NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2017, 8 (6), P. 760–781
Cerium dioxide nanoparticles as third-generation enzymes (nanozymes)
A. L. Popov – Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Biophysics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Pushchino, Moscow region, 142290, Russia
A. B. Shcherbakov – Zabolotny Institute of Microbiology and Virology, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv D0368, Ukraine
N. M. Zholobak – Zabolotny Institute of Microbiology and Virology, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv D0368, Ukraine
A.Ye. Baranchikov – Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry of Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 119991, Russia
V. K. Ivanov – Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry of Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 119991, Russia; van@igic.ras.ru
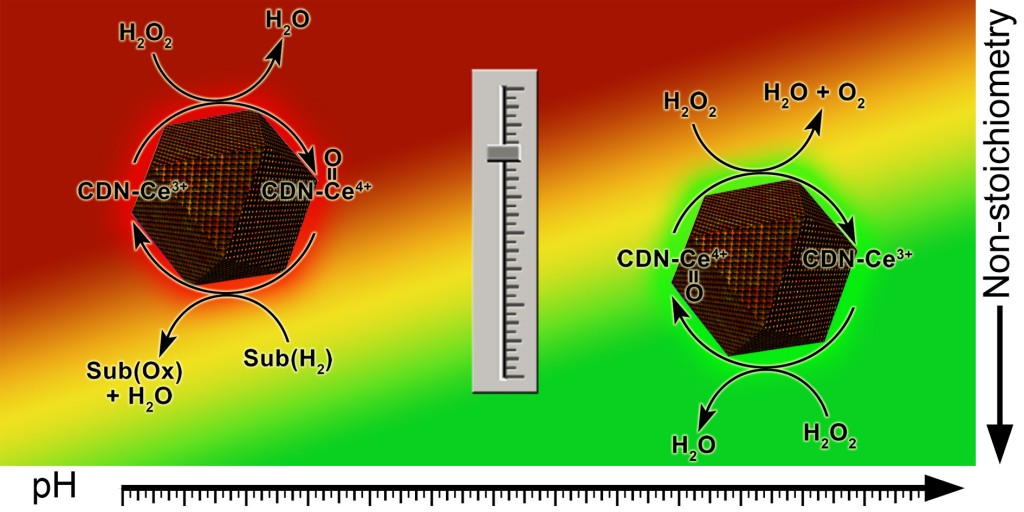
Ceria nanoparticles are capable of performing the function of some enzymes (such as oxidoreductases, phosphatase) and can be classified as nanozymes. In this review, the actual data on the enzymatic activity of ceria were critically analyzed and specific conditions under which the cerium dioxide nanoparticles can act as enzymes were defined. The presented analysis may be useful in the planning, design and synthesis of ceria nanoparticles having the desired enzymatic functions required for various processes, including the development of the nanodrugs, which exhibit the therapeutic effect depending on their composition and pH of media, development of molecular sensors and biosensors, etc.
Keywords: ceria, nanomaterials, nanozymes, peroxidase, catalase, phosphatase, superoxide dismutase.
PACS 87.55.ne, 87.85.Rs, 81.07.Bc
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2017-8-6-760-781