NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 2019, 10 (5), P. 520–529
Recombination radiation associated with A+-centers in quantum dots in an external magnetic field
V. D. Krevchik – Penza State University, Krasnaya str., 40, Penza, 440026, Russia; physics@pnzgu.ru
A.V. Razumov – Penza State University, Krasnaya str., 40, Penza, 440026, Russia
P. S. Budyansky – Penza State University, Krasnaya str., 40, Penza, 440026, Russia
M. B. Semenov – Penza State University, Krasnaya str., 40, Penza, 440026, Russia
I. M. Moyko – Penza State University, Krasnaya str., 40, Penza, 440026, Russia
N. N. Khvastunov – Mordovian State Pedagogical Institute named after M. E. Yevseviev, Studend str., 11 “a”, Saransk, Mordovian Rep., 430007, Russia
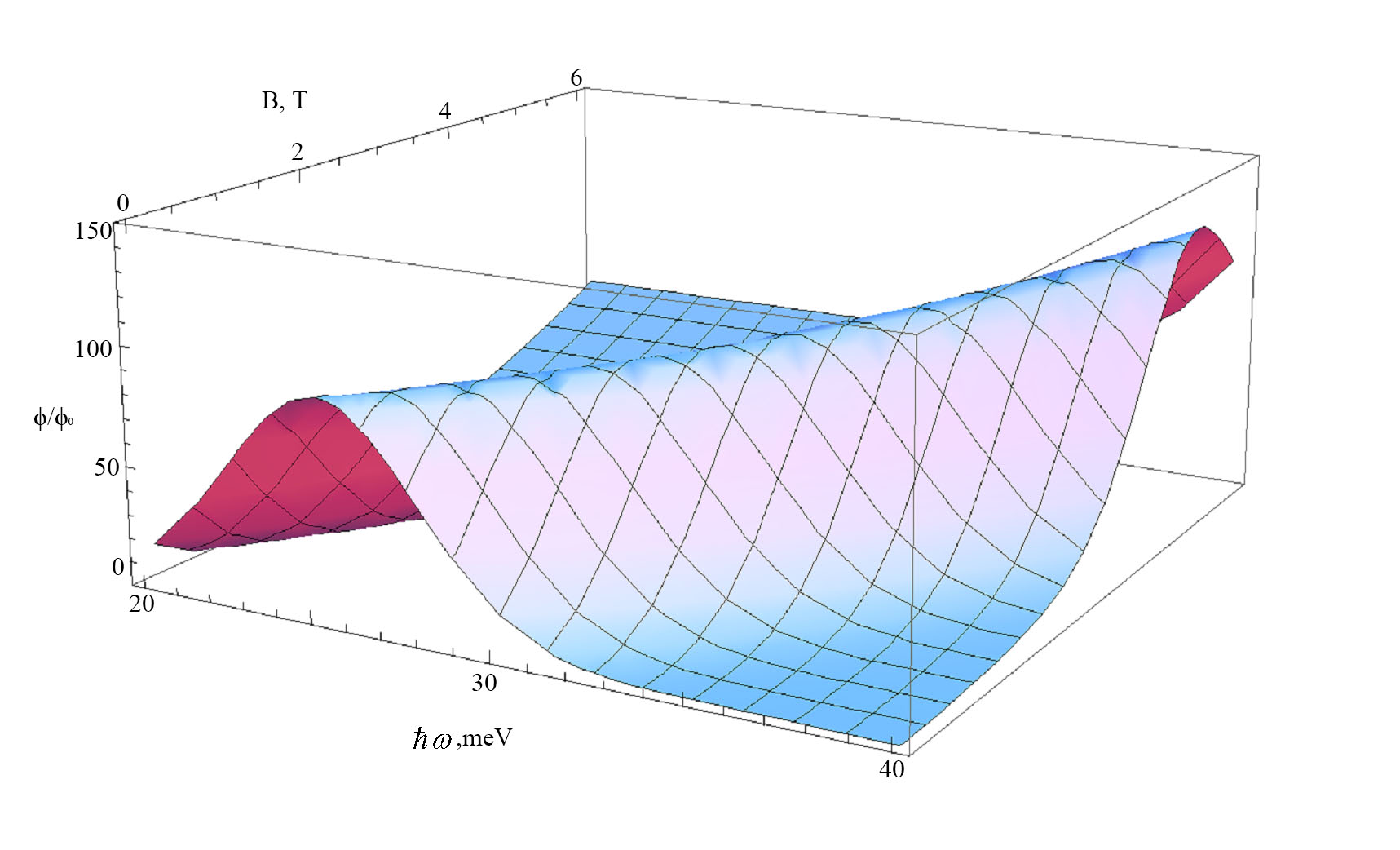
The effect of an external magnetic field on the binding energy of a hole in an impurity complex A++e in a spherically symmetric quantum dot, as well as frequency dependence of the spectral intensity of recombination radiation of the quasi-zero-dimensional structure with impurity complexes A++e have been investigated. It is shown that in an external magnetic field there is a spatial anisotropy for the binding energy of A+-state due to hybrid quantization in the quantum dot radial plane and dimensional quantization in the direction of an external magnetic field. It is shown that in an external magnetic field the spectral intensity curve of the recombination radiation shifts to the short-wavelength region of the spectrum and probability of the radiative transition of an electron to the level of A+-center increases, which is caused by increase in the overlap integral of the envelope wave functions of a hole bound at the A+-center and of an electron localized in the ground state of quantum dot.
Keywords: recombination radiation, quantum dots.
PACS 73.40.Gk, 03.65.Xp
DOI 10.17586/2220-8054-2019-10-5-520-529