NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2018, 9 (4), P. 521–531
Capillary filling of carbon nanotubes by BiCl3: TEM and MD insight
E. A. Anumol – Nanostructured Materials Group, Department of Advanced Electron Microscopy, Imaging and Spectroscopy, International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory (INL), Braga, Portugal; leonard.francis@inl.int
F. L. Deepak – Nanostructured Materials Group, Department of Advanced Electron Microscopy, Imaging and Spectroscopy, International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory (INL), Braga, Portugal
A. N. Enyashin – Institute of Solid State Chemistry UB RAS, Ekaterinburg, Russia; enyashin@ihim.uran.ru
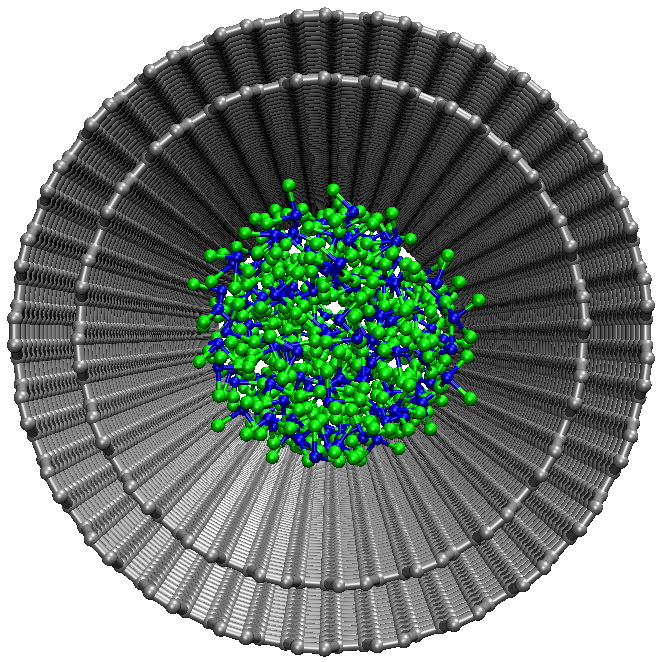
Among numerous trichlorides, the melt of BiCl3 is a distinctly molecular liquid with a relatively low melting point, yet, with a high surface tension. Therefore, the attractiveness of a simple capillary filling technique for fabrication of nanosized BiCl3 by dispersion within a nanocapillary needs a special investigation. Here, we report the successful synthesis and the transmission electron microscopy characterization of the hybrids consisting of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and endohedral BiCl3 crystallites. The main peculiarities of imbibition into carbon nanotubes and an intricate internal organization of molten BiCl3 are established using the developed 4-site force-field model of BiCl3 and consequent molecular dynamics simulations at nanosecond time scale.
Keywords: Bismuth trichloride, carbon nanotubes, capillary, TEM characterization, MD simulations.
PACS 34.30.+h, 34.35.+a, 05.70.Np
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2018-9-4-521-531