Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (6), 867–878
Effect of synthesis method on the structural, conductive and sensor properties of NiO–In2O3 nanocomposites
Mariya I. Ikim – N. N. Semenov Federal Research Center for Chemical Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia; ikimmary1104@gmail.com
Vladimir F. Gromov – N. N. Semenov Federal Research Center for Chemical Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia; vfgromov@mail.ru
Genrikh N. Gerasimov – N. N. Semenov Federal Research Center for Chemical Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia; gerasimovgen@mail.ru
Valentin G. Bekeshev – N. N. Semenov Federal Research Center for Chemical Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia; bvg495@yandex.ru
Leonid I. Trakhtenberg – N. N. Semenov Federal Research Center for Chemical Physics RAS, Moscow; Chemical Faculty, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow; Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology(State University), Moscow, Russia; litrakh@gmail.com
Corresponding author: Mariya I. Ikim, ikimmary1104@gmail.com
PACS 73.63.-b
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2024-15-6-867-878
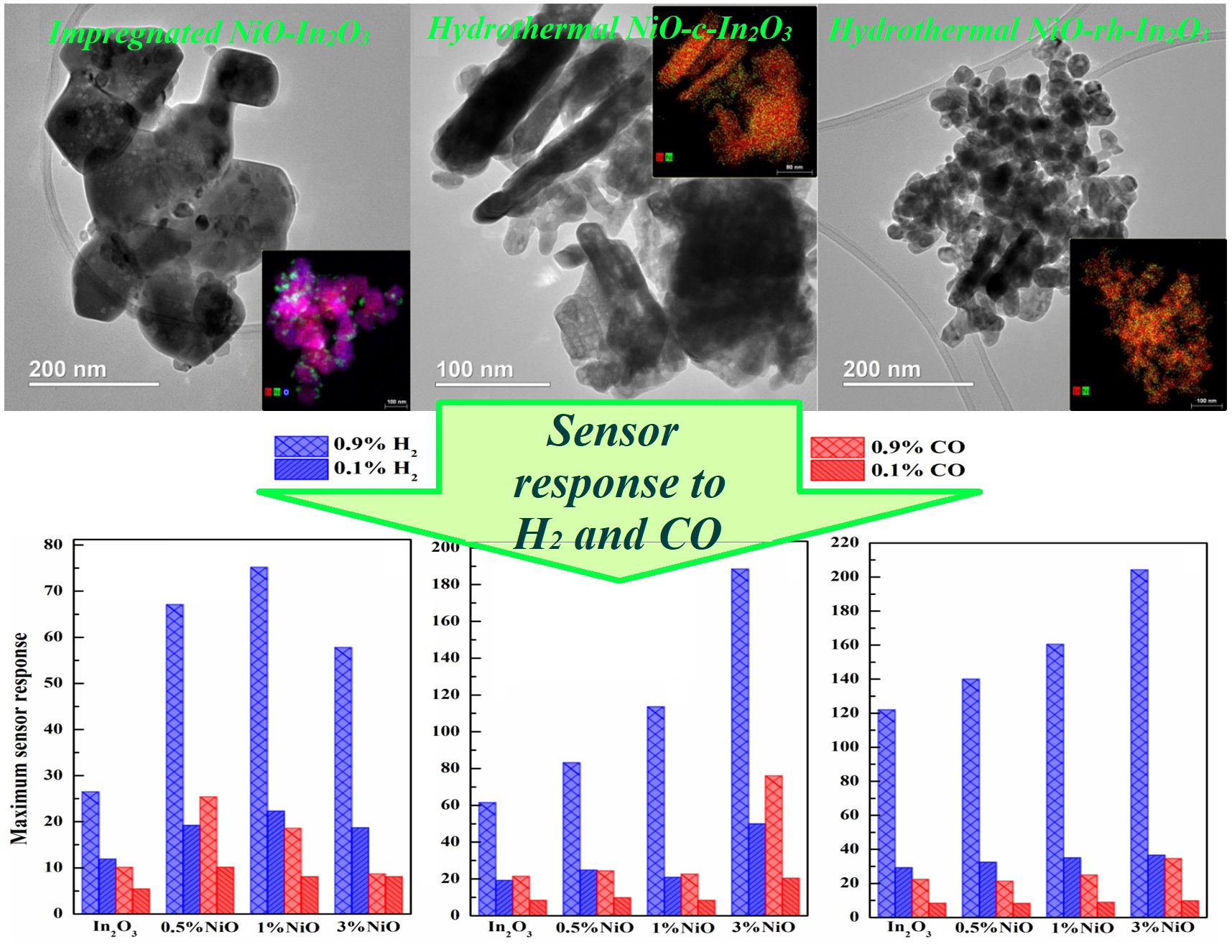
ABSTRACT The structural, conductive and sensor properties of NiO–In2O3 composites synthesized by hydrothermal and impregnation methods are investigated and compared. The mixed oxide considered consists of nanoparticles with electronic (In2O3) and hole (NiO) conduction bands. The lattice parameters of indium oxide decrease with the introduction of NiO into composites synthesized by the hydrothermal method. The addition of 3 % NiO to the hydrothermal composite also increases its specific surface area. The specific surface area and In2O3 lattice parameters in the impregnated samples are essentially independent of the NiO content. The conductivity of impregnated composites is an order of magnitude lower than that of hydrothermal composites. An increase in NiO content leads to a significant enhancement of the sensor response to H2 and CO. In addition, there is a decrease in the optimal operating temperature of hydrothermal and impregnated samples by 60 and 20 °C, respectively.
KEYWORDS composite, hydrothermal method, impregnation, indium oxide, conductivity, sensor response, hydrogen, carbon monoxide
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant No. 22-19-00037).
FOR CITATION Ikim M.I., Gromov V.F., Gerasimov G.N., Bekeshev V.G., Trakhtenberg L.I. Effect of synthesis method on the structural, conductive and sensor properties of NiO–In2O3 nanocomposites. Nanosystems: Phys. Chem. Math., 2024, 15 (6), 867–878.
[In Russian] М.И. Иким, В.Ф. Громов, Г.Н. Герасимов, В.Г. Бекешев, Л.И. Трахтенберг
Влияние метода синтеза на структурные, проводящие и сенсорные свойства нанокомпозитов NiO-In2O3
УДК 543.27
АННОТАЦИЯ Исследованы и сопоставлены структурные, проводящие и сенсорные свойства композитов NiO-In2O3, синтезированных гидротермальным способом и методом импрегнирования. Рассмотренный смешанный оксид состоит из наночастиц с электронной (In2O3) и дырочной (NiO) проводимостью. Параметр решетки оксида индия уменьшается при введении NiO в композиты, синтезированные гидротермальным методом. Добавление 3% NiO в гидротермальный композит также увеличивает его удельную поверхность. Удельная поверхность и параметры решетки In2O3 в импрегнированных образцах практически не зависят от содержания NiO. Проводимость импрегнированных композитов на порядок ниже, чем у гидротермальных композитов. Увеличение содержания NiO приводит к значительному увеличению сенсорного отклика на H2 и CO. Кроме того, происходит снижение оптимальной температуры эксплуатации гидротермальных и импрегнированных образцов на 60 °С и 20 °С, соответственно.
КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ СЛОВА композит, гидротермальный метод, пропитка, оксид индия, проводимость, отклик сенсора, водород, оксид углерода.