NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2018, 9 (1), P. 117–119
Kinetics of the Cu(II) sorption from aqueous solutions by carbon nanomaterials
A.V. Babkin – Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, Russia; flex_trol@mail.ru
I.V. Burakova – Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, Russia; iris_tamb68@mail.ru
A. E. Burakov – Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, Russia; malex1983@yandex.ru
E. A. Neskoromnaya – Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, Russia; lenok.n1992@mail.ru
A. E. Kucherova – Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, Russia; anastasia.90k@mail.ru
D. A. Kurnosov – Tambov State Technical University, Tambov, Russia; ozikimoziki@mail.ru
The present paper contains comprehensive studies on the adsorption properties of graphene oxide (GO), coconut activated carbon (AC) and “Taunit-M”
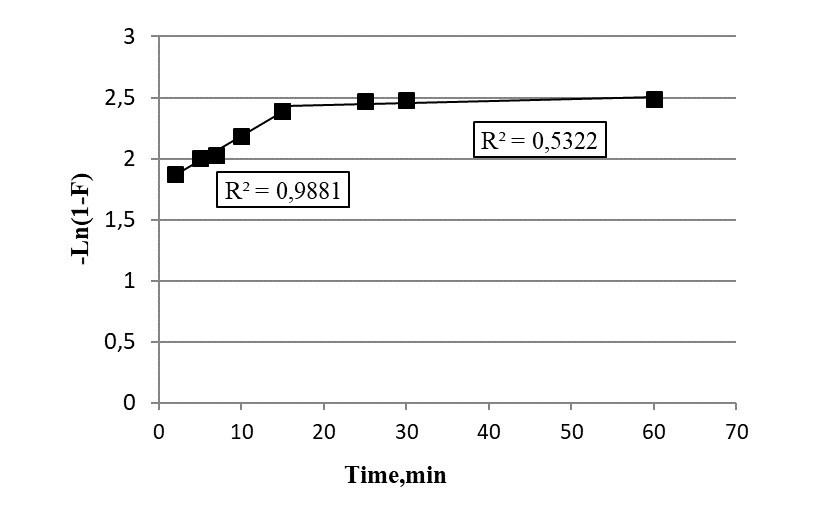
carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Cu(II) ions served as extracted component. Measurements of the Cu(II) content in water were performed using electrothermal atomization atomic absorption spectroscopy. The obtained experimental data indicate high adsorption capacity of the GO along with CNTs and AC. Kinetic parameters of the adsorption process on the graphene oxide were calculated using standard models (pseudo-first- and pseudo-second-order, external and intraparticle diffusion, and Elovich models). The presented results demonstrate the prospects of using the GO in selective extraction of heavy and rare-earth metal ions from aqueous media.
Keywords: sorption, graphene oxide, kinetic study, copper.
PACS 81.05.U, 81.07.De, 89.60.Ec
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2018-9-1-117-119