NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2018, 9 (4), P. 468–472
Heat-treated nano-structured shungite rocks and electrophysical properties associated
S.V. Kovalevskii – “Shungiton” Ltd Company, Petrozavodsk, Russia; semen_tlg@bk.ru
I. A. Moshnikov – Institute of Geology, Karelian Research Center, RAS, Petrozavodsk, Russia; igorm@krc.karelia.ru
V.V. Kovalevski – Institute of Geology, Karelian Research Center, RAS, Petrozavodsk, Russia; kovalevs@krc.karelia.ru
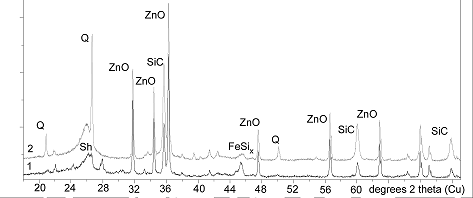
Shungite rocks of two different types were treated at ~ 1400 °C and a set of nanomaterials have been obtained. Among the different materials obtained were: carbon hollow fibers; spherical or ellipsoid particles; silicon carbide amorphous; crystalline nanofibers and nanoparticles having different morphologies; iron and iron silicide nanoparticles encapsulated into carbon shells. Measurements were performed for shielding effectiveness (SE) and the electrical conductivity (σ) of untreated and heat-treated shungite rocks. The shungite rock with dominated hyperfullerene carbon is remarkable for a two-fold increase in the σ and a 10 dB increase in SE with a slight decrease of the carbon content by 1.5 % in relation to the untreated sample. In contrast, the treated shungite rock with high SiC nanofiber content is characterized by a halving of the σ and a 10 dB decrease in SE with a decrease of the carbon content by 6 % relative to the original sample.
Keywords: shungite rocks, carbon, carbon nano-sized shells and fibers, SiC nanosized fibers, shielding effectiveness, electrical conductivity.
PACS 68.37.Og, 61.48.-c
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2018-9-4-468-472