a substantial deficiency of organic fuel (glycine, f = 0.05), followed by heat treatment of X-ray amorphous
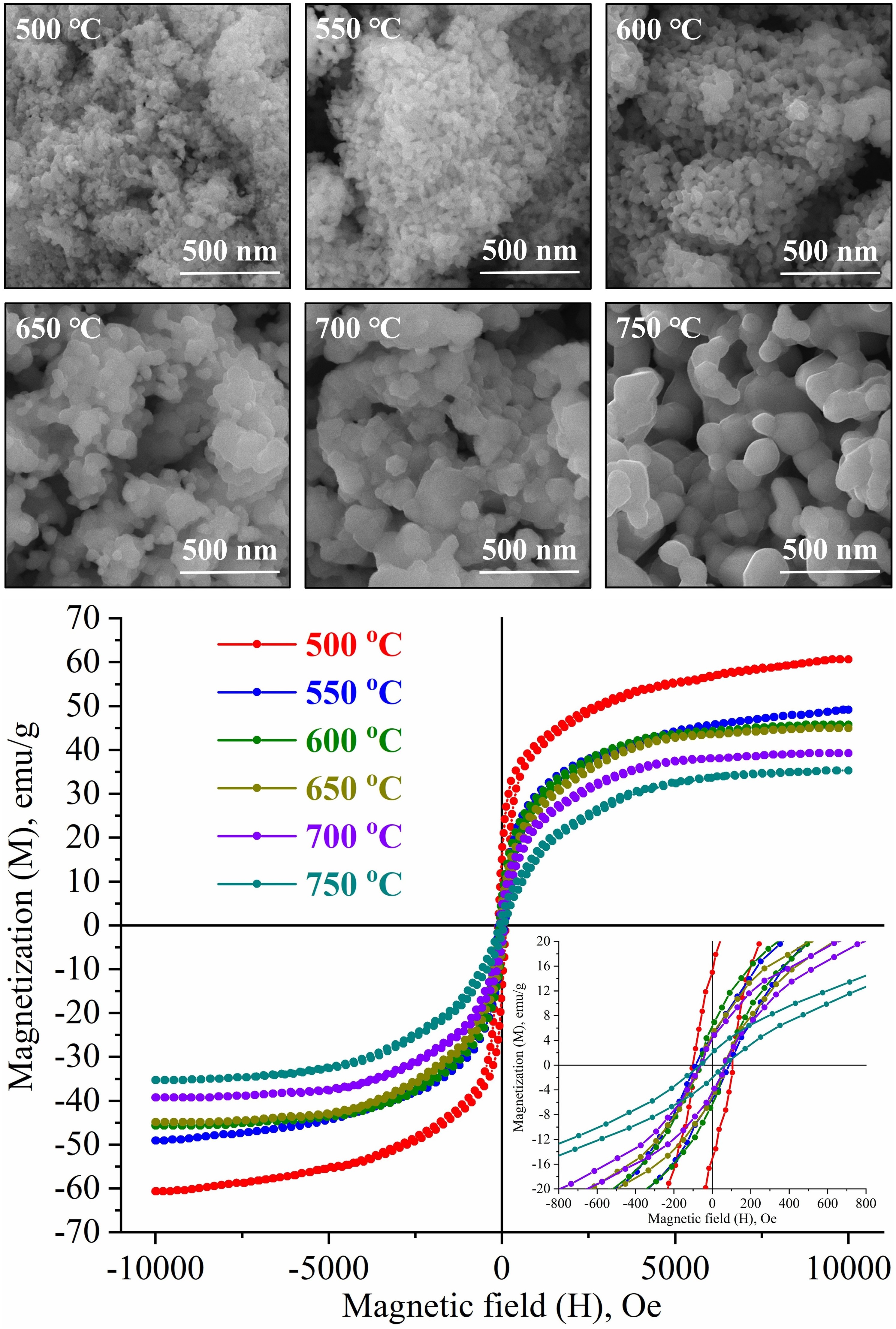
combustion products at temperatures ranging from 500 to 750 °C. Comprehensive characterization was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM). The results indicate significant morphological and structural changes in the nanopowders depending on the heat treatment temperature. Average particle sizes ranged from 14.2 to 59.5 nm, while crystallinity varied from 89.4% to 62.8%. Magnetic properties also varied, with coercivity (Hc) between 58.4 and 102.4 Oe, residual magnetization (Mr) from 5.2 to 15.4 emu/g, and saturation magnetization (Ms) from 35.1 to 60.7 emu/g. These findings demonstrate that pure lithium ferrite nanoparticles, free from impurity oxide phases, can be produced through controlled heat treatment of X-ray amorphous combustion products. Furthermore, the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles are highly sensitive to the specific heat treatment temperature, indicating that thermal processing conditions play a crucial role in determining their magnetic behavior.
KEYWORDS solution combustion synthesis, lithium ferrite, spinel ferrites, nanocrystals, soft magnetics
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors of the article express their gratitude to the Institute of Applied Materials Science of the Joint-Stock Company “Almaz Antej – Obuhovskij zavod” for assistance in conducting the study of morphology and structure. This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education within the framework of a State Assignment of the Ioffe Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, project no. FFUG-2024-0036.
FOR CITATION Martinson K.D., Popkov V.I. Solution combustion approach to the phase pure nanocrystalline lithium ferrite (Li0.5Fe2.5O4) with spinel structure and magnetically soft behavior. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (6), 814–820.
[In Russian] К.Д. Мартинсон, В.И. Попков
Метод растворного горения чистого нанокристаллического феррита лития (Li0.5Fe2.5O4) со структурой шпинели и магнито-мягким поведением
УДК 537.6, 544.1, 543.5
АННОТАЦИЯ Наночастицы феррита лития (Li0.5Fe2.5O4) синтезированы методом сжигания раствора при существенном дефиците органического топлива (глицина, f = 0.05) с последующей термической обработкой рентгеноаморфных продуктов сгорания при температурах от 500 до 750 °C. Комплексная характеристика проводилась с использованием сканирующей электронной микроскопии (СЭМ), энергодисперсионной спектроскопии (ЭДС), атомно-абсорбционной спектрометрии (ААС), порошковой рентгеновской дифракции (РФА) и вибрационной магнитометрии (ВМ). Результаты свидетельствуют о значительных морфологических и структурных изменениях в нанопорошках в зависимости от температуры термической обработки. Средние размеры частиц составили от 14,2 до 59,5 нм, а кристалличность — от 89.4% до 62.8%. Магнитные свойства также варьировались: коэрцитивная сила (Hc) составляла от 58.4 до 102.4 Э, остаточная намагниченность (Mr) — от 5.2 до 15.4 эме/г, а намагниченность насыщения (Ms) — от 35.1 до 60.7 эме/г. Эти результаты показывают, что чистые наночастицы феррита лития, свободные от примесных оксидных фаз, могут быть получены путем контролируемой термической обработки рентгеноаморфных продуктов сгорания. Кроме того, магнитные свойства наночастиц очень чувствительны к конкретной температуре термической обработки, что указывает на то, что условия термической обработки играют решающую роль в определении их магнитного поведения.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА метод растворного горения, феррит лития, ферриты-шпинели, нанокристаллы, мягкие магнетики